![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
patient examinations with persistent disequilibrium/postural disorders |
present with normal clinical examinations
difficulty with stairs
increased gait problems on uneven surfaces or without adequate lighting |
|
|
patient population with age related fall tendencies |
borderline sensory abnormalities
reduction in processing time |
|
|
clinical uses for balance testing |
physiotherapy based on balance training to improve balance and reduce risk of falls
motoring progress using the sensory organization test (SOT)
identifying non organic, physiologic, and malingering patients
identifying organic disorders (deficits in vestibular) |
|
|
aphysiologic |
performance is relatively better on more difficult conditions of sensory conflict on easier ones |
|
|
ellipses for balance test |
|
|
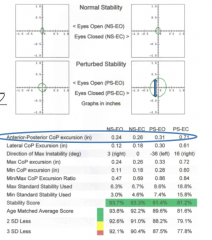
anterior-posterior CoP excursion (in) |
length of projection of ellipse in vertical axis
magnitude of movement in sagittal plane
smaller = better |
|
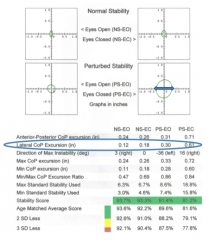
lateral CoP Excursion (in) |
length go projection of ellipse in horizontal plane
magnitude of movement in lateral plane
smaller = better |
|
|
direction of max instability (deg) |
amount of counter-clockwise rotation to bring horizontal axis to the major semi axis
expressed in degrees
indicates primary direction of movement
can have any value
+90 indicates movements to the right
by convention positive angles are to the right |
|
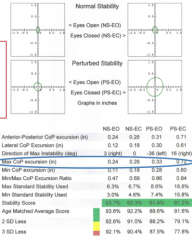
max of CoP excursion (in) |
major axis of ellipse
Amax
indicates magnitude of movement in direction of maximum movement
smaller = better |
|
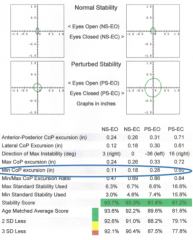
min CoP excursion (in) |
minor axis of ellipse
Amin
indicates magnitude of movement in direction of minimum movement
smaller = better |
|
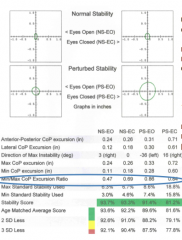
Min/Max CoP excursion ratio |
aspect ratio of the ellipse
indicates directionality of movement
0 = narrow ellipse (movement was mainly in one direction)
1 = round ellipse (movement did not well define primary direction) |
|
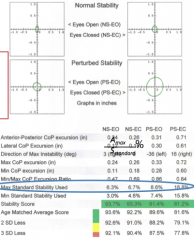
max standard stability used |
score of the patient's ability to maintain balance during the test (calculated by equation Amax/Sstandard%) |
|
|
Amax |
major semi axis of the 95% confidence ellipse |
|
|
Sstandard |
represents standard limit of stability (based on the patient's height)
smaller = better |
|
|
100% standard |
patient used entire standard of limit of stability (all of stability) during test |
|
|
0% standard |
patient maintained complete stillness (may indicate error in testing) |
|
|
less than 100% standard |
patient has some stability margin left before losing balance |
|
|
exceeding 100% standard |
theoretically the patient was unable to maintain balance during the test |
|

|
... |
|
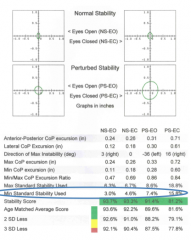
min standard stability used |
score of the patients ability to maintain balance during the test - calculated by equation
same as max standard stability used only based on Amin (of minimum movement during testing) |
|
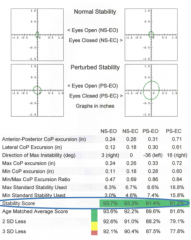
stability score |
score of patients ability to maintain balance during the vest |
|
|
values for stability score
|
between 0 and 100% (larger = better)
100% = perfect stillness 0% = patient used entire standard limit of stability - theoretically - patient was unable to maintain balance throughout the test |
|
|
age matched average score |
based on patient's height and age |
|
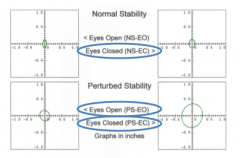
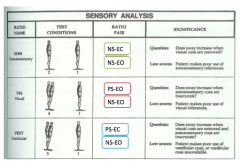
notmal stability eyes closed (NS-EC) |
patient finds it difficult to maintain balance without visual references (NS-EC) |
|
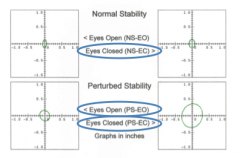
eyes open (PS-EO) |
patient has problems maintaining balance when the support surface is not a hard level surface (PS-EO) |
|
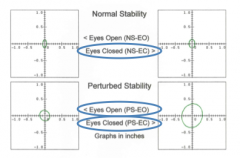
eyes closed (PS-EC) |
patient has problems when the support is not a level and hard surface without visual cues - may indicate that the patient makes poor use of vestibular cues when they are not available (PS-EC) |
|
|
limit of stability (LoS) |
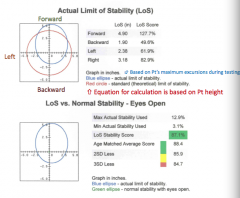
|
|
|
limit of stability (LoS) |
comparison between standard limit of stability and limit of stability ellipse - represents how much of the Standard Limit of Stability was used
larger ellipse = better
smaller = not all limit of stability was used |
|
|
LoS score in inches |
maximum excursion Smax of center of pressure path in specified direction |
|
|
LoS score |
represents how patients limit of stability compares with standard limit of stability (based on height) |
|
|
LOS scores |
0% = patient was unable to lean
less than 100% = patient has a reduced ability to lean without loosing balance or using some additional form of support
100% or greater = patient was awesome - greater ability to lean |
|
|
a (low/high) LOS score indicates that PT is less stable than age matched peers = more likely to fall |
low |
|
|
LOS compares back to condition (1/2/3/4/5/6) |
1 |
|
|
know know know know |

