![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
With DISH, what spinal structure is most commonly found calcified?
|
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
|
|
|
Which is not another name for DISH?
a. Forestier's Disease b. spondylosis hyperostotica c. spondylitis ossificans ligamentosa d. Japanese Disease e. all of the above are psuedonyms for DISH |
d. Japanese Disease (OPLL)
|
|
|
How many vertebral segments need to be involved to correctly diagnose DISH on an x-ray?
a. 1 b. 2 c. 4 d. 5 e. 12 or more |
c. 4
|
|
|
What area of the vertebrae is most commonly affected by DISH?
a. cervicals b. thoracics c. lumbars d. sacrum e. no predilection |
b. thoracics
|
|
|
True/False
DISH will commonly show reduced disc height. |
False
|
|
|
True/False
DISH rarely shows a reduced disc space. |
True
|
|
|
What antigen is found to be positive in 40% of patients with DISH?
|
HLA-B8
|
|
|
True/False
Will DISH or AS (ankylosing spondylitis) affect the vertebrae's facet joints? |
AS does - DISH doesn't -- This is how you differentiate them on films
|
|
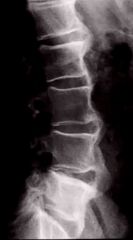
51 year old male with Type 2 diabetes presents with this x-ray. What's the most likely diagnosis?
|
DISH (note the calcification of the ALL) for at least 4 segments, yet no loss of disc space.
|
|
|
What vertebral area is most likely to show OPLL?
|
Cervicals
|
|
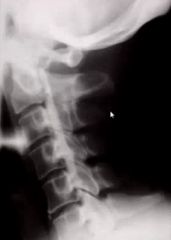
49 year old Japanese woman presents with this radiograph. What is the most likely dx?
|
OPLL (aka Japanese Disease)
|
|
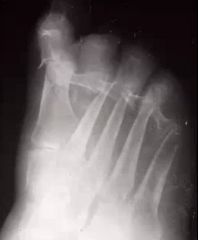
1. Name this syndrome.
2. Name the 2 types of imaging forms this syndrome can present as on plain film. 3. Which is this one presented as? |
1. Neuropathic Arthritis (aka Charcot Joint)
2. Hypertrophic & Atrophic 3. Atrophic |
|
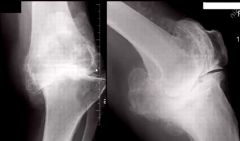
What type of neuropathic arthritis is shown here?
|
Hypertrophic
|
|
|
In the USA, what is the most common cause of neuropathic arthopathy?
|
Diabetes Mellitus
|
|
|
If neuropathic arthopathy is diagnosed in the shoulder, what is most likely to be the cause?
a. Diabetes b. Syringomyelia c. Multiple Sclerosis d. Alcoholism e. Spina bifida vera |
b. syringomyelia (also NA + syringomyelia usually means bilateral involvement!)
|
|
|
What is the most common other name of neuropathic arthritis? (hint: named after the physician that first described it
|
Charcot Joint
|
|
|
Japanese Disease is another name for ____
|
OPLL (ossification of the PLL)
|
|
|
The ___ ____ is the m/c affected area in OPLL
|
cervical spine
|
|
|
_% of OPLL is associated with DISH
|
50
|
|
|
What are the lab findings for OPLL?
|
They are normal...radiographic Dx is most dependable
|
|
|
OPLL is best seen on a ____ radiograph?
|
lateral view
|
|
|
T/F Erosive osteoarthritis has a significant inflammatory component
|
FALSE: does NOT have a significant inflammatory component
|
|
|
Erosive osteoarthritis has a _____ distribution
|
symmetrical
|
|
|
Erosive osteoarthritis m/c affects midle aged ____ (sex) in their _-_ decades of life
|
females; 4-5th decades of life
|
|
|
What are the lab findings for erosive osteoarthritis?
|
-normal or slightly increased ESR
-negative for Rf |
|
|
"Gull wing' is a characteristic response to what disease process? What does it look like?
|
Erosive osteoarthritis; erosions are characteristically central in location and on the proximal portion of the joint
|
|

29 year old male.
Bilateral or unilateral? Symmetric or asymmetric? Diagnosis? |
Bilateral, symmetrical
AS |
|
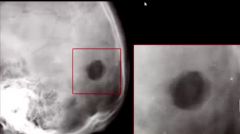
What's the named sign in the skull?
What is the opacity in the center of the lesion called? Dx? |
Hole within a hole
Button Sequestrum EG |
|

What are the 3 visible signs here?
What are the 3 Diff Dx's? If it started in the vertebral body, what would your Dx be? |
1. Lytic, expansile, spine
2. Osteoblastoma, GCT, ABC 3. GCT |
|
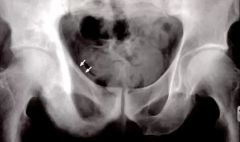
Name this disease.
Name the 4 stages this disease goes through. |
1. Paget's
2. Lytic, Mixed, Blastic, Malignant degeneration |
|
|
What is the radiographic sign in the skull for Paget's disease, in stage 1?
|
Osteoporosis circumscripta
|
|
|
What is the radiographic sign in the long bones for Paget's disease in stage 1?
|
Candle flame or blade of grass
|
|
|
What is the radiographic sign in the vertebrae for Paget's disease in stage 2?
|
Picture frame
|
|
|
What is the radiographic sign in the skull for stage 2 Paget's disease?
|
Cottonwool
|
|
|
What is the radiographic sign in the vertebrae for stage 3 Paget's disease?
|
ivory vertebrae
|
|

Is this (bilateral/unilateral) and (symmetric/asymmetric)?
What is the name of the disease pattern? |
Psoriatic arthritis
|
|
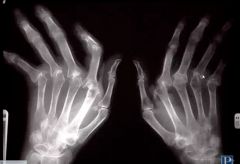
Name this disease.
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis
|
|
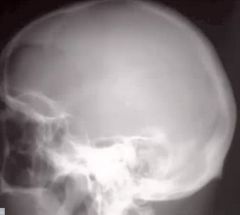
What is the name of this disease?
What is the specific name of this stage of disease? |
Pagets
Stage 1 - Ostetitis Circumscripta |
|
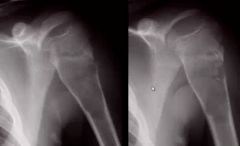
What is the diagnosis here?
What sign is evident on the right image? Is this active or latent? |
1. Simple bone cyst
2. Fallen fragment sign 3. latent (not touching the growth plate) |
|

1. If this is a juvenile, what are some specific names for the affected segment?
2. What is the name of this lesion? 3. How can we differentiate this from Rickets? |
1. Vertebra plana, silver dollar vertebrae, coin-on-edge
2. Eosinophilic Granuloma 3. EG affects one segment, rickets affects multiple segments |
|
|
What is the named sign if EG is found in the mandible?
|
"Floating tooth sign"
|
|
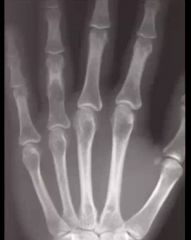
1. What is this lesion most likely to be?
2. What is the most severe complication of this lesion? |
1. Enchondroma
2. Metastatic degeneration |
|
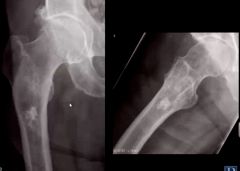
1. Describe the calcification pattern
2. What is this lesion most likely to be in this image? |
1. Stippled, flocculent pattern
2. Enchondroma |
|
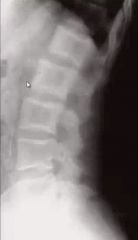
1. What is this most likely to be?
2. What stages are possible? |
Paget's
2 or 3 |
|

1. What bone(s) are involved in this lesion?
2. What is this lesion most likely to be? 3. What imaging modality is this (be specific)? |
1. Sacrum
2. ABC 3. T2 MRI |
|
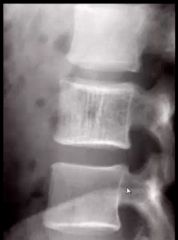
1. What is this likely to be?
2. What feature is missing that eliminates Paget's Disease? |
1. Hemangioma
2. No picture frame vertebrae, no enlargement of VB |
|
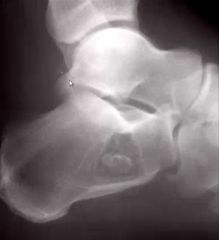
1. What is the name for the calcification in the center of the lesion?
2. What is this most likely to be? |
1. Target Sign
2. Lipoma |
|
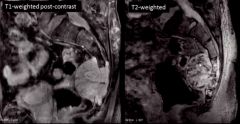
1. What is this lesion?
2. What is the space anterior to the sacrum that's important to measure with this lesion? |
1. Chordoma
2. Retrorectal or presacral space (>2 cm is concerning) |
|
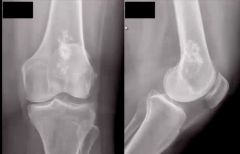
1. Most likely diagnosis?
|
Enchondroma
|
|

Patient is a 19 year old female
1. 3 differentials? |
1. Ewing's, Osteosarcoma, osteomyelitis
|
|
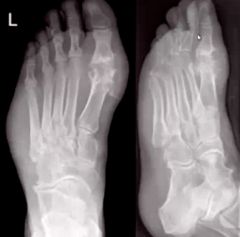
1. What segment is affected?
2. What are two names for the likely Dx? |
1. 1st MTP
2. Gout, Podagra |
|
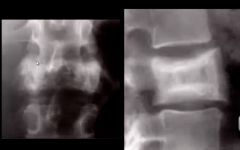
1. What disease is this likely to be?
2. What stage and sign is visible? |
1. Paget's
2. Picture frame vertebrae, stage 2 |
|

1. What is the name of the sign the arrows are pointing to?
2. What is the diagnosis? |
1. Star sign
2. Anklyosing spondylitis |
|

1. The middle arrow is pointing to what sign?
2. The outside arrows are pointing to what sign? 3. Diagnosis? |
1. Dagger sign
2. Trolley Track sign 3. Ankylosing spondylitis |
|

Most likely Diagnosis?
|
OPLL
|
|
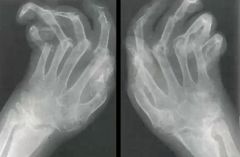
1. What are two possible diagnoses?
2. If negative Rf is found, what is the likely dx? |
Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic |

