![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What veins join to form the external jugular v.?
|
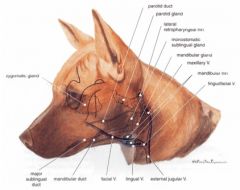
Maxillary and linguofacial veins.
|
|
|
What are the veins of the head that we should know? (9)
|
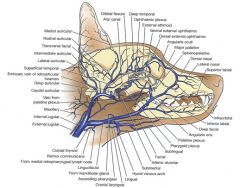
External jugular v.
Maxillary v. Linguofacial v. Hyoid venous arch Facial v. Lingual v. Deep facial v. Dorsal nasal v. Angularis oculi v. |
|
|
What does the hyoid venous arch connect in dogs and cats?
|
Dogs - it connects the lingual vv.
Cats - it connects the linguofacial vv. |
|
|
What are the superficial branches of the Facial nerve?
|
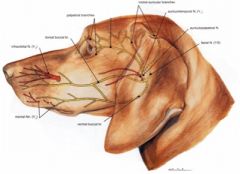
Auriculopalpebral n. (which further branches into rostral auricular brs. and palpebral n.) and the dorsal and ventral buccal brs.
|
|
|
What forms the rostral auricular plexus? Where is it located?
What does it provide innervation to? |
It is formed by the palpebral n. off of auriculopalpebral n. of facial n.
It is located between the eye and ear and innervates the rostral auricular mm. and levator nasolabialis m. |
|
|
Which branches of the trigeminal nerve have sensory and which have motor function?
|
Ophthalmic n. has only sensory function.
Maxillary n. has only sensory function. Mandibular n. has both sensory and motor function. |
|
|
What is the branch off of the mandibular nerve from trigeminal that connects to facial n.?
What does it provide innervation to? |
The auriculotemporal nerve.
It provides sensory innervation to the rostral part of the ear and skin over the caudal aspect of the cheek. |
|
|
From which foramen does the mandibular n. of trigeminal n. exit?
|
The oval foramen.
|
|
|
From which foramen does the maxillary n. of trigeminal n. exit?
|
In dogs, it exits from the rostral alar foramen.
In cats, it exits from the oval foramen. |
|
|
Is the thyroid gland more cranially or caudally located in the cat than in the dog?
|
In the cat, the thyroid gland is located further caudal in the cervical region.
|
|
|
What is the largest lymph node in the head and neck?
|
The medial retropharyngeal lymph node.
|
|
|
What does the medial retropharyngeal ln. drain lymph from?
What other lnn. does it receive lymph from? What do its efferent vessels form? |
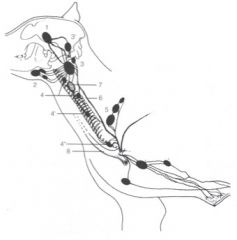
Medial retropharyngeal ln (3 and 3')
Afferents drain lymph from deep structures of the head including the tongue, nasal cavity, pharynx, salivary glands, external ear, larynx and esophagus Receives lymph from the mandibular (2) and parotid (1) lnn. Efferents form the tracheal lymph trunk |
|
|
Where is the medial retropharyngeal ln. located in relation to the thyroid gland?
|
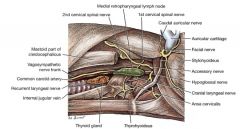
It's located cranial to the thyroid gland.
|
|
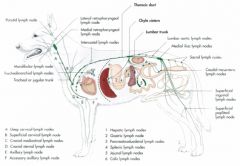
Let's review the lymph drainage of the body.
|
Good job! You're going to be a great vet!
|

