![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Periods of Medieval Art |
Germanic, Hiberno Saxon, Viking: 400-800 CE Carolingian: 750-900 Ottonian: 900-1000 Romanesque: 1000-1150 Gothic: 1150-1300 Late Gothic & Proto-Renaissance: 1300-1400 |
|
|
Major Culture Shifts |
Leadership moved from Mediterranean to France, Germany, and British Isles Christianity triumphed over paganism and barbarianism Emphasis shift from here-and-now to afterlife; human body now viewed as corrupt People live in fear of Hell Religious revival: popularity in monks and monasticism, resulting in pilgrimages and competition between communities to build best church |
|
|
Changes to Basilica Plan |
Enlarged due to increased worshipers Longer naves/wider transepts Apsidal chapels for more display area Aisles added on either side of transept Ambulatory added behind apse/altar |
|
|
Changes to construction methods |
Stone roof: fire prevention, acoustics, and aesthetics Vaulted ceilings for higher buildings (barrel/tunnel vault, ribbed vault, pointed arches) Large stone piers beneath arches, resulting in huge exterior doors Buttresses for more support Small windows for solid, sturdy walls |
|
|
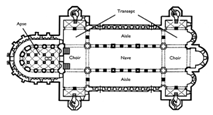
Abbey Church of St. Michael; Hildesheim, Germany 1001-1031 |
|

|
Bayeux Tapestry; Romanesque Embroidered linen telling the story of Norman conquest of England Battle of Hastings-turning point in Norman victory Duke William dubbed William the Conquerer Story told as eyewitness account in Latin |
|
|
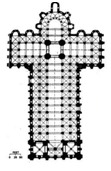
St. Sernin; Toulouse, France; Romanesque 1070-1120 Basilica plan with wide transepts (cross shape), ambulatories, and altars Accommodates many visitors |
|

|
Last Judgment, west tympanum of St. Lazare; Autun, France 1120-1135 Stylized figures used to teach Many stories depicted Hierarchical scale Decorative with animal abstractions (monsters) |
|
|
Gothic Architecture |
1150s saw a new style of architecture Coincidence with central monarchy in France Incorrectly called Gothic by Italian invaders thinking it was made by Germanic Goths |
|
|
Gothic Conventions |
height and light vertical lines color in stained glass natural imagery combined with idealism desire to instruct viewers |
|

|
Ekkehard and Uta; Naumburg Cathedral, Germany 1250-1260 statues of donors to church not freestanding (attached to columns) wear contemporary costumes known for accuracy in sculpting |
|

|
Virgin of Paris; Notre Dame Cathedral Early 1300s shown as earthly queen with jeweled crown Christ child as infant prince eye contact shows slight tenderness not seen previously in depictions of Mary beginnings of Humanism Mary's body forms Gothic Sway or S-curve |
|
|
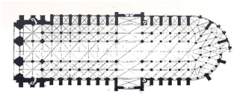
Notre Dame Cathedral; Paris 1163 designed for large, continuous space Abbot Suger directed architects towards lots of light and open space Louis VI moves to Paris, requiring an impressive cathedral flying buttresses introduced for weight support |
|

|
Chartres Cathedral; France 1134 first High Gothic building ceiling contains quadripartite vaults rose window shows Mary surrounded by Holy Spirit & eight angels |
|

|
Reims Cathedral; France 1211-1290 figures above rose window are very elongated aspects stretched tall and thin stained glass replaces tympanum carvings sculptures and jamb figures show more detail and realism |

