![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are Faraday's and Maxwell's Laws?
|
Farady= An oscillating magnetic field will induce an oscillation current
Maxwell= An oscillating current will unduce an oscillating magnetic field |
|
|
Know the Larmor Equation
|
w=gammaBo
w= resonant frequency gamma=gyromagnetic ratio Bo= Field strength For H, w = 42.58/Tesla therefore w= 63.87 for 1.5 Tela magnet and 127.6 for 3 Tesla |
|
|
How is spatial encoding performed?
|
Through the use of a magnetic gradient. By applying a field gradient, protons will precess at different frequencies as defined by Larmor frequency.
Gradients can be applied in different directions to generate orthoganol image slices |
|
|
How do we determine slice thickness?
|
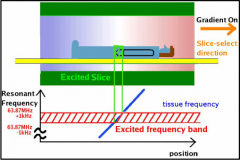
A field gradient is applied causing protons to precess at different speeds spatially. A specific RF pulse is released with a narrow frequency bandwidth which will excite protons in a selected region of the spatial curve. The stronger the magnet, the steeper the curve (blue) the thinner the slice.
Slice thickness is dependent upon gradient field strength and the transmit RF bandwidth |
|
|
How does thickness relate to image detail?
|
Just like CT, when slice thickness is smaller, spatieal resolution and image detail is enhanced.
|
|
|
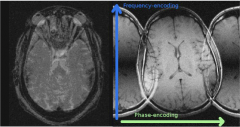
How does phase encoding work:
|
In excited slice, magnetic gradient is applied resulting in protons precessing at different frequencies along the phase direction (protons in areas of stronger field will precess faster and gain phase). The gradient is then removed with the protons all precessing at the same speed but the phase difference remains.
|
|
|
What happens during frequency encoding?
|
A magnetic gradient is applice perpendicular to the phase encoding direction. This causes a phase gain in the protons on the stronger side of the gradient. Unlike the phase encoding step, the gradient is kept on during readout.
|
|
|
What does spin echo mean?
|
After initial RF pulse is applied, the signal within a voxel will gradually deteriorate (T1,T2 and T2*). In order to strengthen the signal, a refocusing pulse is applied at 1/2 TE to "boost" the signal. This realignment is referred to as (re) spin followed by the echo.
|
|
|
How does readout work?
|
the tissue excited, then a phase encoding gradient is applied which de-phase the protons. The phase gradient is turned off. The frequency encoding gradient is applied perpendicularly which subsequently speeds up the phases. This is kept on during readout. During readout, snapshots of these signals are compared to determine location of signal.
|
|
|
How is the image formed?
|
The MRI only senses bulk tissue magnetization within a slice, not individual voxels.
To create the image protons which are in phase are grouped into sets called ensembles. By "listening" for pairs of ensembles you can determine their location (known as inverse Fournier transform) The frequency encoding is what allows the ensembels to move during readout It is done this way because to decipher for each voxel individually would take substantially longer. |
|
|
What's the difference between 2D and 3D MR acquistion
|
2D: Stack of 2D slices each with 1 frequncy encoding and 1 phase encoding steps.
3D: "Slab" of tissue for which there is 1 frequency encoding and 2 phase encoding steps (perpendicular to frequency encoding) Therefore Artifacts that appear predominantly along the phase encoding can appear along 2 axes in 3D imaging sequences |
|
|
What are the advantages of 2D and 3D MR acquisiton
|
2D: Quicker, Phase encoding artifacts in only 1 direction
3D: Smaller voxels with good signal to noise, isovolumetric voxels possible (prostprocessing) |
|
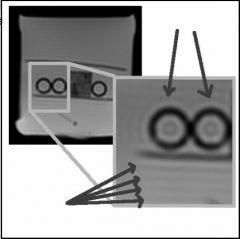
What is this artifact?
|
Gibbs artifact - number of samples in k-space too small
remedy: more phase encodings (and more samples acquired ruing frequency encoding) |
|
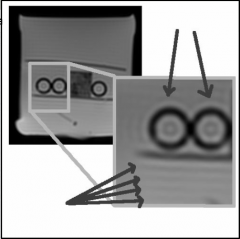
What is this artifact?
|
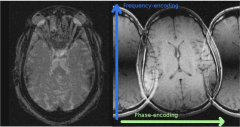
Gosting (Nyquist N/2)
Phase-encoding direction. Errors in phase between readouts related to imperfections in gradient performance |
|
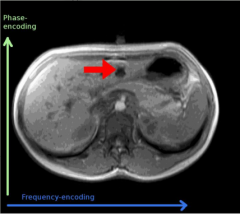
What is this artifact?
|
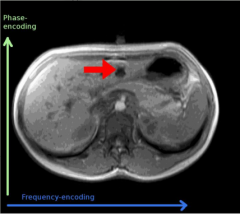
Motion artifact
Phase encoding remedy; flip the phase and frequency encoding directions |
|
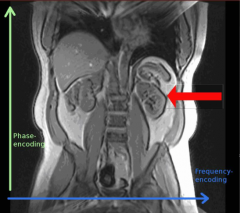
What is this artifact?
|
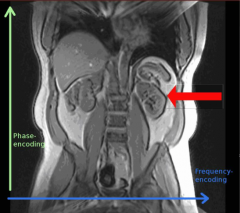
Chemical shift artifact
frequency encoding direction |
|
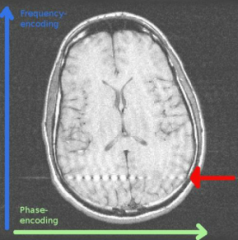
What is this artifact?
|
Zipper Artifact
Phase encoding high frequency noise |
|
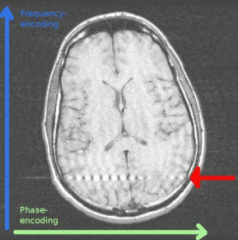
What is this artifact?
|
Noise band
phase encoding high frequency noise |
|
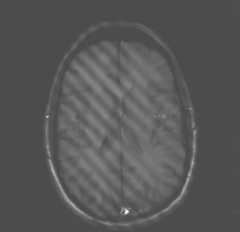
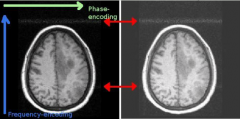
What is this artifact?
|
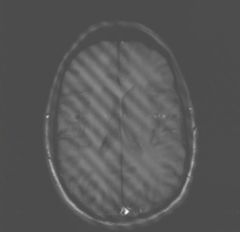
Spike artifact
phase encoding clump of data in k-space elevated by noise |
|
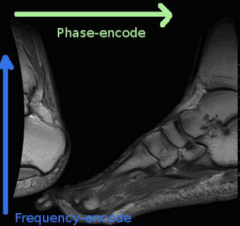
What is this artifact?
|
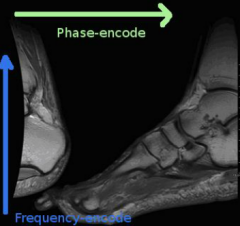
Aliasing (wrap around)
Phase encoding field of view in the phase-encoding direction is smaller than the anatomy that is being imaged Phase encoding should be done in short axis or organ being imaged. |
|
|
During image formation the only thing that changes to acquire the next row of k-space is______________
|
phase encoding
|

