![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Match site with Dermatome.
Upper lateral portion of the arm. |

Upper lateral portion of the arm: C5
|
|
|
Match site with Dermatome.
Thumb (palmar surface) |
Thumb C6
|
|
|
Match site with Dermatome.
Middle three digits (more particularly the palmar surface of index finger) |
C7
|
|
|
Match site with Dermatome.
Little digit = digit minimi |
C8
|
|
|
Tapping the biceps brachii tendon tests...
|
C6
|
|
|
Tapping the triceps brachii tendon (near olecranon) tests
|
C7
|
|
|
Match site with Dermatome.
Medial portion of the arm near the armpit. Is this area supplied by the brachial plexus? |
Medial portion of the arm near the armpit. - T2
Supplied by intercostobrachial nerve of T2-NOT from brachial plexus |
|
|
Match site with Dermatome.
Medial portion of distal arm& near elbow joint on medial side |
T1
|
|
|
Is the superficial fascia INTERNAL or EXTERNAL to the investing layer of the fascia?
Which veins does the superficial fasia in the upper limb contain? |
The superficial fascia is EXTERNAL to the investing layer of the fascia
Cephalic & Basilic Veins |
|
|
Where do the Cephalic & Basilic Veins arise from?
|
From dorsal venous arch of hand
|
|
|
The Investing Layer of Fascia lies ______________ to cephalic & basilic veins in the forearm and lies to veins in upper portion of the arm.
|
The Investing Layer of Fascia lies INTERNAL to cephalic & basilic veins in the forearm and likes EXTERNAL to veins in upper portion of the arm.
honestly, so darn random at the moment--think of it investing layer as an iceberg, the top is EXTERNAL. |
|
|
Note when talking about brachial fascia, antebrachial fascia and palmar aponeurosis ...these are all
INVESTING Fascia. |
These are ALL CONTINUOUS w/each other.
|
|
|
Is the Cephalic vein the SUPERFICIAL FASCIA or INVESTING FASCIA in the dorsum of the hand and forearm?
|
The cephalic vein is in the SUPERFICIAL FASCIA in the dorsum of the hand.
|
|
|
The cephalic veins runs on the LATERAL side of anterior surface of the forearm.
At the cubital fossa, cephalic vein communicates with the basilic vein via the ________________ |
Median cubital vein
|
|
|
As the cephalic vein travels up the arm, it pierces the brachial fascia (investing layer) and enters the _______________ triangle.
After this triangle, the cephalic veins pierces the _________________ FASCIA and will become tributary to the __________ VEIN. |

SMELL YOUR ARMPIT. Go ahead...That's right, your cephalic area just paid TRIBUTE TO YOUR AXILLA. As does the cephalic vein.
As the cephalic vein travels up the arm, it pierces the brachial fascia (investing layer) and enters the DELTOPECTORAL triangle. After this triangle, the cephalic veins pierces the CLAVIPECTORAL FASCIA and will become tributary to the AXILLARY VEIN. |
|
|
Basilic vein originate on the medial side of the dorsal venous arch, in hand, and on forearm. As the basilic vein travels up arm, it pierces the brachial fascia.
The Basilic vein, along with the brachial vein will contribute to the formation of the vein. |
The Basilic vein, along with the brachial vein will contribute to the formation of the _____________ Axillary vein.
|
|
|
REMEMBER, that the cephalic and basilic veins run in the SUPERFISCIAL FASCIA until they reach around middle of upper arm
|
REMEMBER, that the cephalic and basilic veins run in the SUPERFISCIAL FASCIA until they reach around middle of upper arm
|
|
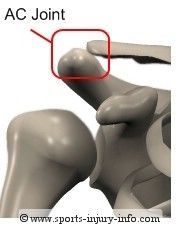
What type of joint is this?
|

Acromioclavicular joint is a SYNOVIAL PLANAR joint. They're SYNING IN ACROpolis...Twerk it, Tito!
|
|
|
Most common dislocation of shoulder joint (aka SHOULDER JOINT dislocation) is displacement of HUMERUS, IN WHICH direction? _______________
|

Most common dislocation of shoulder joint is displacement of HUMERUS ANTERIOR & INFERIORLY
Happens when you try to pull the arm forward (boxing), like this cat who suffered a shoulder dislocation after this. Yeah, this just got dark... |
|
|
A SHOULDER SEPARATION is a dislocation of the ________________ JOINT, w/ a rupture of the __________________ LIGAMENT.
|
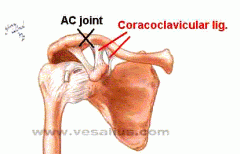
A SHOULDER separation is a dislocation of the acromioclavicular joint T, w/ a rupture of the coracoclavicular LIGAMENT.
|
|
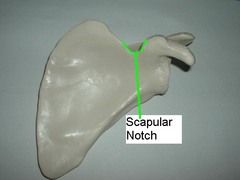
The top portion of the supra scapular notch is covered by the _______________ ligament. The suprascapular nerve, from the ____________ trunk of Brachial plexus is touching it.
|
The top portion of the supra scapular notch is covered by the SUPERIOR TRANSVERSE ligament. The suprascapular nerve, from the SUPERIOR trunk of Brachial plexus is touching it.
|
|
|
Army over navy, etc. BUT
Above the superior transverse ligament run the suprascapular artery and vein-the suprascapular Artery is a branch of WHAT? |
Above the superior transverse ligament run the suprascapular artery and vein-the SUPRASCAPULAR Artery is a branch of THYROCERVICAL trunk of SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY?
|
|
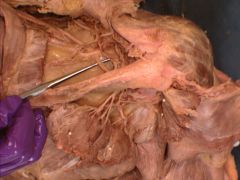
Image is showing suprascapular nerve runing below ligament.
Calcification of the superior transverse scapular ligament an impinge on the suprascapular nerve, causing loss of innervation to WHICH 2 muscles? A patient will have trouble in ABDUCTION or ADDUCTION? |

Calcification of the superior transverse scapular ligament an impinge on the suprascapular nerve, causing loss of innervation -spinatus muscles (infra+supra).
A patient will have trouble with ABDUCTION of the arm. NO more boyfriend raising his arm over your shoulder. TOPANGA, what are we GONNA DO?!!? jiojdfdkljs |
|
|
Supraspinatus Muscle
Function: Abduction-BOYFRIEND ARM Actually with the Cory-Topanga disease (impingement of suprascapular nerve leading to loss of the "boyfriend arm", affecting the infra& supraspinatus) a lot has been covered. Innervation of supraspinatus: Suprascapular nerve Inserts: WHERE? |
Supraspinatus muscle inserts in superior facet greater tubercle of humerus. That makes sense the suprapinatus muscle is on very top...
|
|
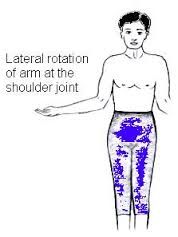
The motion is accomplished by which -spinatus muscle?
|
The infraspinatus muscle assists in lateral rotation of arm.
Infraspinatus muscle ALSO inserts in GREATER tubercle. |
|
|
All of the four muscles of the rotator cuff (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis) INSERT in to the GREATER tubercle of the humerus, EXCEPT....
|
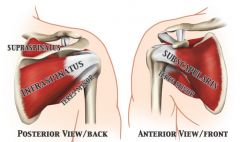
The subscapularis muscle is the ONLY muscle of the rotator cuff that inserts into the Lesser tubercle of the humerus.
|
|
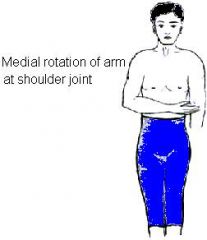
Which muscle of the rotator cuff accomplishes this motion?
|

Subscapularis muscle = medial rotation of arm.
The subscapularis muscle is actually the largest muscle of your rotator cuff & provides 50% of function. Indeed, sometimes you need all the muscle you can get to humble yourself and pray. Here this man, has medially rotated his arms to pray, with all the strength the has. |
|
|
Innervation of all the Rotator Cuff Muscles
Supra & infraspinatus muscle = suprascapular nerve. Teres MINOR = ___________ Nerve Subscapularis Mucle= ___________________ Nerve, ________ cord of Brachial plexus. |
Supra & infraspinatus muscle = suprascapular nerve.
Subscapularis Mucle= lower subscapular Nerve of POSTERIOR cord of brachial plexus. The only nerve that's not intuitive is teres minor= axillary nerve. |
|
|
What is function of Teres Major?
|

Medial rotation of Arm = necessary to pray.
Again, PRAYING is a major part of Life. It takes your majorly strong subscapularis muscle & the TERES MAJOR muscle to do so. Fitting. |
|
|
Where does Teres Major insert on humerus?
(Hint: As expected, since teres major is not part of the rotator cuff muscles it doesn't get to insert where all the other rotator cuff muscles gets to insert on humerus.) |
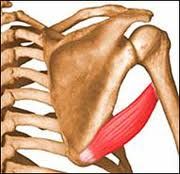
Teres major inserts on medial lip of intertubucular sulcus on anterior surface of humerus
See: You can't see insertion of teres major from the posterior view, b/c it inserts on the ANTERIOR surface of humerus! |
|
|
Teres major is innervated by ___________ nerve
|
Teres major is innervated by inferior subscapular nerve
So the only nerve innervations not intuitive in shoulder region are Teres minor = axillary nerve Teres minor = inferior subscapular nerve |
|
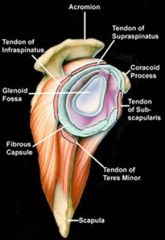
All 4 MUSCLES of the rotator cuff (-spinatus muscl es, teres minor, subscapularis) are EXTRASYNOVIAL at and EXTERNAL to the glenohumeral joint.
|
All 4 MUSCLES of the rotator cuff (-spinatus muscl es, teres minor, subscapularis) are EXTRASYNOVIAL at and EXTERNAL to the glenohumeral joint.
|
|
|
Most common muscle torn of rotator cuff muscles is the ______________________-
|

Supraspinatus muscle.
Typical, person on TOP ALWAYS gets hated on! HATERs.Tell em, Bey. |
|
|
Supraspinatus muscle is separted from the acromion by the ______________ bursa.
|
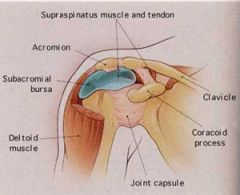
|
|
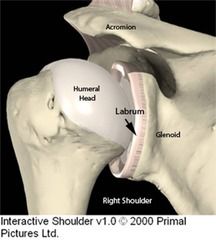
Here's a cartoon of a glenoid labrum. Now see it on a cadaver on flip side.
|
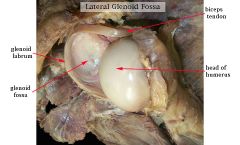
|
|
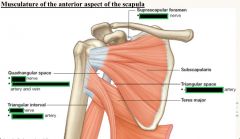
Fill in nerve /artery in each box
Note all spaces are POTENTIAL SPACES for impingement of traversing stuctures. |
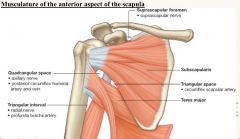
|
|
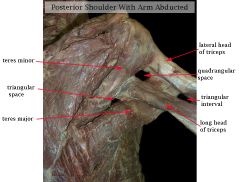
Note that the long head of the triceps brachii muscle passes _____________ to the teres major abut _____________ to the teres minor muscle, at it heads to the infraglenoid tubercle on the scapula.
|
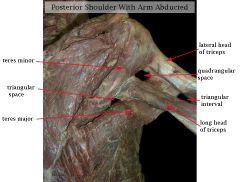
Note that the long head of the triceps brachii muscle passes POSTERIOR to the teres major abut ANTERIOR to the teres minor muscle, at it heads to the infraglenoid tubercle on the scapula.
|
|
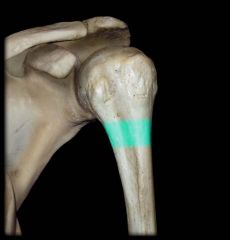
Fracture of the region here will lead to
Loss of WHAT Nerve Function Loss of Innervation to WHAT muscle Inability to ..... |
Shown in the pic was the surgical neck of the humerus
Loss of AXILLARY NERVE LOSS OF DELTOID MUSCLE Inability to abduct arm to horizontal position & laterally rotate arm (do u remember what rotator cuff muscles abducted & laterally rotate?) Laterally rotate--infraspinatus ABduct: supraspinatus |
|
|
All of the 3 muscles of the anterior compartment do FLEXION. When asked just for goodness sakes, say FLEXION as you would have said in Kindergarten, cause that's all we did with our biceps anyway.
BUT of the corachobrachials, brachialis and biceps brachii,which is responsible for flexion of ARM (not forearm) |
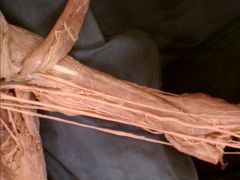
Corachobrachialis is responsible for flexion of ARM at glenohumeral joint. Heck it doesn't even go down the forearm!!
Probe is pointing to corachobrachialis with musculocutaneous nerve piercing it. |
|
So, as established, biceps brachii is responsible for flexion & supination.
Biceps brachii Inserts on the Radial or Ulnar Tuberosity? |
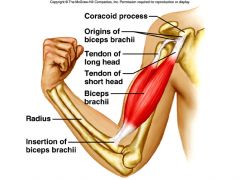
BICEPS BRACHII INSERTS ON THE RADIAL TUBEROSITY
|
|
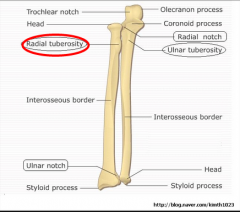
Brachialis muscle Inserts on the Radial or Ulnar Tuberosity?
|
Brachialis muscle Inserts on the Ulnar Tuberosity.
|
|
|
All muscles in forearm are INTERNAL to fasica.
The nerve supplying motor innervation to the anterior compartment of the arm is the MUSCULUTANEOUS nerve. Which muscle does the MUSCULUTANEOUS nerve pierce? Which muscle does it lie between? |
The MUSCULUTANEOUS nerve pierces the Coracho brachialis
& then lies b/w the other 2 muscles of the anterior compartment, brachialis & biceps brachii. Ain't hard. Next. |
|
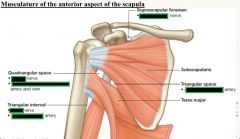
Fill in nerve/ artery- Yup, again if you like! B/c it'll prob be on test.
|
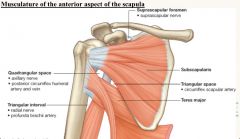
|
|
|
The __________________ NERVE travels with the Brachial artery within the arm.
|
The MEDIAN
NERVE travels with the Brachial artery within the arm. |
|
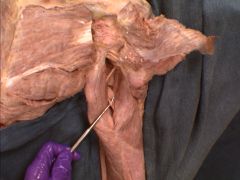
Shown here is profundaa brachii artery (should be running with the radial nerve) in the triangular interval.
What is the terminal branch of this artery called? And what does its terminal branch anastomose with? |
The terminal branch of the profundaa brachii artery is called: The radial collateral artery.
This kinda makes sense (I had a debate teacher who once told me - watch out who you hang out...b/c you'll start sounding like them) Profundaa Brachii artery has been hanging with the radial nerve long enough...it has finally adopted its neighbor's name. Radial Collateral Artery anastomoses with the Radial Recurrent Artery from the Radial Artery |
|
|
Note that the collateral always anastomes within its family.
Radial collateral Artery anastomoses with Radial Artery Ulnar collateral artery anstomoses with Ulnar Artery |
Radial collateral Artery anastomoses with Radial Artery
Ulnar collateral artery anstomoses with Ulnar Artery |
|
|
Then the ulnar collateral always break "classes" when it anastomoses with the recurrents.
|
Superior Ulnar collateral with the POSTERIOR ulnar recurrent
Inferior Ulnar collateral with the Anterior ulnar recurrent |
|
|
Posterior compartment: The triceps brachii & anconeus muscle are both working in extension of forearm.
What innervates this compartment? What provides blood supply? |
What innervates this compartment? RADIAL nerve
What provides blood supply? PROFUNDA BRACHII |
|
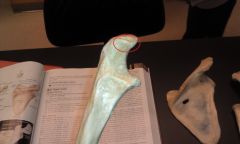
What muscle inserts here?
First of...what the heck is this ? |
The triceps brachii inserts on the OLECRANON of the ULNA.
|
|
|
Loss of RADIAL nerve function leads to what clinical symptom?
|

WRIST DROP.
Remember the scenario of the drunken guy sitting on the bench, with his posterior compartment of the arm on the bench--that impinged the radial nerve--WRIST drop |
|
|
Inflammation of the ELBOW
|
OLECRANON BURSITIS
|
|
|
Remember GOD'S Fascia! Bicipital Aponeurosis LIES EXTERNAL to the brachial artery & median nerve.
|
GOD'S Fascia! Bicipital Aponeurosis LIES EXTERNAL to the brachial artery & median nerve.
|
|
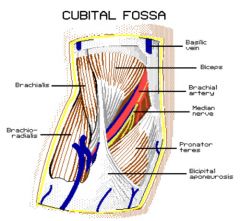
T-A-N : Tendon, Artery, Nerve.
Lateral to Medial |
Lateral to Medial
Bicipital Tendon, Brachial Artery, Median Nerve. |
|
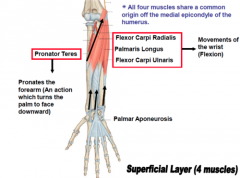
P- F-P- F.
All muscles' origin is off _______________ Tendon, which attaches to ________ epicondlye of humerus. All innervated by median (except ulnaris of course) All Function in Flexion. What ever is "radialis" is always ABduction What ever is "ulnaris" is always Adduction |
All muscles' origin is off COMMON FLEXOR Tendon, which attaches to MEDIAL epicondlye of humerus.
|
|

The brachial artery splits into the ulnar & radial artery. The probe is showing the ulnar artery (the thumb is upwards in the pic)
The ULNAR artery gives off the _____________________ artery, which splits into the ___________________ arteries. |

The ULNAR artery gives off the COMMON interosseus artery, which splits into the anterior & posterio interosseus arteries.
That's the common inerosseus artery. Do you see how it splits into an anterior & posterior artery? |
|
|
The __________________ nerve gives off the anterior interosseus nerve (which travels with the anterior interossserus artery)
|
MEDIAN nerve
|
|
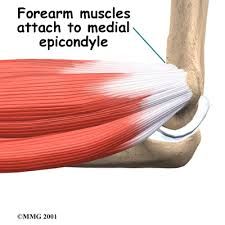
INFLAMMATION of the common flexor tendon near its origin at THE medial epicondlye
|
MEDIAL EPICONDYLITIS
|
|
|
If you have golfer's elbow (medial epincondylitis), the pain is really all the time.
|
It's upon ACTIVE flexion of forearm and passive extension of the forearm (So the golfer's one is the one that's intuitive)
|
|
|
Inflammation of the COMMON EXTENSO tendon AT LATERAL epincodyle of humerus bone
|
Lateral epicondyltis (Tennis elbow)
|
|
|
Lateral epicondylitis this pain…to me, that's non-intuitive
|
It's upon ACTIVE etension of forearm and passive flexion of the forearm (So the golfer's one is the one that's intuitive)
|
|
|
The pisiform sits on what structure?
|
The triquetrum
|
|
|
From the HamPtons to the Trailer. This stucture expens from the hamate & pisiform to the trapezium
|
Flexor Retinaculum
|
|
|
Fractures of the scaphoid bone threaten the
|
RADIAL artery
|
|
|
DAP & PADs innervated by the _____________
|
DEEP branch of the ulnar nerve. So dorsal and palmar interosseus muscles are innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve. I'm just gonna think of it as radial nerve only does stuff near thumb.
|
|
|
MEDIAL TWO Lumbrical muscles, innervated by the ____________
|
deep branch of the ulnar nerve. This is the only nerve innervation that doesn't seem to follow trend, so it'll probably be tested.
|
|
|
LATERAL TWO LUMBRICAL via the _________
|
via the median nerve
|
|
|
LUMBRICAL = PUPPET HANDS. Describe functions
|
Flexion at Mp joints & extension at PIP & DIP
|
|
|
Superficial palmar arch is mainly contributed via
|
ULNAR ARTERY (in fact, let the cadaver help you. If you look at the superficial branch, it almost always makes a really nice "U". The deep palmar branch is usually not so nicely shaped)
|
|
|
Deep palmar arch is mainly contributed via
|
RADIAL artery
|
|
|
The superficial palmar arch (mainly contributed by ulnar artery) gives rise to really simple-named arteries: three ___________ arteries. That's why it's called "superficial"
|
common palmar digital
|
|
|
Anatomical snuffbox is between tenons of the _______ & __________
|
"LB" Like Lbean the shop. Extensor pollicis longus & Extensor pollicis brevis
|
|
|
The floor of the snuffbox is the…
|
SCAPHOID BONE
|
|
|
Suprascapular nerve
|
C5, C6 (superior trunk)
|
|
|
This question will likely be on ….exam-Injury to the upper portion of the brachial plexus will affect THIS NERVE
|
MUSCULUTANEOUS nerve
|
|
|
Injury to lower portion of the brachial plexus will affect THIS nerve
|
ULNAR NERVE
|
|
|
Referred pain from the heart can shoot down medial side of arm and forearm. WHY?????
|
B/c the Median Antebrachial cutaneous nerve (sensory information) (T1) joins with the INTERCOSTOBRACHIAL nerve from T2.
|
|
|
All the major nerves of the brachial plexus are DEEP to the brachial fascia (remember this is a type of an investing layer) . ANY NERVE WITH CUTANEOUS IN THE NAME IS EXTERNAL TO BRACHIAL FASCIA
|
ANY NERVE WITH CUTANEOUS IN THE NAME IS EXTERNAL TO BRACHIAL FASCIA
|
|
|
The rest was brachial plexus- besout to learn that via drawing! You can do all in things in Christ, who strenghtens you!
|
Deuces.
|

