![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Blood vessels are made of ____ which deliver the blood enriched in O2 from the heart to the tissues, of ____ which constitute the exchange network also called C____ B____, and of ____ which drain blood from the tissues back to the heart where it is pushed toward the lungs to regain O2 from the respiratory circuit. |
- arteries - capillaries - Capillary - Beds - veins |
|
|
The opening of a blood vessel is called the ____ while its wall is usually made of 3 layers: ____, ____ and ____. |
- lumen - tunica intima - tunica media - tunica externa |
|
|
Arteries have H____ B____ P____ while veins have L____ B____ P____, so they require V____ to prevent backflow. |
- High - Blood - Pressure - Low - Blood - Pressure - Valves |
|
|
The decrease of the blood vessel diameter is called ____ and is made possible by the contraction of ____ within the wall of the blood vessel. |
- vasoconstriction - smooth muscle |
|
|
V____ and V____ are called capacitance vessels because they contain up to 65% of the total blood. |
- Veins - Venules |
|
|
Blood vessels interconnect through ____ to provide alternate pathway and ensure continuous blood flow. |
- anastomoses |
|
|
An ____ is when there is abnormal accumulation of liquid in tissues. |
- edema |
|
|
Abnormally high blood pressure is called ____. |
- hypertension |
|
|
True or false: the femoral artery is the largest artery of the body |
False |
|
|
True or false: leaky valves on veins can lead to varicose veins |
True |
|
|
True or false: only arteries run deep, veins are mostly superficial |
False |
|
|
True or false: arterial pressure in the pulmonary circulation is much higher than in the systemic circulation because its proximity to the heart |
False |
|
|
True or false: blood returning from the large intestine and the rectum leaves the inferior mesenteric to go directly to the inferior vena cava |
False |
|
|
True or false: an increase in blood viscosity will cause a decrease in peripheral resistance |
False |
|
|
True or false: capillaries are made of only 1 layer of endothelial cells |
True |
|
|
What is pulse pressure? And the MAP? |
Pulse pressure: difference between systolic and diastolic pressure (SP-DP) MAP: mean arterial pressure, pressure that propels blood to tissues. Calculated by adding diastolic pressure + 1/3 pulse pressure. MAP=SV×HR×R |
|
|
What is a vascular shunt? |
- channel that connects arteriole directly with venule (metarteriole-throughfare channel) |
|
|
What is the relationship between the blood flow, the blood pressure and the resistance? |
- BF is directly proportional to BP gradient (if pressure gradient increases, BF speeds up). - BF is inversely proportional to PR (if R increases, BF decreases). - If R increase, BP increases - F=BP/R or BP=FxR |
|
|
Define the terms filtration and reabsorption |
Filtration: net fluid flow OUT at arterial end, (movement of blood from blood vessel to tissue) Reabsorption: net fluid flow IN at venous end, (movement of blood from tissue to blood vessel) |
|
|
If a person stands up suddenly from the prone position, they may feel a sudden dizzy or lightheadedness. What physiological response can explain this situation? |
- orthostatic hypotension |
|
|
Label the veins appropriately |
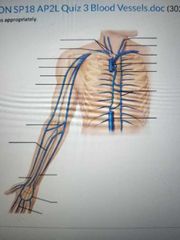
|
|
|
Label the veins appropriately |
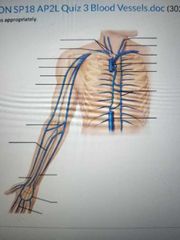
Left side= - Right brachiocephalic vein - Right subclavian vein - Right axillary vein - Right brachial vein - Right cephalic vein - Right basilic vein - Right median cubital vein - Right median antebrachial vein - Right ulnar vein - Right radial vein - Right superficial venous palmar arch - Right digital veins Right side: - Left internal jugular vein - Left external jugular vein - Left subclavian vein - Superior vena cava - azygos vein - hemiazygos vein - Inferior vena cava |

