![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
80% of Upper respiratory diseases (URI) are caused by (bacteria/virus) |
Virus! |
|
|
|
2 main bacterial pathogens assoc w/ URI |
Group A streptococcus staphylococcus aureus
|
|
|
|
fever inflammatory edema of nasal mucosa initially clear secretions |
rhinitis |
|
|
|
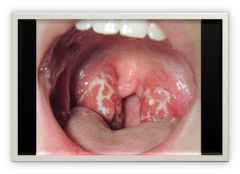
sore throat red and swollen pharynx exudates and/or petechial hemorrhagic spots enlarged tender ant cervical lymph nodes |
pharyngitis and tonsillitis |
|
|
|
URI that presents w/ headache, runny nose, fever, body ache is most likely (viral/bacterial) |
viral
(bacterial is likely lymph enlargement, difficulty swallowing) |
|
|
|
pharyngitis or tonsilitis
+ vesicles and ulcers on pharyngeal (& oral) mucosa. |
HSV****(herpes = vesicles)
and pharyngeal candidiasis |
|
|
|
pharyngitis or tonsilitis + pseudomembrane in oral cavity. |
pharyngeal diphtheria |
|
|
|
Multiple ulcers on oral mucosa extending to tongue lips and face is referred to as ____________ |
stomatitis |
|
|
|
Stomatitis can also present as oral thrush in pts w/ ____________________ This is normal in infants but abnormal in adults, usually signifies immunocompromised host. |
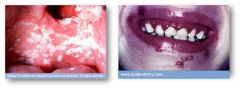
candidiasis (fungus) (L image)
(R is typical stomatisis in herpes) |
|
|
|
single or multiple painful ulcers with irregular margin in the oral cavity. Recur in relation to stress, menses, local trauma and other non-specific stimuli. |
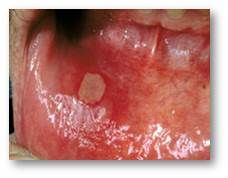
aphthous stomatitis
(unknown pathogen) |
|
|
|
severe gangrenous type of URTI that progresses beyond the mucus membrane to involve soft tissue, skin, and sometimes bone |
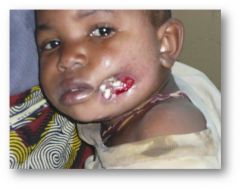
Noma or cancrum oris
|
|
|
|
in what population is noma usually found? |
Severly malnutritioned children very poor oral hygeine or immunocompromised adults |
|
|
|
what is the etiology of noma? |
fusobacterium, bacteroids, and p.aeruginosa |
|
|
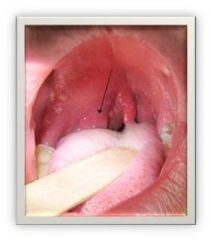
local pain (hard to swallow), tonsillar asymmetry with 1 tonsil usually displaced medially by the abscess |
peritonsillar and retrotonsillar abcesses
(untreated URI can cause ^)
|
|
|
|
what population is peritonsillar abscess most commonly found? |
children above 5 years age and adults |
|
|
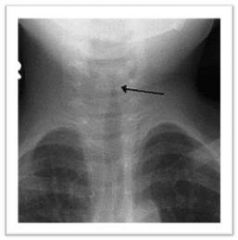
Sx: pain, change in phonation, extended neck (inc distance btwn cervical spine & post. pharyngeal wall) |
retropharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal abcesses
(caused from complication of pharyngitis^) |
|
|
|
most commonly affect is infants and children under 5 years of age and may arise as a complication of pharyngitis. |
retropharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal |
|
|
|
what do you always do first when presented with an abscess? |
* give antimicrobials then drain the abscess
(prevents aspiration pneumonia &/or hemorrhage)
|
|
|
|
what do you treat & diagnose S. pyogenes infection with? |
tx: rapid strep test dx: penicillin
(for pharyngitis/tonsilitis, usually do strep test, if neg assume viral & do nothing/tx symptoms) |
|
|
|
If strep - & clinical suspicion for C. diptheriae & N. gonorrhioeae, how do you diagnose? |
gram stain culture (diptheria is +) |
|
|
|
What do you use to treat N. gonorrhoeae & C. diptheria? |
N. gonorrohea- antibiotics C diptheria- antibiotics + antitoxins |
|
|
|
throat and neck pain, inspiratory stridor, muffled phonation, difficulty in swallowing. |
epiglottitis. (middle respiratory infection, usually bacterial) |
|
|
fever, inspiratory stridor, hoarse phonation, harsh barking cough. (brassy cough). steeple sign (x-ray) |
laryngitis and croup (MRI, stridor is specific to MRI)
(steeple sign caused by inflammed glottis in croup, obstructs airway) |
|
|
|
critters to blame for laryngitis and croup?
esp. #1 cause in infants?!! |
Viruses to blame: Parainfluenza viruses, influenza viruses, adenoviruses, and RSV
#1= parainfluenza |
|
|
|
sputum and bubbling ronchi, cough, and fever |
Bronchitis or tracheobronchitis (^can be caused by untreated laryngitis) |
|
|
|
more common in people who have an underlying lung condition. Lack functional integrity and are susceptible to infections with members of oropharyngeal flora. (2-3 months per year for 3 yrs) |
chronic bronchitis |
|
|
|
two most common infections occur chronic bronchitis |
S. pneumonia and H. influenza |
|
|
|
Which of the following is the ONLY one that is more commonly bacterial (not viral)? Epiglottitis Laryngitis/Croup Tracheitis Bronchitis
What is the most common bacterial pathogen? |
Epiglottis!
#1 bacterial pathogen = Haemophillus influenza |
|
|
|
what is the main cause of acute bronchitis in kids? |
B. pertusis |
|
|
|
what is the appropriate medium for B. pertusis?
|
chocolate blood agar (w/ gram stain) |
|
|
|
If viral infection is suspected you do not do gram stain. For what common bacterial infections do you NOT use gram stain? why? |
mycoplasma pneumoniae- no cell wall chlamydia pneumoniae- intracellular
(neither will stain, due serology instead) |
|
|
|
What do you ALWAYS do in respiratory infection treatment? |
maintain airway!!! (nasotracheal tube, tracheostomy) |
|
|
|
what is the cut off point between URTI and MRTI?
|
epiglottis
|
|
|
|
3 ways a LRTI may result from
|
may result from aspiration of pathogens (immitis, TB, anthracis), hematogenous spread from a distant site, extension of MRTI. |
|
|
|
(LTRI) Acute or chronic pneumonia is NEVER caused by a virus |
chronic (lung abscess & empyema also never viral)
(these all may be bacterial or fungal)
|
|
|
|
How is pneumonia identified on a radiograph? |
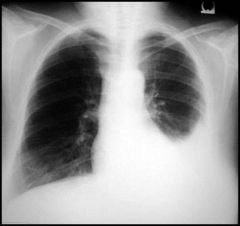
*loss of costophrenic angle = 1st sign (on R) |
|
|
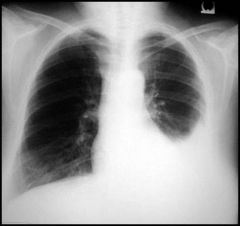
Why does pneumonia cause pleural effusion (exudation of fluid in pleural space) |
inflammation of lung parenchyma causes injury to blood vessels, allowing fluid to leak out into pleural space
(high protein content in exudation) |
|
|
|
fever, cough, productive purulent SPUTUM. |
acute pneumonia
(sputum is best way to determine pathogen) |
|
|
|
what critter is to blame for 2/3 of community acquired pneumonia? |
streptococcus P |
|
|
|
what two pathogens cause acute pneumonia in immunocompromised individuals?
|
candida albicans and pneumocystis
|
|
|
|
what pathogen is #1 in AIDS patients for causing acute pneumonia? |
pneumocystis
|
|
|
|
Sx: fever, night sweats, sleeplessness, dyspnea, sputum-long term. cough w/o sputum |
chronic pneumonia
|
|
|
|
what are the two common pathogens for chronic pneumonia?
|
mycobacterium Tb and mycobacterium Nocardia
|
|
|
|
purulent infection of pleural space (either from infected lung or abdominal infection). |
empyema
|
|
|
|
what pathogens cause empyema? |
anaerobes and S. aureus |
|
|
|
sx: fever, cough, foul-smelling sputum. |
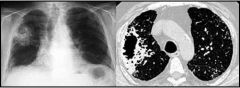
lung abscess in lung parenchyma |
|
|
|
What is the tx procedure for lung abscesses &/or empyema? |
intervention (drain/remove) + antibiotic |
|
|
|
what does true sputum show? |
an abundance of inflammatory cells (neutrophils) and NO squamous epithelial cells |
|
|
|
what does saliva usually show? |
SQUAMOUS eipthelial cells and mixed bacterial population. |
|
|
|
3 Gram + Cocci |
SES staphylococcus streptococcus enterococcus |
|
|
|
3 Gram - Cocci |
MAN Moraxella Acinetobacter Neisseriaceae (Gonorrhoeae & Miningitidis)*
|
|
|
|
Which gram - cocci causes BOTH upper & lower respiratory infections? |
Moraxella |
|
|
|
Gram + bacilli |
spore formers & N-CLAM
spore formers= bacillus & clostridium N= nocardia C= corynebacterium (diptheria) L= listeria A= actinomyces |
|
|
|
4 Aerobe gram - bacilli |
BBFP Bordetella Brucella Francisella Psuedomonas |
|
|
|
4 lactose fermenting gram- bacilli |
CEEK citrobacter enterobacter escherechia klebsiella |
|
|
|
ONLY obligate anaerobe gram - bacilli |
bacteroides |
|
|
|
6 oxidase - gram - bacilli |
MY PSSS Morganella Yersenia Proteus Salmonella Shitrella Serretia |
|
|
|
2 oxidase + gram - bacilli |
HP Haemophilus Pasturella |
|
|
|
ABC Bacilli anaerobes |
Actinomyces (+) Bacteroides (-) Clostridium (+)
(likes repel, aren't by each other^ & bacteroide is ONLY - anaerobe) |
|
|
|
what is the causative organism for bacterial strep throat, which is the #1 URI? |
streptococcal pyogenes
(not diptheria bc it is vaccinated against) |
|
|
|
#1 cause of CAP? |
S. pneumoniae |
|
|
|
Morphology: gram positive oval cells growing in chains. Non acid Fast, not spore forming, nonmotile |
streptococcal pyogenes |
|
|
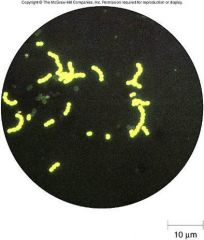
what is this a culture of? |
streptococcal pyogenes
(chainlike arrangement, NOT a catalase producer) |
|
|
|
3 complications of untreated strep- |
acute glomerulonephritis* acute rheumatic fever* scarlet fever |
|
|
|
What type of hypersensitivity is acute glomerulonephritis? acute rheumatic fever? |
acute glomerulonephritis- type 3 acute rheumatic fever- type 2 |
|
|
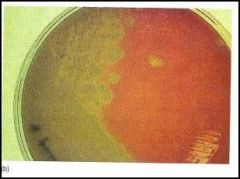
what type of hemolysis is this an example of?
|
alpha
|
|
|

what type of hemolysis is this (in blood agar enriched medi)? |
Beta
(both A & B streptococci are beta hemolytic) |
|
|
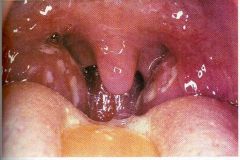
diagnosis?
|
streptococcal pharyngitis and tonsilitis |
|
|
|
How do cell wall proteins M & G cause streptococcus pyogenes virulence? |
M- degrades C3b preventing opsonization G- binds to Fc portion, preventing phagocytosis
|
|
|
|
______________ produces disease unrelated to strep; scarlet fever, toxix shock, & flesh eating necrotizing factor |
SPEs (streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins) |
|
|
|
what two pathogen categories produce superantigen? what does this cause? |
staph aureus and strep pyogenes. (gram + cocci)
Induces polyclonal T cell activation which leads to DIC, hypovolemia, MOF.= toxic shock syndrome |
|
|
|
What enzymes are responsible for strep pyogenes invasion into deeper tissue layers? |
streptokinase, hyluronidase, DNase, protease |
|
|

what is this an example of? |
GAS rapid method test for strep pyogenes
(antigen + antibody= agglutination, L dish)
(old strep test) |
|
|
|
What is the current strep test? |
rapid strep test = solid phase ELISA
(on test strip) |
|
|
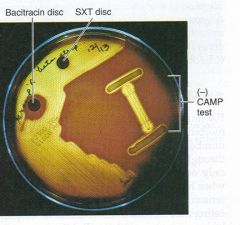
what is this test? what is it for?
|
Bacitracin sensitive; + testing for Group A streptococcus (pyogenes)
(group B (agalactis) are resistant, use CAMP for group B) |
|
|
|
What is the 1st choice tx for strep? |
penicillin
(then erythromycin & cephalexin) |
|
|
|
sx: strawberry tongue
|
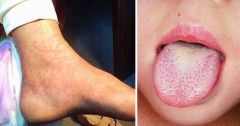
scarlet fever |
|
|
|
Result of infection with s. pyogenes strain that is itself infected with a bacteriophage (T12).
Tx? |
scarlet fever
is self-limiting but usually give penicillin |
|
|
|
complication of untreated streptococcus pyogenes. Antibodys cross-react w/ antigenic epitopes. Usually begins 3 weeks post infection. |
rheumatic fever |
|
|
|
5 Major criteria: carditis, arthritis, chorea, erythema marginatum, subcutaneous nodules |
rheumatic fever |
|
|
|
Minor criteria: fever, joint pain, ASO titer> 200, EKG change
How many criteria should you meet to diagnose rheumatic fever? |
2 major or 1 major + 2 minor |
|
|
|
how do you treat the infection, pain and inflammation, and chorea of rheumatic fever?
|
infection- penicillin (ten day or single injection of Pencillin-G + 5 yr maintanence dose), pain and inflammation- aspirin chorea (CNS jerk)- diazepam or haloperidol |
|
|
|
what is a (type 3 hypersensitivity) complication that may arise from S. pyogenes infection? |
acute glomerulonephritis |
|
|
|
Sx: runny nose, fever with shaking chills, sputum that is rust colored.
|
Pneumococcal pneumonia |
|
|
|
Causative agent of pneumococcal pneumonia__________________ ONLY gram + diplococcus thick capsule (virulence factor) alpha-hemolysin |
streptococcus pneumoniae
(causes 2/3 of CAP) |
|
|
|
what is the only other alpha-hemolysin |
s. viridans |
children over 5
S pyogenes |
|
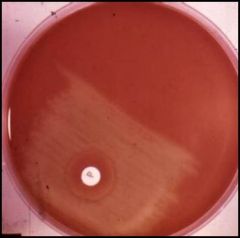
what is this disc? what is it testing for? |
Optochic disc for s. pneumonia *used to differentiate btwn S viridans & S. pneumonia |
|
|
|
what medium is used to determine the pathogen associated with pneumococcal pneumonia? what is a rapid test that can be done? |
optochin disc; bile solubility: clear is positive, cloudy is negative.
(+ for strep. pneumonia) |
|
|
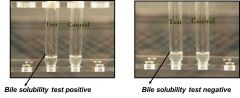
what will this test prove?
|
rapid bile solubility test of pneumococcal pneumonia via Streptococcal pneumonia = clear + |
|
|
|
what is the pathogen associated with alcohols who contract pneumococcal pneumonia? what type of pneumonia is presented here? |
Streptococcus Pneumonia; lobar pneumonia |
|
|
|
what is the #1 pathogen for adults that can cause meningitis? |
S. pneumoniae |
|
|
|
what is the tx for pneumococal pneumonia? what is the S. pneumoniae is resistant to all other antibiotics?
|
penicillin and its derivatives; use ketolides.
|
|
|
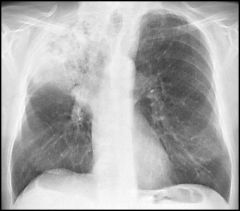
diagonsis?
|
lobar pneumonia
(whole lobe, homogenous infiltrate) |
|
|
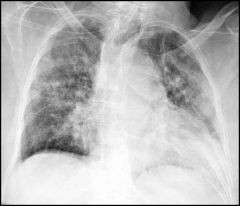
diagnosis?
|
bronchopneumonia
(patchy infiltrate, surrounding bronchioles) |
|
|
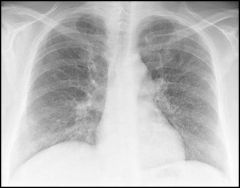
diagnosis?
|
interstitial pneumonia
(ground glass appearance, streaks from hilum to periphery) |
|
|
|
what is the leading cause of interstitial pneumonmia in; immunocompetent pt- immunocompromised pt (HIV)- bone marrow transplant pt- |
immunocompetent- viral immunocompromised (HIV)- pneumocystis bmt- cmd |
|
|
|
___________ hemloytics are NOT hemolytic at all.
What test can differentiate enterococcus sp, an example of this hemolytic? |
gamma
bile esculin agar (high salt)- the ONLY thing that will grow is enteroccoccus |
|

