![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
a) The chloroplast ATP synthase shares structural similarities with F-type enzymes from mammalian mitochondria and bacteria but differs in the number of c subunit. Chloroplasts are thought to have _______ subunits in the c-ring.
1) 2, 2) 10, 3) 12, 4) 14, 5) 32, 6) none of the above. |
4) 14,
|
|
|
b) The metabolism of which of the following compounds may ultimately give rise to new glucose in mammals?
1) acetyl-CoA, 2) palmatoyl-CoA, 3) alanine, 4) lysine, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
3) alanine,
|
|
|
c) In the Calvin Cycle, the enzyme that catalyzes the capture of carbon dioxide and the formation of 3-phosphoglycerate is:
1) phosphoglycerokinase, 2) triose phosphate isomerase, 3) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, 4) RUBISCO, 5) ribulose-5-phosphate kinase, 6) none of the above. |
4) RUBISCO,
|
|
|
d) The following enzyme pathways or enzyme reactions are located in the cytosol:
1) pentose phosphate pathway, 2) fatty acid biosynthesis, 3) cholesterol synthesis, 4) glycolysis, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
5) all of the above,
|
|
|
e) Slow-twitch muscles:
1) are deficient in mitochondria but high in glycolytic enzymes, 2) are also designated as white-muscle, 3) commonly metabolize fatty acids and ketone bodies, 4) mainly metabolize glycogen and often generate high levels of lactate, 5) both 1 & 2 above, 6) none of the above. |
3) commonly metabolize fatty acids and ketone bodies,
|
|
|
f) In a tissue that metabolizes glucose via the pentose phosphate pathway, radioactively labeled C-1 of glucose would be expected to end up principally in:
1) glycogen, 2) phosphoglycerate, 3) carbon dioxide, 4) ribulose 5-phosphate, 5) pyruvate, 6) none of the above. 7) all of the above. |
3) carbon dioxide,
|
|
|
g) Consider RUBISCO catalytic activity; the oxygenase function leads to the formation of which compound?
1) ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate, 2) fructose-1,6-bisphosphate 3) phosphoglycolate, 4) phosphoenolpyruvate, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
3) phosphoglycolate,
|
|
|
h) Given the appropriate precursor, which of these can be synthesized by plants but not by humans?
1) palmitate (16:0), 2) arachidonate [20:4(Δ5,8,11,14)], 3) palmitoleate [16:1(Δ9)], 4) linoleate [18:2(Δ9,12)], 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
4) linoleate [18:2(Δ9,12)],
|
|
|
i) In C4 plants like corn, the bundle sheath chloroplasts:
1) have few granal stacks, 2) are enriched in photosystem I 3) carry out Calvin cycle reactions, 4) all of the above, 5) none of the above. |
4) all of the above,
|
|
|
j) A fatty acid with an odd number of carbons will enter the citric acid cycle as acetyl-CoA and ______?
1) α-ketoglutarate, 2) Malate, 3) succinyl-CoA, 4) citrate, 5) butyrate, 6) none of the above. |
3) succinyl-CoA,
|
|
|
k) Of the following sequences, which shows the correct molecules and components through which electrons flow in non-cyclic electron transport?
1) PS I complex, plastoquinone, cyt b6/f complex, plastocyanin, PS I. 2) H2O, PS I complex, UQ, cyt b6/f complex, plastocyanin, PS II, NADP+. 3) H2O, PS I complex, plastoquinone, cyt b6/f complex, plastocyanin, PS II, NADP+. 4) H2O, PS II complex, plastoquinone, cyt b6/f complex, plastocyanin, PS I, NADP+. 5) H2O, PS I complex, plastocyanin, cyt b6/f complex, plastoquinone, PS II, NADP+. 6) None of the above. |
4) H2O, PS II complex, plastoquinone, cyt b6/f complex, plastocyanin, PS I, NADP+.
|
|
|
l) Scatchard analysis may give information about:
1) the ligand binding constant (Kb) of a protein, 2) the number of ligand binding sites on a protein, 3) the type of homotropic cooperativity associate with ligand binding, 4) all of the above, 5) none of the above. |
4) all of the above,
|
|
|
m) Which of the following is required in non-cyclic electron transport?
1) plastocyanin (PC), 2) photosystem I complex, 3) cytochrome b6f complex , 4) photosystem II complex, 5) plastoquinone, 6) all of the above, 7) none of the above. |
6) all of the above,
|
|
|
n) Which of the following is an excretion product of cholesterol:
1) acetoacetic acid, 2) lactate, 3) cholic (a bile) acid, 4) β-hydroxybutyrate, 5) acetone, 6) none of the above. |
3) cholic (a bile) acid,
|
|
|
o) The final product of purine degradation in humans is:
1) NH3, 2) allantoic acid, 3) allantoin, 4) uric acid, 5) urea, 6) none of the above. |
4) uric acid,
|
|
|
p) Fast-twitch muscles:
1) are deficient in mitochondria but high in glycolytic enzymes, 2) are also designated as white-muscle, 3) sometime use phosphocreatine in ATP synthsis, 4) mainly metabolize glycogen and often generate high levels of lactate, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
5) all of the above,
|
|
|
n) Which of the following is produced in association with non-cyclic electron transport in chloroplasts?
1) NADPH, 2) O2, 3) ATP, 4) all of the above, 5) none of the above. |
4) all of the above,
|
|
|
r) Cholesterol synthesis is thought to be regulated by:
1) phosphorylation of HMG-CoA reductase, 2) down regulation of HMG-CoA reductase synthesis, 3) proteolysis of HMG-CoA reductase, 4) all of the above, 5) none of the above. |
4) all of the above,
|
|
|
s) Mammalian tissues and cells from other organisms generally metabolize glucose at a high rate under anaerobic conditions; but when oxygen is added glucose metabolism is diminished significantly. This phenomenon is known as the:
1) Crabtree effect, 2) Warburg effect, 3) Pasteur effect, 4) Hill effect, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
3) Pasteur effect,
|
|
|
t) All of the oxidative steps of the citric acid cycle are linked to the reduction of NAD+ except the reaction catalyzed by:
1) isocitrate dehydrogenase, 2) malate dehydrogenase, 3) the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, 4) succinate dehydrogenase, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
4) succinate dehydrogenase,
|
|
|
u) Which two triose phosphates are produced during the Calvin cycle and are the starting points for starch and sucrose synthesis?
1) dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glycerate-1,3-bisphosphate. 2) 3-phosphoglycerate and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate. 3 3) dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. 4) 3-phosphoglycerate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. 5) ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate and glycerol phosphate. 6) none of the above. |
3) dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
|
|
|
v) The maximum theoretical amount of ATP produced from the complete aerobic oxidation of glucose via glycolysis, pyruvate dehydrogenase and TCA cycle employing the malate-aspartate shuttle is?
1) 0, 2) 2, 3) 30, 4) 32, 5) 106, 6) none of the above. |
4) 32,
|
|
|
w) The protein thioredoxin may be involved in which of the following processes?
1) regulation of the Calvin cycle, 2) reduction of NTP's, 3) regulation of HMG-CoA reductase, 4) reduction of folic acid, 5) both 1) and 2) above, 6) none of the above. |
5) both 1) and 2) above,
|
|
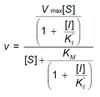
x) The equation below is characteristic of what type inhibitor?
1) competitive, 2) uncompetitive, 3) non-competitive, 4) mixed, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
2) uncompetitive,
|
|
|
y) Jagendorf and Uribe performed the “acid bath” experiment that provided experimental evidence for Mitchell’s Chemiosmotic Coupling Hypothesis. What model system did they use in the study?
1) bovine liver mitochondria, 2) E. coli cells, 3) chloroplast thylakoids, 4) cyanobacterial cells, 5) both 1) and 2) above, 6) none of the above. |
3) chloroplast thylakoids,
|

