![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
principle of relativity |

consider a particle in inertial frame A following a path. in another frame of reference B, it's moving with constant velocity along a new path |
|
|
einsteins postulates |
1. the laws of physics are identical in different inertial frames 2. the speed of light is constant for observers in inertial frames |
|
|
time dilation |
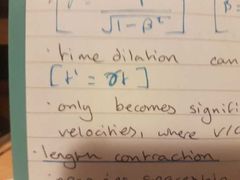
observes a slower time |
|
|
time dilation derivation |

|
|
|
lorentz factor |

only becomes significant at super high velocities |
|
|
length contraction |

|
|
|
difference in time in train thought experiment |

|
|
|
an event |
something that happens at a particular moment and at a particular place |
|
|
spacetime diagrams |

|
|
|
moving frame f' diagram |

tilted axes |
|
|
invariant interval |

represents separation between two events in space time. has a - because interval can be imaginary. interval is the same for all observers, is independent of reference frame |
|
|
lorentz transformations |
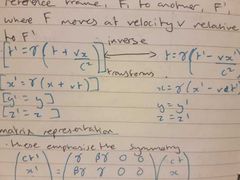
how time and space change when changing reference frames |
|
|
matrix representation of lorentz transforms |

emphasise symmetry |
|
|
velocity addition rule |

|
|
|
twin paradox |

|
|
|
bell's paradox |

|
|
|
mass energy equivalence |
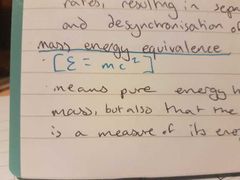
bitch u already know |
|
|
rest mass and energy |
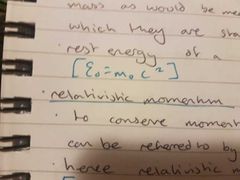
normal newtonian mass that would be measured if in a stationary frame. invariant |
|
|
relativistic mass |
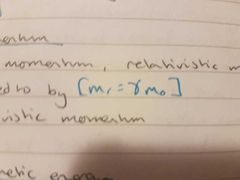
|
|
|
relativistic momentum |
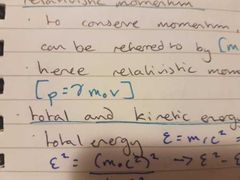
|
|
|
total energy |
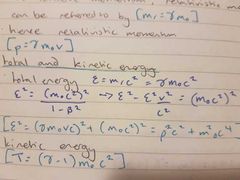
|
|
|
kinetic energy |
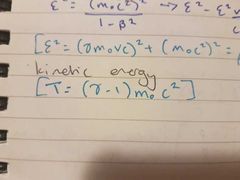
|
|
|
atmospheric muon problem |
muons move close to speed of light, so when they travel to earth it should take like 30*10^-6s. but their half lives are 1.6*10^-6s so you would think not many make it, but loads do. solved by 1. lorentz factor ~ 5, extending half lives through time dilation to 8*10^-6s. 2. muons view earth as coming towards them, distance through length contraction is about 2km, arrives in 6*10^-6s |
|
|
relativistic doppler effect |

takes time dilation of source into account |
|
|
special relativity and magnetism |

|
|
|
proper time and distance |
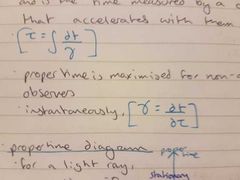
lengths and times measured in frames in which they are stationary. applied to an accelerated observer, is the time measured by a clock accelerating with them |
|
|
proper time diagram |
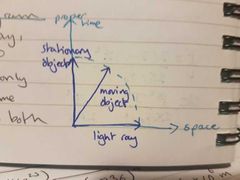
|
|
|
4 velocity |

magnitude always = c |
|
|
4 momentum |

|
|
|
acceleration in special relativity |

|
|
|
principle of equivalence |
observers in freefall cannot determine their acceleration by any local measurement. similarly, observers at rest on a planet would find the same physics as an observer accelerating through space far from gravitational sources |
|
|
general relativity implication |
light bends in a gravitational field, therefore time runs slower in gravitational fields |
|
|
geometry of spacetime |
gravity super affects the curvature of space. free falling objects are following straight lines in curved spacetime. |
|
|
definition of black hole |
an object where its gravitational field is sufficient enough to keep even light from escaping |
|
|
gravitational redshift |

time slowing effect from light bending causes this |
|
|
schwarzschild radius |

light is infinitely redshifted is emitted here, so time stops at this point for an observer. |

