![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
describe the two major functions of the respiratory system |
1. air conduction, air filtration, gas exchange (O2 and CO2) 2. speech, smell, endocrine (hormone production), immune response |
|
|
describe generally the characteristic changes in tissue from the bronchi down to the alveolar sacs |
diameter of lumen decreases thickness and rigidity of wall decreases (cartilage is replaced with smooth muscle) height of epithelial lining decreases (ciliated pseudostratified columnar to simple squamous) number of glands decreases to none |
|
|
what are the cell types found in the trachea and bronchi |
ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium goblet cells (single cell glands producing mucus) brush cells (short columnar cells with blunt cilia, epithelio-dendritic synapses, sensory) small granule cells (granules containing transmitters and hormones, neuromodulator and endocrine) basal cells (replenish dead cells) |
|
|
what are the layers of the tubular structures |
tunica mucosa-- epithelium, lamina propria mucosae (loose connective tissue), lamina muscularis mucosae (smooth muscle)** separates from submucosa tunica submucosa-- (loose connective tissue with vessels, nerves, glands) tunica muscularis-- (smooth muscle) tunica serosa or adventitia-- (loose connective tissue covered by serous epithelium [simple squamous]) |
|
|
describe the trachea wall |
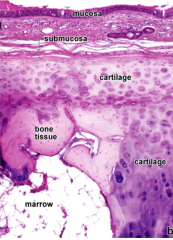
C shaped cartilagenous membrane fibroelastic membrane against esophogeal border notice ossified cartilage |
|
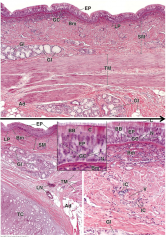
label this image of the trachea |
tunica mucosa, basal membrane tunica submucosa, smooth muscle, glands tunica muscolaris (large portion, must be membranous part not cartilagenous part) cilia, columnar epithelial cells (ovoid nuclei, perpendicular) hyalin cartilage |
|
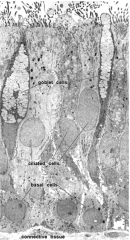
describe the cell types in this image |
ciliated psuedostratified columnar epithelium goblet cells basal cells not pictured: brush cells, granule cells |
|
|
what are the characteristics of the bronchi |
right and left bronchi, lobar bronchi (3 and 2): pulmonary lobes segmental bronchi: bronchopulmonary segments terminal bronchi hyaline cartilage (rings or plates) ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet, granules, brush and basal cells continuous smooth muscle layer mucinous glands |
|
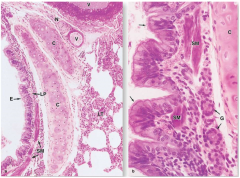
label this bronchus tissue |
lumen, epithelia (tunica mucosa) cartilage (smaller than trachea) epithelia, basal cells, smooth muscle cells, glands |
|
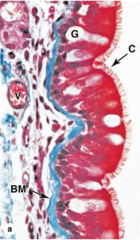
identify the major cells of this bronchus |
ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium goblet cells basal membrane connective tissue vessels |
|

identify the major cell types in this SEM of the bronchus |
goblet cells brush cells |
|
|
what are the bronchopulmonary segments? |
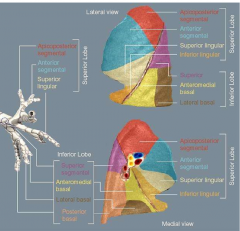
superior lobe apicoposterior anterior segmental superior lingular inferior lingular inferior lobe superior anteromedial basal lateral basal posterior basal |
|
|
identify the key differences between a bronchus and a bronchiole |
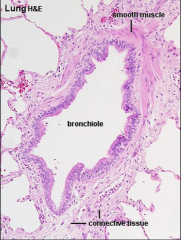
smooth muscle only (no cartilage) no glands |
|
|
define bronchus terminalis |
end point of bronchus where it transitions into bronchiole last evidence of cartilage |
|
|
define pulmonary lobule and pulmonary acinus |
lobule: bronchioli, (AND)
acinus: terminal bronchioli, respiratory bronchioli, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, alveoli |
|
|
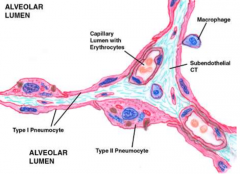
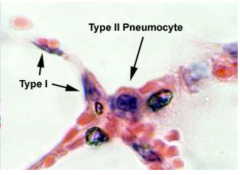
what are the cell types present from bronchioli to alveoli |
single columnar, ciliated epithelium (bronchioli) Clara cells (cuboid, dome shaped apical surface, very characteristic) (terminal and respiratory, alveolar ducts) type 1 alveolar cells (type 1 pneumocytes) type 2 alveolar cells (type 2 pneumocytes) (alveolar sacs) intraalveolar macrophages (small granule cells, brush cells, dendritic cells) (from trachea to bronchioli) |
|
|
what does BADJ stand for and why is it clinically relevant |
broncho-alveolar duct junction (contains broncho-alveolar stem cells [BASC]) site of lung cancer |
|
|
describe granule cells |
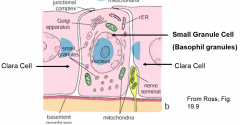
endocrine cells for secretion, surrounded by nerve terminals and clara cells |
|
|
describe clara cells |
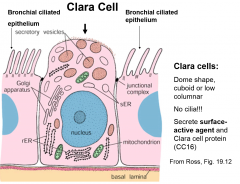
dome shaped, cuboid or low columnar no cilia secrete surfactant and clara cell protein (CC16) |
|
|
describe brush cells |
low columnar cells with blunt microvilli basal surface has synaptic contact with afferent nerve endings |
|
|
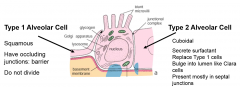
describe Type 1 alveolar cells |
squamous, have occluding junctions, barrier, do not divide |
|
|
describe Type 2 alveolar cells |
cuboidal, secrete surfactant, replace Type 1 cells, bulge into lumen like clara, mostly present in septal junctions |
|
|
what is the total surface area of alveoli
|
roughly 75m^2
150 to 250 million of them about 0.2mm thick |
|
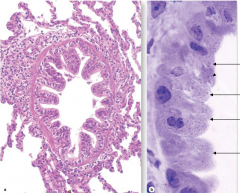
what are the cell types and location |
simple columnar (ovoid nucleus), no cilia clara cells (round nucleus) basal membrane terminal bronchiole |
|
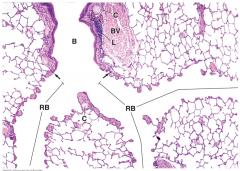
describe this image from top to bottom |
bronchus, bronchus terminales (cartilage stops), bronchiole respiratory bronchiole (epithelium flattens, clara cells for gas exchange) |
|
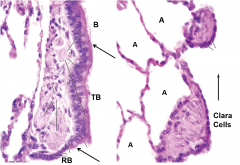
describe these two zoomed images of cell layers |
left epithelium changes from psudostratified to columnar to cuboidal (clara) bronchus to terminal bronchiole to respiratory bronchiole right alveoli (type 1 and 2 cells) and clara cells |
|
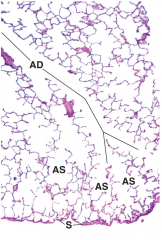
describe the structures in this image |
alveolar duct into alveolar sac with alveoli surface of lung covered by squamous epithelium (visceral pleura) |
|
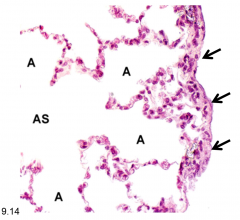
describe the structures in this image |
alveolar sac with alveoli and lung surface (simple squamous, visceral pleura) |
|
|
what germ layer do the lungs develop from |
endoderm |
|
|
what is a major problem associated with premature childbirth |
underdeveloped alveoli, babies need respirator and complex oxygen supply |

