![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
--- Competitive ---
1) Graph? 2) What is the same? 3) What is different? |
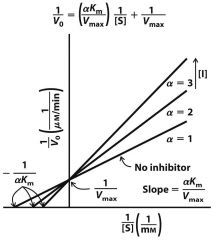
2) Vmax
3) Km |
|
|
a) The microsomal ethanol oxidizing system (MEOS)?
1) is a mixed function oxidase, 2) is associated with the endoplasmic reticulum, 3) requires NADPH, 4) requires O2, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
5) all of the above,
|
|
|
--- Uncompetitive ---
1) Graph? 2) What is the same? 3) What is different? |
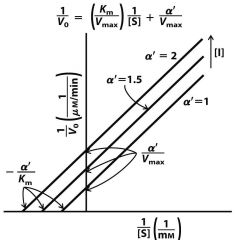
2) nothing
3) Km Vmax |
|
|
g ) Which carbohydrate is a “so-called” reducing sugar?
1) sucrose, 2) trehalose, 3) lactose, 4) maltose, 5) both 1) and 2) above, 6) both 3) and 4) above. |
6) both 3) and 4) above.
|
|
|
--- Pure Non-Competitive ---
1) Graph? 2) What is the same? 3) What is different? |
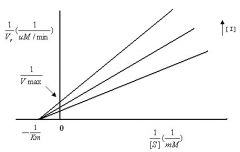
2) Km
3) Vmax |
|
|
h) Lactose is hydrolyzed by the catalytic active of lactase to generate?
1) glucose only, 2) glucose and galactose, 3) glucose and fructose, 4) fructose only, 5) fructose and mannose, 6) none of the above. |
2) glucose and galactose,
|
|
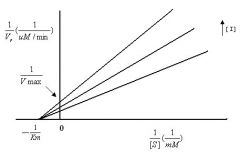
|
Pure
Non-Competitive |
|
|
i) Which of the following energy sources provides about 7 kcal/g?
1) proteins, 2) fats, 3) carbohydrates, 4) alcohol, 5) both 1) and 2) above, 6) none of the above. |
4) alcohol = 7
fats = 9 carbs =4 |
|
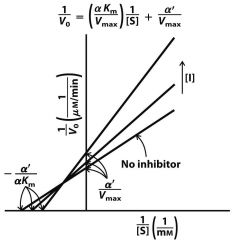
|
Uncompetitive
mixed |
|
|
k) Which of the following may serve as a precursor for the synthesis of new glucose?
1) acetoacetic acid, 2) ethanol, 3) palmitic acid (16:0), 4) acetyl-S-CoA, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
6) none of the above.
|
|
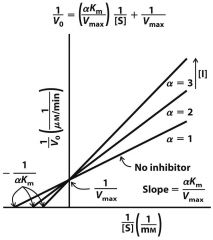
|
Competitive
|
|
|
m) A Hill plot may give us information about the following:
1) h, the number of binding sites on a protein, 2) Kh, the binding constant for a ligand binding to a protein, 3) whether a plot is hyperbolic or sigmoidal, 4) all of the above, 5) none of the above. |
4) all of the above,
|
|
|
--- Mixed Competition ---
1) Graph? 2) What is the same? 3) What is different? |
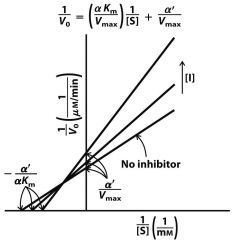
2) none
3) Vmax Km |
|
|
n) An enzyme exhibiting negative homotropic cooperativity?
1) should give an h value less than 1, 2) should exhibit neither hyperbolic or sigmoidal kinetics, 3) may be consistent with the Koshland model, 4) is inconsistent with the MWC model, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
5) all of the above,
|
|
|
Uncompetitive
|
|
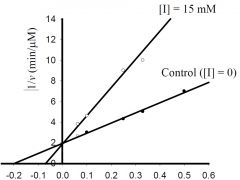
b) What is the approximate KM for the control?
1) 5 mM, 2) -0.5 mM, 3) 0.5 μmol/min, 4) -0.2 mM, 5) 2 μmol/min 6) none of the above. |
1) 5 mM,
|
|
|
What units are Kcat in?
AKA... |
reciprocal time --- s-1
turnover number |
|
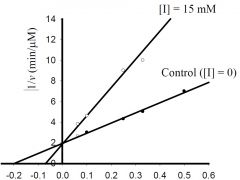
c) What is the approximate Vmax for the control?
1) 5 μM/min, 2) 5 mM, 3) 0.5 μM/min, 4) 100 μM/min, 5) 20 mM, 6) none of the above. |
3) 0.5 μM/min,
|
|
|
How is Kcat calculated?
|
Vmax
---------- [ET] ET=total enzyme |
|
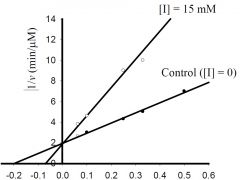
d) What type inhibitor is I?
1) competitive, 2) uncompetitive, 3) pure-noncompetitive, 4) mixed, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
1) competitive,
|
|
|
Kcat is the measure of...
|
enzyme's catalytic efficiency @ saturation
|
|
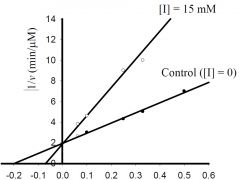
e) What is the approximate value for KI or KI’?
1) 0.2 mM, 2) 2 min-1, 3) 3 mM, 4) 5 μM/min, 5) 20 mM, 6) none of the above. |
6) none of the above.
|
|
|
--- Specificity Constant ---
What are the units? How is it calculated? |
sex-1 M-1
Kcat ------- Km |
|
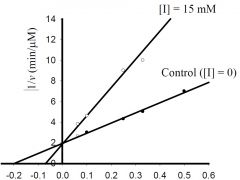
f) If [ET] = 0.025 μM, kcat is about?
1) 2 mM, 2) 2 min-1, 3) 0.2 μM/min, 4) 20 min-1, 5) 5 μM/min, 6) none of the above. |
4) 20 min-1,
|
|
|
The *** is more useful for comparing catalytic efficiencies under real-life cellular conditions.
|
specificity constant
|
|
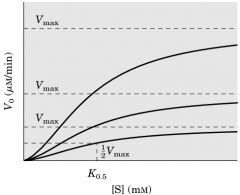
j) The observed curves are indicative of:
1) a Michaelis-Menten type enzyme, 2) a K-series enzyme, 3) a V-series enzyme, 4) all of the above, 5) none of the above. |
3) a V-series enzyme,
|
|
|
--- Pure Non-Competitive ---
What is the formula for KI? |
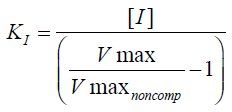
|
|
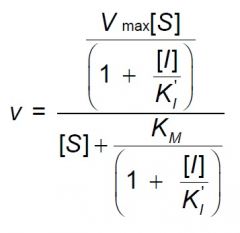
l) The equation below is characteristic of what type inhibitor?
1) competitive, 2) uncompetitive, 3) non-competitive, 4) mixed, 5) all of the above, 6) none of the above. |
2) uncompetitive
|
|
|
--- Mixed Non-Competitive ---
What is the formula for KI? |
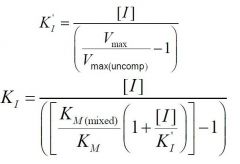
|
|
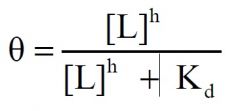
r) Consider the equation:
If h = 2, this equation predicts what type of ligand binding curve? 1) hyperbolic, 2) sigmoidal, 3) neither hyperbolic or sigmoidal, 4) linear, 5) none of the above. |
2) sigmoidal
|
|
|
--- Uncompetitive ---
What is the formula for KI? |
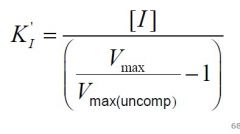
|
|
|
o) According to the MWC model, an allosteric (heterotropic) inhibitor should have what effect on the relative value of L?
1) increase L, 2) decrease L, 3) have no effect on L, 4) all of the above, 5) none of the above. |
1) increase L,
|
|
|
--- Competitive ---
What is the formula for KI? |
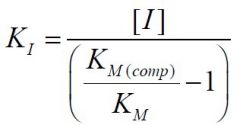
|
|
|
__________p) Which of the following compounds may be converted to new glucose in mammals?
1) palmitic acid (16:0 fatty acid), 2) malic acid, 3) acetate unit of acetyl-S-CoA, 4) none of the above, 5) all of the above. |
4) none of the above,
|
|
|
--- General Inhibition ---
What is the formula? |
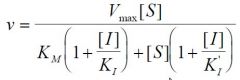
|
|
|
q) In a Scatchard plot the following parameters are plotted on the y-axis?
1) [Bound], 2) [Free], 3) [Free]/[Bound], 4) [Bound]/[Free]), 5) none of the above. |
3) [Free]/[Bound],
|
|
|
--- Graphical Inhibition Estimation ---
What is it called? What is used to chart it? |
Replot Method
X-Axis = [I] mM Y-Axis = Km/Vmax(slope) for Ki Y-Axis = 1/Vmax for Ki' |
|
|
s) Which of the following compounds can act as a substrate for the enzyme, hexose kinase?
1) glucose, 2) fructose, 3) mannose, 4) all of the above, 5) none of the above. |
4) all of the above,
|
|
|
--- Hill Equation ---
1) X-Axis = ??? 2) Y-Axis = ??? 3) Hill coefficient (h or **) derived from? 4) Dissociation constant (***) derived from? |
1) X-Axis = log [S]
2) Y-Axis = log (V/Vmax-V) OR log(0/(1- 0) 3) nh = slope 4) -log Kd = y-intercept |
|
|
t) If h is 2, the cooperativity index is?
1) 1, 2) 3, 3) 4, 4) 9, 5) 81, 6) none of the above. |
4) 9,
|
|
|
*** ***: a measure of cooperativity between binding sites.
|
Hill Coefficient
|
|
|
--- Animal Cells ---
GLYCOGEN to LACTIC ACID Pathway Intermediates? |
GLYCOGEN > glucose-1-P > glucose-6-P > steps in glycolysis > pyruvate > LACTIC ACID
|
|
|
Units for disassociation constants?
|
mol/L
|
|
|
--- Animal Cells ---
GALACTOSE to synthesis of new GLYCOGEN Pathway Intermediates? |
GALACTOSE > UDP-galactose > UDP-glucose > GLYCOGEN
|
|
|
--- Animal Cells ---
ETHANOL to GLUCOSE Pathway Intermediates? |
ethanol cannot serve as a precursor of new glucose in animals
|
|
|
--- Lineweaver-Burke Plot ---
1) Km? 2) Vmax? |
1) -1/x
2) 1/y |
|
|
--- Ethanol Metabolism ---
1) High energy at *#* kcal/gram while 2) carbs/fats contains are ***/*** 3) Not created in mammals because of... |
1) 7
2) 4/9 3) pryuvate decarboxylase |
|
|
--- Disaccharides ---
1) galactose --- glucose 2) fructose --- glucose 3) glucose --- glucose α(1→4) 4) glucose --- glucose α,α-1,1- |
1) Lactose
2) Sucrose 3) Maltose 4) Trehalose |
|
|
Name two reducing sugars.
|
Lactose
Maltose |
|
|
Name two nonreducing sugars.
|
Sucrose
Trehalose |
|
|
--- MWC Model ---
Basis for Action of Allosteric Effectors 1) Inhibitors bind/stabilize the ***-form, *** the value of L. 2) Activators bind/stabilize the ***form, *** the value of L. 3) These enzymes will fall into either ***-Series or ***-Series. |
1) T --- increasing
2) R --- decreasing 3) K --- V |
|
|
1) These are classifications of the *** Model
2) ***-Series enzymes change apparent Vmax not Km. 3) ***-Series enzymes change apparent Km not Vmax. |
1) MWC
2) V-Series 3) K-Series |
|
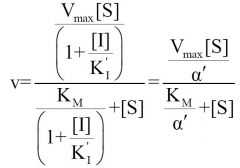
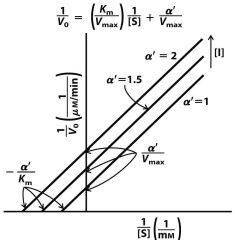
Inhibition type?
|
Uncompetitive
|
|
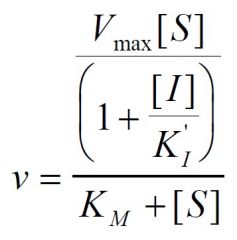
Inhibition type?
|
Non-Competitive
|
|
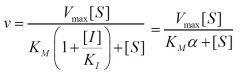
Inhibition type?
|
Competitive
|
|
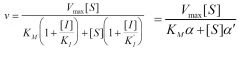
Inhibition type?
|
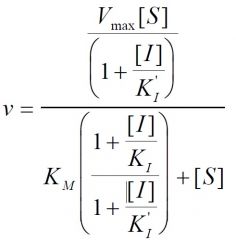
Mixed
|
|
|
*** Inhibition Is a Special Case of Mixed Inhibition
|
Noncompetitive
|
|
|
--- Hill Equation ---
What THREE things does it tell us? 1) ***(measurand) 2) ***(measurand) 3) if the plot is... |
1) h = cooperativity of B.S.(# of B.S.)
2) Kh = binding constant for ligand & proteins(or Kd) 3) hyperbolic or sigmoidal |
|
|
*** effects: binding of ligand influences binding of a DIFFERENT ligand at DIFFERENT site.
|
heterotropic
OR allosteric |
|
|
*** effects: binding of ligand alters subsequent binding of IDENTICAL ligands at DIFFERENT site.
|
homotropic
|
|
|
*** *** cooperativity: Binding of 1st ligand increase affinity for binding other different ligands. (e.g. CO2 on O2).
|
Heterotropic Positive
|
|
|
*** *** cooperativity: Binding of 1st ligand decreases affinity for binding other similar ligands. (e.g. O2 on O2).
|
Homotropic Negative
|
|
|
*** Model accounts for BOTH positive & negative homotropic cooperativity.
*** Model accounts for ONLY positive homotropic cooperativity. |
KNF
MWC |
|
|
--- Hill Coefficient---
1) h > 1 a LIGAND shows *** cooperativity. 2) h < 1 a LIGAND shows *** cooperativity. 3) h = 1 a LIGAND shows *** cooperativity |
1) positive --- ligand increases affinities
2) negative --- ligand decreases affinities 3) no |
|
|
--- Hill Equation ---
*** is the binding constant. *** is the dissociation constant. |
Kh
Kd |
|
|
-- Hill Coefficients---
When the h value for an effector goes 1) lower it means it's acting as an... 2) higher it means it's acting as an... |
1) positive heterotropic effector(activator)
2) negative heterotropic effector(inhibitor) |
|
|
--- Hill Equation ---
1) Effector: higher h means it's a *** effector. 2) Ligand: higher h than 1 means has *** cooperativity. |
1) negative effector
2) positive |
|
|
1) KNF Model?
2) MWC Model? 3) *** Model is AKA the Concerted or Symmetry model. |
1) Koshlad-Nemethy-Filmer Model
2) Monod-Wyman-Changeux Model 3) MWC |
|
|
Enzyme w/negative homotropic cooperativity....
1) h value is *** than 1, 2) exhibits hyperbolic/sigmoidal kinetics, 3) is ***sistent with Koshland model, 4) is ***sistent with MWC model. |
1) less
2) sigmoidal 3) consistent 4) inconsistent |
|
|
--- MWC Model ---
An ENZYME exhibiting postive homotropic cooperativity gives h values *less/more* than 1. |
more
|
|
|
--- MWC Model ---
1) Allosteric inhibitors *** L and increase *** curve character. 2) Allosteric activators *** L and increase *** curve character. |
1) increase --- sigmoidal
2) decrease --- hyperbolic |
|
|
--- Scatchard Plot ---
[Bound]\[Free] is on the ***-axis. |
Y-Axis?
|
|
|
--- Scatchard Plot ---
1) Y-Axis? 2) X-Axis? |
1) [Bound]\[Free] or [MS]\[S]
2) [Bound] or [S] |
|
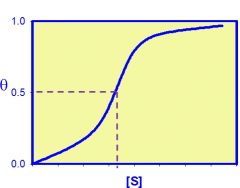
What type of curve is this?
|
sigmoidal curve
|
|
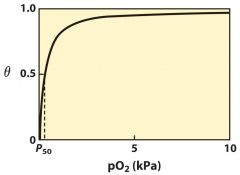
What type of curve is this?
|
hyperbolic curve
|
|
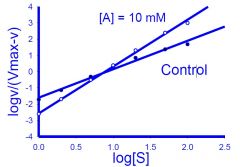
What type of plot is this?
|
hill plot
|
|
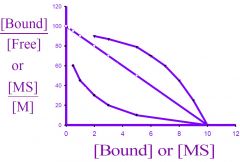
What type of plot is this?
|
scatchard plot
|
|
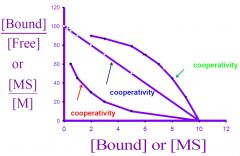
--- Scatchard Plot ---
Top Green? Middle Blue? Bottom Red? |
positive cooperativity
no cooperativity negative cooperativity |
|
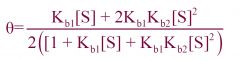
1) What equation is this?
2) Describing what? |
1) Adair Equation
2) binding of a ligand to a dimeric protein. --- Describes binding under the KNF model. |
|
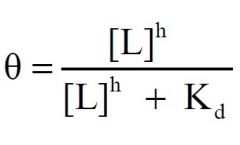
1) Type of curve?
2) Ligand Binding Model? Two other forms? |
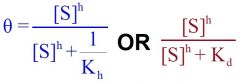
1) Sigmoidal Curve
2) Hill |
|
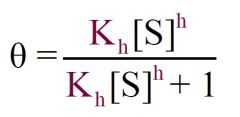
Equation multiplied by Kd???
1) Type of Curve? 2) Ligand Binding Model? |
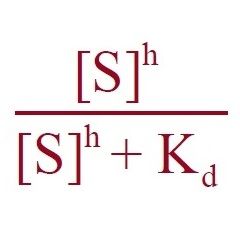
1) Sigmoidal Curve
2) Hill |
|
|
--- Hexose Kinase ---
Three sugars? |
glucose
fructose mannose |
|
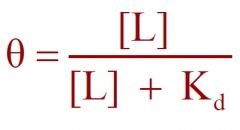
1) Type of curve?
2) Ligand Binding Model? |
1) Hyperbolic Curve
2) Langmuir |
|
|
--- Cooperativity Index ---
1) Unit is *** 2) Formula... |
1) Rx
2) 81^(1/h) |
|
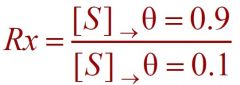
What formula is this?
|
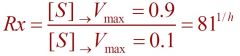
Cooperativity Index
|
|
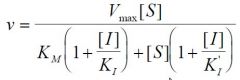
Inhibition type?
|
General Inhibition
1 ligand 1 binding site |
|
|
--- Cooperativity Index ---
1) If h > 1 a protein shows... 2) If h < 1 a protein shows... 3) If h = 1 a proteins shows... 4) if h = 1 then Rx is... |
--81^(1/h)--
1) positive cooperativity 2) negative cooperativity 3) no cooperativity 4) 81^(1/1) = 81 |
|
|
--- Hill Equation---
General formula? -Mills said we should know- |
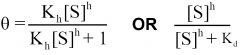
|
|
|
--- MWC Equation ---
General formula? -Mills said we should know- |
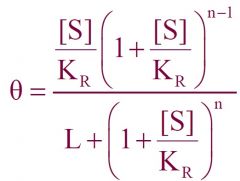
|
|
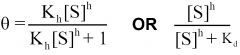
What equation is this?
|
General Hill Equation
|
|
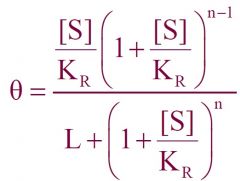
What equation is this?
|
General MWC Equation
|
|
|
--- Analysis Technique ---
1) Hyperbolic Plot uses... Y-Axis = ??? X-Axis = ??? 2) Sigmoidal Plot uses... Y-Axis = ??? X-Axis = ??? |
1) Lineweaver-Burke Plot
X-Axis = 1/[S] Y-Axis = 1/Vmax 2) Hill Plot X-Axis = log [S] Y-Axis = log (V/Vmax-V) |
|
|
--- Adair Equation ---
Equation? Protein w/*** ligand binding sites. -Mills said we should know |
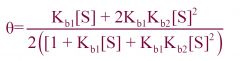
two
--- Describes binding under the KNF model. |
|
|
--- Structural Formulas ---
1) Ethanol 2) Acetaldehyde 3) Acetate/Acetic Acid |
1) CH3-CH2-OH
2) CH3-CHO 3) CH3-COOH |
|
|
--- Units ---
1) Kb 2) Kd 3) kcat 4) Specificity constant |
1) Kb
2) Kd 3) (mM/min) or (molecules/sec) 4) M-1 s-1 (kcat/KM) |
|
|
printerd
|
printerd
|
|
|
--- Replot Method ---
What is it used for? What's the main difference used w/in the method? |
Y-Axis
Ki = Km/Vmax(slope) Ki' = 1/Vmax X-Axis = [I] mM |

