![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many lobes in the right lung? Left lung? |
R = 3 lobes L = 2 lobes How to remember: The heart takes the space of the left third lobe. |
|
|
How do you calculate pack years? |
# packs a day x # years they smoked |
|
|
How many cigarettes are in a pack? |
20 |
|
|
Calculate the pack years: 10 cigs/day for 22 years |
1/2 a pack X 22 = 11 pack years |
|
|
Calculate the pack years: 1.5 packs/day for 15 years |
1.5 packs x 15 years = 22.5 pack years = ~23 pack years |
|
|
Which is a faster process, inspiration or expiration? |
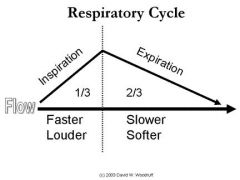
Inspiration |
|
|
Describe Tachypnea |
Rapid and shallow breaths |
|
|
Describe Hyperypnea |
Rapid and deep breaths |
|
|
Describe Bradypnea |
Slow Breathing Low RR |
|
|
Respirations per minute for: Adults Adolescents School Age Toddler Newborn |
Adults = 12-20 bpm Adolescents = 12-16 bpm School Age = 18-30 bpm Toddler = 24-40 bpm Newborn = 30-60 bpm |
|
|
Describe Cheyne-Strokes breathing When would you see it? |
Periods of deep breathing alternate with apnea End of life Children and elders may show this breathing in sleep |
|
|
Normal Chest Diameter Anterior/posterior ratio? |
1:2 (twice wide as it is deep) |
|
Describe this persons chest. Caused by? Associated with what disease? |
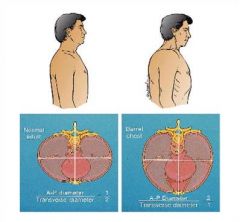
Costal angle is > 90 degrees Caused by over inflation Associated with COPD |
|

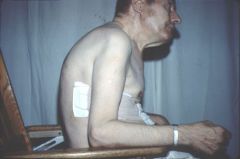
Who is this? What does he have? |

Cody Miller Funnel chest Pectus excavatum He also has an olympic gold medal |
|
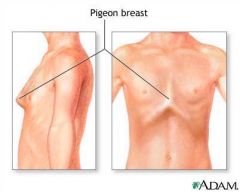
|
Pigeon Chest Pectus carinatum |
|
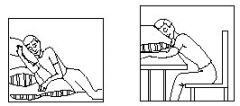
What is this? Why would a patient want to rest like this? |
Orthopnea Labored breathing that occurs when lying flat, and is relieved by sitting up |
|
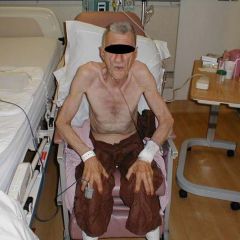
What type of breathing is this man doing? |
Tripod breathing |
|

What is causing the blue? Where can you assess for blue? |
Cyanosis Lips, fingers, toes |
|
|
What causes clubbing? Which body systems can cause clubbing? |
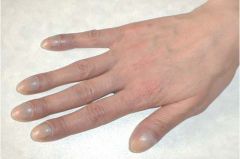
Chronic hypoxia Pulmonary/cardiac conditions |
|
|
High pitched, loud breath sounds
Expected location? |
Bronchial
Over trachea |
|
|
Moderate pitch, medium intensity breath sounds? |
Bronchovesicular |
|
|
Low pitched, soft breath sounds Expected location |
Vesicular Peripheral lung fields |
|
|
Define Crackles (fine and coarse) What's a common cause of crackles? |
Fine = hair-like Coarse = velcro-like Heart failure (pulmonary edema?), pneumonia, asthma |
|
|
Define Wheeze Commonly associated with which COPD? |
High pitch, whistle-like Asthma |
|
|
Define Ronchi What causes ronchi? |
Low pitch, snoring-like Chronic bronchitis, tracheal/bronchial obstruction |
|
|
Define Stridor What causes stridor? |

High pitch Harsh Very loud - can be heard without auscultation SUPER SERIOUS! Laryngeal/tracheal obstruction (i.e. tumor) |
|
|
Define Friction Rub |
Low pitch
Coarse Rubbing/grating |
|
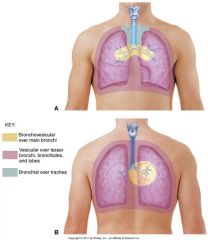
Normal breath sounds |
|
|
|
How can you discern if underlying tissue is air or fluid filled? |
Percussion Air = resonant Fluid = dull |
|
|
What do you examine when palpating thoracic expansion? |
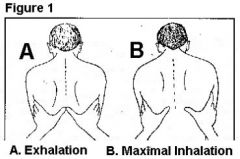
Equal movement bilaterally |
|
|
Pneumothorax vs Hemothorax? |
Pneumothorax = air in pleural space Hemothorax = blood in pleural space |
|
|
Pleural effusion |
Fluid buildup in pleural cavity |
|
|
Pneumothroax vs Atelectasis |
Pneumothroax = air in the pleural cavity Atelactasis = alveolar collapse (due to having no air in alveoli) |
|
|
Tactile fremitus Feeling for what? Increased = ...? Decreased = ...? |
"ninety-nine" Feeling for symmetrical vibration Increased vibration = pneumonia, consolidation Decreased vibration = pleural effusion/pneumothroax |
|
|
Atopy Asthma Allergies COPD Are all forms of what? |
Chronic respiratory problems |
|
|
URI (upper respiratory infection) PNA (pneumonia) Pleural effusion TB Pulmonary embolism Are all forms of what? |
Acute respiratory problems |
|
|
ARDS |
Acute/adult respiratory distress syndrome |
|
|
Upper respiratory infections Short of long lived? Contagious or noninfectious? Acute or chronic? Antibiotics used ...? |
Short lived Contagious Acute infection (nose, sinus, pharynx, larynx) Antibiotics used judiciously |
|
|
Pneumonia Infection of ...? Caused by...? Signs/symptoms? |
Infection of terminal bronchioles Caused by viral, bacterial, aspiration Signs/symptoms: Fever, cough (may not be productive), malaise, fatigue, pleuritic pain, decreased breath sounds/crackles, tachypnea, dullness with percussion May have absent breath sounds |
|
|
Tuberculosis Where can it affect? Signs/Symptoms? |
Mycobacterium tuberculi Mostly affects lungs, can be found in kidney, bone, lymph node, meninges Typically asymptomatic Signs/symptoms: Cough, night sweats, weight loss, hemoptysis, fatigue, anorexia |
|
|
A loss of synchrony between left and right lung indicates a ... ? |
Red flag! |
|
|
Presence of stridor indicates a ... ? |
Red flag! |
|
|
Secondary muscle use indicates a ... ? |
Red flag! |
|
|
Expiratory grunt indicates a ... ? |
Red flag! |
|
|
Cyanosis indicates a ... ? |
Red flag! |
|
|
What is Rhino-sinusitis? |
Common cold |
|
|
What is a BCG? |
Vaccine for TB Bacillus Calmette-Guerin |
|
|
PPD testing tests for what? What type of injection? |
TB Intradermal |
|
|
Hyper reactive reversible airway disease |
Asthma |
|
|
What is the common cause of asthma in children? |
Allergies |
|
|
What is the common cause of asthma in older adults? |
Infection |
|
|
Match these types of asthma: Type 1 Moderate persistent Type 2 Sever persistent Type 3 Mild intermittent Type 4 Mild persistent |
Type 1 = mild intermittent (<2x a week) Type 2 = mild persistent (2x a week) Type 3 = moderate persistent (inhaler used daily) Type 4 = severe persistent (hospitalized) |
|
|
What is the common acute treatment of asthma? |
Bronchodilators |
|
|
What is the common chronic treatment of asthma? |
Glucocorticoids - anti-inflammatory (Steroid inhaler) |
|
|
Risk factors of lung CA |
Tobacco smoke Asbestos Radon Marijuana? Age Personal history FH Vitamin A deficiency and excess |
|
|
Hyper secretion of mucus by goblet cells Productive cough (minimum 3 mo - 2 years) Ronchi, crackles Symptoms of...? |
Chronic bronchitis |
|
|
Enlarged alveola Barrel chest Dyspnea Pursed lip breathing Tripod position Decreased breath sounds Crackles, wheezing Symptoms of...? |
Emphysema |
|
|
Blue bloater vs Pink puffer |
Blue bloater = more CO2 retention = more hypoxia Pink puffer = no CO2 retention |
|
|
Round infant chest... Normal or abnormal? |
Normal Chest of newborn is generally round until ~2 years old |
|
|
Child chest wall showing thinner and bony structures ... Normal or abnormal? |
Normal Child chest wall is more prominent and yielding than in adults |
|
|
Mechanical and biochemical factors of pregnant women lead to changes in .... ? |
Respiratory function Due to enlarging uterus Increased progesterone |
|
|
Does respiratory rate change with pregnancy? |
No, RR remains unchanged |
|
|
Anatomical changes of pregnancy |
-Lower ribs flare -Diaphragm rises above usual position -Major workload is on diaphragm -Minute ventilation increases due to increased tidal volume |
|
|
Describe these types of pneumothroax: Closed pneumothorax Open pneumothroax Tension pneumothorax |
Closed = spontaneous traumatic, iatrogenic Open = due to penetration Tension = air leak into pleural space |
|
|
Symptoms of Lung CA |
Persistent cough Anorexia Weight loss Hemoptysis Normal to decreased breath sounds |
|
|
Is barrel chest common in older adults? |
Yes, due to loss of muscle strength in thorax and diaphragm and loss of lung resiliency |
|
|
Dorsal curve of thoracic spine is common in...? |
Older adults
White Asian Women |
|
|
Is loss of alveoli elasticity common in older adults? |
Yes |
|
|
Are mucous membranes drier in older adults? |
Yes |
|
|
Is decrease in vital capacity and increase in residual volume common in older adults? |
Yes |
|
|
Example of Documenting Normal Findings |
General: Patient appears comfortable, in no apparent distress Lungs: Thoracic expansion symmetric. Respiration unlabored, no secondary muscle use. Lungs CTAB |

