![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Inhibition type?
|
Uncompetitive
|
|

Inhibition type?
|
Non-Competitive
|
|

Inhibition type?
|
Competitive
|
|

Inhibition type?
|

Mixed
|
|
|
*** Inhibition Is a Special Case of Mixed Inhibition
|
Noncompetitive
|
|
|
--- Hill Equation ---
1) X-Axis = ??? 2) Y-Axis = ??? 3) Hill coefficient (h or nh) is derived from... 4) Dissociation constant is derived from... |
1) log [S]
2) log (V/Vmax-V) OR log(θ/(1-θ) 3) slope 4) -log Kd (y-intercept) |
|
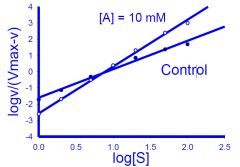
What type of plot is this?
|
hill plot
|
|
|
--- X-Axis of Hill Equation ---
1) Protein Ligand Binding Case? 2) Kinetic Binding? 3) Hill coefficient? 4) Dissociation constant? |
1) log (θ/(1-θ)
2) log (V/Vmax-V) 3) slope 4) -log Kd (y-intercept) |
|
|
--- ATP Synthase C-Ring SU ---
1) Chloroplast 2) Mammalian Mitochondria 3) Bacteria 4) Yeast Mitochondria |
1) 14
2) 8 3) 12-15 4) 10 |
|
|
--- New Glucose in Mammals ---
1) Bad Amino Acids? 2) Main compound? 3) acetyl-CoA? 4) palmatoyl-CoA? |
1) leucine and lysine
2) pyruvic acid 3) NO 4) NO |
|
|
--- Calvin Cycle ---
Enzyme catalyzing the capture of CO2 to form 3-phosphoglycerate is... |
RUBISCO
|
|
|
Key Steps of Calvin Cycle
1) R 2) P 3) T 4) G 5) T 6) R |
1) RuBisCo
2) PhosphoGlyceroKinase 3) triose phosphate isomerase, 4) GlycerAldehyde-3-Phosphate DeHydrogenase 5) Triose phosphate isomerase 6) Ribulose-5-Phosphate Kinase |
|
|
--- RuBisCO ---
1) Carboxylase products? 2) Oxygenase products? |
1) (2) phosphoglycERATE
2) (1) phosphoglycERATE, (1) phosphoglycOLATE phosphoglycerate = PGA |
|
|
--- Cytosolic Enzyme Pathways ---
Name 4... |
pentose phosphate pathway
fatty acid biosynthesis cholesterol synthesis glycolysis |
|
|
--- Pentose Phosphate Pathway ---
Glucose Metabolism 1) C1? 2) C2? 3) C6? |
1) CO2
2) C1 of ribulose 5-phosphate 3) C5 of ribulose 5-phosphate |
|
|
--- Fatty Acid Synthesis ---
1) Humans are unable to... 2) Humans are able to... |
1) 1 >>> 2
2) 0 >>> 1 Poly >>> Poly Can't make linoleate [18:2(Δ9,12)] |
|
|
--- C4 Plants ---
Bundle Sheath Chloroplasts.... 1) Have these PS... 2) Have few *** stacks. 3) Have many *** ***. |
1) PS I
2) granal Lamellae 3) unstacked Stroma Lamellae |
|
|
Odd # fatty acid enter Citric Acid Cycle as...
|
acetyl-CoA
and succinyl-CoA |
|
|
--- Scatchard Analysis ---
Tells us what about a ligand/protein? 1) *** Constant 2) # of *** 3) Type of *** |
1) Ligand Binding Constant (Kb)
2) ligand binding sites 3) homotropic cooperativity |
|
|
--- Cholesterol ---
Excretion products? |
bile salts
bile acids cholic acid |
|
|
--- Purine Degradation ---
Final product in.... 1) Humans? 2) Aquatic invertebrates? 3) Non-primates, reptiles and mollusks |
1) uric acid
2) ammonia [NH3] 3) allantoic acid or urea[CO(NH2)2] |
|
|
--- Citric Acid Cycle ---
All oxidative enzymes reduce NAD+ except... |
succinate dehydrogenase
|
|
|
--- Starch and Sucrose Synthesis ---
Triose phosphates from Calvin cycle are... 1) ***hydroxy*** phosphate and 2) glycer***-3-phosphate. |
1) Dihydroxyacetone P
2) glyceraldehyde-3-P |
|
|
--- ATP Synthesis from Glucose Metabolism ---
Glycolysis, Pyruvate Dehydrogenase, TCA Cycle 1) Aerobic w/ malate-aspartate shuttle? 2) Aerobic w/ glycerol-phosphate shuttle? 3) Anaerobic? |
1) 32
2) 30 3) 2 |
|
|
--- Thioredoxin ---
Regulates what? |
1) Calvin cycle
2) reduction of NTP to dNTP |
|
|
The protein *** regulates...
1) Calvin cycle 2) reduction of NTP to dNTP |
Thioredoxin
|
|
|
Jagendorf and Uribe famous experiment used...
|
chloroplast thylakoids
|
|
|
--- Non-Cyclic Electron Transport ---
1) First? Last? 2) Sequence of e- flow... |
1) H2O --- NADP+
2) [Typical Z-Scheme] |
|
|
--- Cyclic Electron Transport ---
1) First? Last? 2) Sequence of e- flow... |
1) PS I --- PS I
2) PS I Fd Cyt b/f PC PS I |
|
|
--- Pseudocyclic Electron Transport ---
1) First? Last? 2) Sequence of e- flow... |
1) H2O --- H2O
2) [Typical Z-Scheme] except... Fd O2 H2O |
|
|
--- Chloroplast Electron Transport ---
What is the typical Z-scheme process? |
H2O > PS II >
PQ > Cyt b/f > PC > PS I > Fd > NADP+ [plastoquinone] [plastocyanin] [ferredoxin] |
|
|
1) PQ?
2) PC? 3) Fd? 4) Cyt b/f? |
1) plastoquinone
2) plastocyanin 3) ferredoxin 4) cytochrome b6f complex |
|
|
--- Non-cyclic, Cyclic, Pseudocyclic ---
1) *** produces ATP, NADH, O2 2) *** produces ATP 3) *** produces ATP, H2O |
1) Non-cyclic
2) Cyclic 3) Pseudocyclic |
|
|
--- Non-Cyclic, Cyclic, Pseudocyclic ---
1) Non-Cyclic produces... 2) Cyclic produces... 3) Pseudocyclic produces... |
1) ATP, NADH, O2
2) ATP 3) ATP, H2O |
|
|
--- Regulation of Cholesterol Synthesis ---
1) phosphorylation of... 2) down/up regulation of its synthesis, 3) proteolysis of.... |
1) HMG-CoA reductase
2) down 3) HMG-CoA reductase |
|
|
--- *** Effect ---
Seen in many tumors exhibiting higher-than-normal rates of glycolysis under aerobic conditions. |
Warburg Effect
|
|
|
--- *** Effect ---
High glucose metabolism under anaerobic conditions and diminished under aerobic. |
Pasteur Effect
|
|
|
What are the aspartate-family amino acids?
|
methionine
lysine threonine |
|
|
GPDH?
|
Glycerol-3-Phosphate DeHydrogenase
|
|
|
ACC?
|
Acetyl-Coa Carboxylase
|
|
|
PDC?
|
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex
|
|
|
FAS?
|
Fatty Acid Synthase
|
|
|
DHAP?
|
DiHydroxyAcetone Phosphate
|
|
|
GNG?
|
GlucoNeoGenesis
|
|
|
What AA can't be converted to OAA?
|
leucine and lysine
|
|
|
A protein kinase functions to...
|
phosphorylate other proteins
|
|
|
HIF-1?
|
Hypoxia-Induced transcription Factor 1
|
|
|
HK?
|
hexokinase
|

