![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why is how and when MR signals are mapped into K spaces important
|
How and when the MR signals are mapped into the k-space cause great differences in the spatial, temporal and contrast resolution of the resulting MR images
|
|
|
What does the location of the datas in K-space depend on
|
The location of the datas in k-space depends on the net strength and duration of the phase encoding gradient and frequency encoding gradient:
|
|
|
What does low amplitude or short duration gradient events encode
|
A low-amplitude or short-duration gradient event encodes low-spatial-frequency information
|
|
|
What does high amplitude or long duration gradient events encode
|
A high-amplitude or long-duration gradient event encodes high-spatial-frequency information
|
|
|
Where are the low spatial frequency informations maped
|
The low-spatial-frequency informations are mapped near the center of k-space and the
|
|
|
Where are high spatial frequency informations mapped
|
high-spatial-frequency informations are mapped to the periphery of k-space
|
|
|
Where is most MR image information located in K-space
|
Most MR image information (contrast and general shape) is contained in the center of k-space
|
|
|
What does the image information stored in the center of K-space look like
|
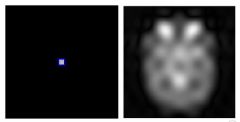
|
|
|
What information is stored in the center of K-space
|
Low-spatial-frequency data have the highest amplitude, giving the greatest changes in gray levels (contrast).
|
|
|
What does the high spatial frequency in the periphery do
|
They don't have effect on contrast or general shape but sharpens the image as they encode the edges (rapid changes of image signal as a function of position)
|
|
|
What happens to the image the farther from the center of K space the data is collected
|
Thus, the farther from the center of k-space the data are collected, the higher is the spatial-frequency information and the better the spatial resolution will be
|
|
|
What does the information at the periphery of K space look like
|
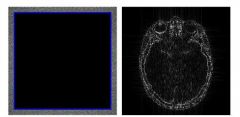
|
|
|
What does it look like if most of the data in the center K space is missing but the periphery is present
|
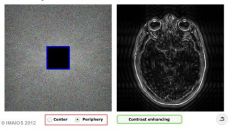
|
|
|
Can you use a line by line rectilinear trajectory to fill K-space
|
yes
|
|
|
What does it look like if K-space is filled by a linear trajectory
|

|
|
|
What is filled first during linear trajectory filling of K-space
|
One line of k-space is fully acquired at each excitation, containing low and high-horizontal-spatial-frequency information (contrast and resolution in the horizontal direction).
|
|
|
What causes a change in the Y direction in the linear trajectory filling of K space
|
Between each repetition, there is a change in phase-encoding-gradient strength, corresponding to a change in ky-coordinate
|
|
|
Since linear trajectory move from top to bottom ( y direction) what is the sequence of information obtained
|
This allows filling of all the lines of k-space from top to botton, acquiring high-positive vertical-spatial-frequency information (resolution in the vertical direction) then low vertical-spatial-frequency information (contrast in the vertical direction) and then high-negative vertical-spatial-frequency information (resolution in the vertical direction again)
|
|
|
What is the appearance of the image as K space is createdd
|
During the filling of k-space, the resulting image is containing at the bigenning the edge information with low contrast, then the general shape and contrast with a blur in the vertical direction that will disappear as high-vertical-spatial-frequency information are completed
|
|
|
Where is the image about contrast and general shape located in K-space
|
the center
|
|
|
Where are the image edges located in K-space
|
the periphery
|
|
|
What improves the spatial resolution
|
data in the periphery of K space
|

