![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is motivation? |
Process in the brain controlling which behaviours and physiological changes occur and when
|
|
|
What does motivation involve? |
Involves goals, actions, behaviour sequences, homoeostasis, drivve and perhaps feelings and emotions |
|
|
Motivation is a concept used to understand the _____________ and to explain _____________. |
Variability of behaviour
decision making |
|
|
How has evolution shaped animals? |
So that the most important behaviours are the most highly motivated -suffer when this is prevented (frustration) |
|
|
Measuring motivation is possible with... |
Demand Experiments |
|
|
Motivational Strength is?
Example? |
The probability of performing a given behaviour and the frequency, or vigour, with which it is performed.
Ex. the more hunger a rat is: the more its going to do what it needs to get food |
|
|
What are four reasons why we study motivation? |
1. Poor welfare due to unfulfilled motivations 2. Understanding stereotypic behaviour 3. Learning and Training 4. Promotes species typical behaviour |
|
|
What do preference and motivation tests measure? |
The tendency for an animal to perform a behaviour (reflect desire to do so) |
|
|
What are the 3 research questions? |
1. Which of several resources satisfies a particular motivation?
2. How important is it that a particular motivation is satisfied at all?
3. If we make a change, what effect does this have on its motivation for a particular resource? |
|
|
What kind of test does each research question use?
1. Which of several resources satisfies a particular motivation?
2. How important is it that a particular motivation is satisfied at all?
3. If we make a change, what effect does this have on its motivation for a particular resource? |
1. Choice Test - different resources 2. Operant Test - animals have to work to get a resource 3. Operant Test |
|
|
What are the advantages to using preference tests? |
Easier to quantify motivational strength than with stereotypy or stress hormones
Easy to interpret: animals shows you what it wants by choosing it (may choose this that aren't good) |
|
|
What are the disadvantages to using preference tests? |
Reveal how badly animals what things when they are available, but not necessarily how badly they miss them when they're absent -may not be aware they are missing something in their environment |
|
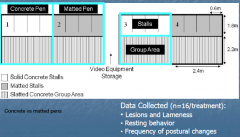
Example: Concrete vs matted pens Outcome? |
Rubber mats can improve welfare by increasing postural changes and reducing lesions (farrowing and gestation housing) |
|
|
Drawing inferences between preference tests and welfare requires we establish how strongly an animal…(3) |
-prefers a chosen option -avoids unpreferred option -is motivation to perform a behaviour that is prevented in some areas |
|
|
Preference strengths (2) |
-strong preferences -weak but consistent preferences (chocolate ice cream vs vanilla - may have a strong preference but that does not mean welfare decreases) |
|
|
Three ways to assess preferences and measure motivation... |
1. learn to perform task - if they learn to perform a task to access than motivation is higher (operant) 2. How hard will an animal work? - price animal is willing to pay 3. Economic analysis - inelastic (necessities - keep trying no matter price) vs elastic (luxuries - only try to certain point) |
|
|
What are the 4 manipulations of the economic model? |
1. Limiting available time (time to gain resource) - reducing income 2. Obstructive techniques - increase cost 3. Operant Conditioning - increase cost 4. Aversion testing - measure avoidance (removes itself from negative stimuli) |
|
|
Limiting the time available is... |
The time to perform activities regarded as income
As time is decreased, luxury activities dropped |
|
|
What was Dawkins (1983) study consist of? |
Limiting available time Hen in apparatus with access to cage with food or cage with litter for 2, 4, or 8 hours per day -no other food -8hours, birds spent more time with litter -2 hours, birds spent more time feeding |
|
|
Measuring Obstructive techniques
What can be a problem? |
-weighted door (access to food or nest box) -space to cross
Potential problem as physical ability may be a limiting factor rather than a motivation |
|
|
Measuring aversion
Example? |
-motivational strength to avoid a stimulus
Example: electro immobilization of sheep reduces distress during restraint for shearing -sheep that get this, became harder to move down the corridor |
|
|
Operant Conditioning tests
Example? |
-Animals learn to make a response in order to gain reward or avoid punishment
Ex. thermal environment for chicks, pigs work more for food than social contact
|
|
|
Skinner rat box |
-Increase the price each day for positive item: have to press button at variable increasing intervals 'elastic and inelastic' demand curves |
|
|
Demand Curves |

Inelastic and Elastic -green is the negative control (no reward) -Red (reward with food) |
|
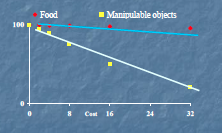
Do pigs need access to forage material? Explain the graph... |
Evidence that growers will work to access manipulate substrates |
|
|
Sow housing - stalls vs group housing |
Motivation for a day's access to a non enriched group pen is no greater in dominant sows than motivation for food when close to satiation
Little evidence that sows are highly motivation for non enriched space with social contact
|
|
|
Space quality and pigs |
A barren pen with some more space may not be worth much to the sow - not very motivated to use extra space when given the option |
|
|
When comparing the motivation of stall housed sows for access to 1 of 4 resources: rubber matt, cotton rope, food in trough (positive control), empty trough (negative control)
What was the hypotheses and predictions? |
Hypothesis: Sow motivation and their willingness to work on an operant panel would be affected by the resource provided Predictions: High motivation for food Low motivation for an empty trough Motivation for enrichments of value would be significantly different from motivation for an empty trough |
|
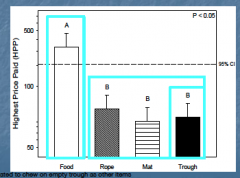
Low motivation for Enrichments - what does this say? |
As motivated to chew on empty trough as other items |
|
|
Questions about aversion…. (cows) |
Does aversion handling impact milk production?
What type of handling do cows prefer/find aversive?
How do we ask the cow? |
|
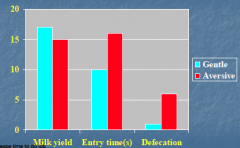
Explain the graph... |
Aversion handling decreases milk yield and efficiency of handling
Also increases the amount of time to do the job and defecation |
|
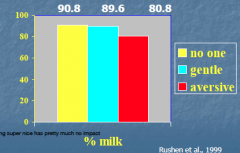
Here some graphs… Less milk obtained when aversive handler present (being nice has pretty much no impact) |
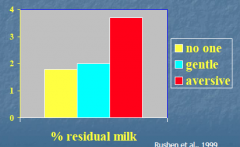
Residual milk is higher when averse handler is present |
|
|
Conclusion of aversive handling and milk production.. |
-decreases milk production -increase residual milk -Decreases the efficiency of milking -Increases defecation and urination in the parlor |
|
|
Soo.. How would we ask the cow which techniques it likes better? (2 techniques) |
Y-maze Aversion corridor |
|
|
Aversion Corridor
What averse handling techniques did they use for the cows?
(animal learned it would get one of these techniques when going down the corridor) |
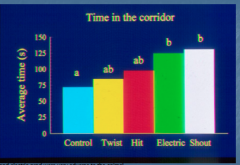
Tail twist, hit, should, electric prod
**shout and electric prod were very adverse |
|
|
Advantages of measuring motivation? |
Measures of motivation tells us directly about an animals feelings
They are more sensitive than many other measures |
|
|
Disadvantages of measuring motivation? |
Animals sometimes want things that are bad for them, or want to avoid things that are good for them |

