![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
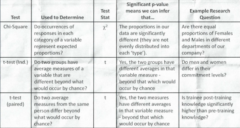
Independent Samples T Test |
is for comparing the means of 2 independent groups in order to determine if there is statistical difference |
|
|
|
|
|
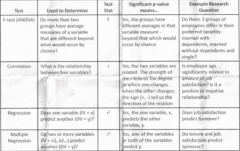
Paired samples Test |
Test is for comparing two means that are fromthe same individual, object, or related units (example: did training help a newemployee? Collect data before and after training) |
|
|
Rules to making categories: |
Segments must be: · Measurable · Accessible · Substantial · Differentiable · Actionable |
|
|
Measurement data |
Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio |
|
|
Mean, Median, Mode |
Mean:regular average Median:middle value Mode: number that is repeated most often |
|
|
Panel Data |
also known as longitudinal or cross- sectionaltime-series data) is a data set in which the behavior of entities are observedacross time. These entities could be states, companies, individuals, countries,etc.Cross sectional = single point in timemeasures of a sample selected from a population |
|
|
Longitudinal |
= repeatedmeasures, over time, of a fixed sample (panels of people) |
|
|
4 steps to Marketing Research Plan: |
1. Formulate Problem 2. Determine Research Design 3. Analyze & Interpret Data 4. Prepare the Research Report |
|
|
Targeting, segmenting, positioning: |
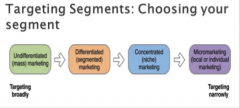
1. To place a product occupies in consumers’ minds relative to competing products. Market segmentation: classifying customerswith similar needs and wants within a specific market -Often best to combine variables and identify smaller, better-defined targetgroups -Demographic segmentation most frequently used segmentation variable |
|
|
Primary Data Secondary Data: |
PrimaryData: : data collected first hand2. SecondaryData: data not collected by the researcher (ie. From articles, books,interviews already done, etc.) |
|
|
Descriptive Research |
concerned with determining the frequencywith which something occurs / describing a population with respect to importantvariables |
|
|
Exploratory Research- |
Best for Clarifying Concepts /Discover ideas and insights Casual- used to establish cause and effect relationships between variables |
|
|
Pros of communication method of collection |
faster & easier |
|
|
Cons of communication method of collection |
not as accurate as observation method (but observation method takes longer) |
|
|
Rules for showing causality |
· Concomitant Variation (change is in effect aligns w/change in given factor :X and Y effect occur together) · Temperalorodering · Control over other possible causes |
|
|
Independent Variables in MKTG |
x |
|
|
Dependent variables in MKTG |
sales (end result studied)
“When experimenter manipulates X and looks at revenueand sales effect, X is independent and sales in dependent.” |

