![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 3 models of conditioning? |
• ‘Classical’ conditioning
|
|
|
What is classical conditioning? |
Salivation reflex at sight of food. |
|
|
What is the change pre-conditioning to post-conditioning? |
• US: food -> UR: salivation
• CS: bell -> CR: salivation |
|
|
What are the applications of classical conditioning? |
• Behaviour Therapy: |
|
|
What is systemic desensitisation? |
• Most used behavioural method for reducing fear and anxiety |
|
|
What is operant/instrumental learning? |
Behaviour -> consequence:
•Consequences of an action for an individual |
|
|
What is the law of effect for operant conditioning? |
• behaviour with satisfying consequence (reinforced) -> become more likely, strengthened |
|
|
What is extinction in the context of conditioning? |
Extinction
|
|
|
What factors alter response? |
• Biological reasons (homeostasis)
|
|
|
What is contingency? |
Schedule of Reinforcement |
|
|
What are the therapeutic applications of operant behaviour? |
1. State goal (lose weight) |
|
|
What is observational learning? Which experiment demonstrates its effect? |
– Importance of learning by observing and
Bobo doll experiment
|
|
|
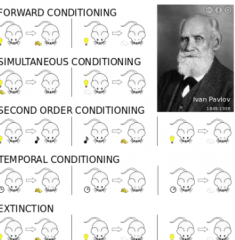
Revise these methods of conditioning. |
|

