![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
504 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
CNS/PNS
come from 3 tissues |
neuroectoderm
neural crest mesoderm |
|
|
|
neuroectoderm gives rise to __ in CNS/PNS
|
CNS neurons
ependymal cells oligodendroglia astrocytes |
|
|
|
neural crest gives rise to __ in CNS/PNS
|
schwann cells
PNS neurons |
|
|
|
mesoderm gives rise to _
in the CNS/PNS |
microglia
|
|
|
|
nissl substance is _
is found where? |
RER
cell body dendrites not axon |
|
|
|
astrocytes' roles (6)
|
physical support
repair maintenance of BBB K+ metabolism removal of excess neurotransmitter reactive gliosis in response to injury |
|
|
|
astrocyte molecular marker
|
GFAP
|
|
|
|
microglia
physical description |
small irregular nuclei
relatively little cytoplasm |
|
|
|
microglia respond to tissue damage by
|
differentiating into large phagocytic cells
|
|
|
|
HIV-infected microglia in the CNS do __
|
fuse to form multinucleated giant cells
|
|
|
|
oligodendroglia
physical description |
small nuclei
dark chromatin little cytoplasm |
|
|
|
_ CNS cells are not readily discernable in Nissl stains
|
microglia
|
|
|
|
_ cells are destroyed in MS
|
oligodendroglia
|
|
|
|
oligodendroglia look like _ on H&E
|
fried eggs
|
|
|
|
schwann cells not only myelinate 1 PNS neuron each
they also |
promote axonal regeneration
|
|
|
|
_ cells are destroyed in Guillain-Barre syndrome
|
Schwann cells
|
|
|
|
a famous tumor of schwann cells
|
acoustic neuroma @
internal acoustic meatus is a type of schwannoma |
|
|
|
free nerve endings
description of fibers |
C--
slow, unmyelinated Adelta-- fast, unmyelinated |
|
|
|
free nerve endings
location in body |
all skin
epidermis some viscera |
|
|
|
free nerve endings sense _
|
pain & temperature
|
|
|
|
large myelinated fibers
include |
Meissner's corpuscles
Pacinian corpuscles Merkel's disks |
|
|
|
Meissner's corpuscles
location |
Glabrous (hairness) skin
|
|
|
|
Pacinian corpuscles
location |
deep skin layers
ligaments joints |
|
|
|
merkel's disks
location |
hair follicles
|
|
|
|
meissner's corpuscles
sense _ |
position
dynamic fine touch adapt quickly |
|
|
|
pacinian corpuscles
sense _ |
vibration
pressure |
|
|
|
merkel's disks sense
|
position
static touch adapt slowly |
|
|
|
Meissner's corpuscles
vs. Merkel's disks |
position
dynamic fine touch adapt quickly position static touch adapt slowly |
|
|
|
endoneurium comments
|
invests single nerve fiber
inflammatory infiltrate in Guillain-Barre |
|
|
|
perineurium comments
|
permeability barrier
surrounds a fascicle of nerve fibers must be rejoined in microsurgery for limb reattachment |
|
|
|
epineurium comments
|
dense connective tissue
surrounds entire nerve (fascicles and blood vessels) |
|
|
|
from smallest to largest...
what 3 things surround nerves? what do they each enclose? |
endoneurium -- single nerve fiber
perineurium -- fascicle epineurium -- entire nerve (fascicles and blood vessels) |
|
|
|
NE
changed ^ v in disease |
^ anxiety
v depression |
|
|
|
NE
location of synthesis |
locus ceruleus
|
|
|
|
dopamine
changed ^ v in disease |
^ schizophrenia
v parkinson's v depression |
|
|
|
5-HT
changed ^ v in disease |
v anxiety
v depression |
|
|
|
ACh
changed ^ v in disease |
v Alzheimer's
v Huntington's v REM sleep |
|
|
|
GABA
changed ^ v in disease |
v anxiety
v Huntington's |
|
|
|
GABA
location of synthesis |
nucleus accumbens
|
|
|
|
ACh
location of synthesis |
basal nucleus of Meynert
|
|
|
|
5-HT
location of synthesis |
raphe nucleus
|
|
|
|
dopamine
location of synthesis |
ventral tegmentum
SNc |
|
|
|
SNc =
|
substantia nigra pars compacta
|
|
|
|
NE
location of synthesis |
locus ceruleus
|
|
|
|
locus ceruleus controls _
|
stress
panic |
|
|
|
nucleus accumbens and septal nucleus control
|
reward
pleasure addiction fear |
|
|
|
_ (part of the brain) does reward, pleasure, addiction, fear
|
nucleus accumbens
septal nucleus |
|
|
|
_ (part of the brain) does stress and panic
|
locus ceruleus
|
|
|
|
raphe nucleus makes
|
5-HT
|
|
|
|
basal nucleus of Meynert makes
|
ACh
|
|
|
|
nucleus accumbens makes
|
GABA
|
|
|
|
ventral tegmentum and SNc make
|
dopamine
|
|
|
|
locus ceruleus makes
|
NE
|
|
|
|
blood brain barrier is formed by 3 structures
|
"TBA"
tight junctions between nonfenestrated endothelial cells basement membrane astrocyte processes |
|
|
|
some molecules that cross the BBB
|
glucose
amino acids cross slowly by carrier-mediated transport ------------------------------------- nonpolar/lipid-soluble substances cross rapidly via diffusion |
|
|
|
a way to cause edema in the brain...
|
infarction destroys endothelial tight junctions
--> vasogenic edema |
|
|
|
places where the BBB does not operate...
general idea-- examples-- |
some brain regions have
fenestrated capillaries no BBB area postrema -- vomiting after chemo OVLT -- osmotic sensing neurohypophysis -- ADH release |
|
|
|
hypothalamus 5 roles
besides adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis |
THATS
thirst and water balance hunger autonomic regulation temperature regulation sexual urges |
|
|
|
inputs to the hypothalamus
|
OVLT (senses change in osmolarity)
area postrema (responds to emetics) |
|
|
|
_ nucleus makes ADH
|
supraoptic
|
|
|
|
_ nucleus makes oxytocin
|
paraventricular
|
|
|
|
leptin - and + what in the hypothalamus?
meaning? |
- lateral area
+ ventromedial area inhibits hunger stimulates satiety |
|
|
|
lateral nucleus of hypothalamus mediates _
medial nucleus mediates _ |
hunger
satiety |
|
|
|
destruction of lateral nucleus of hypothalamus -->
|
anorexia
failure to thrive (infants) |
|
|
|
destruction of medial nucleus of hypothalamus -->
|
e.g. by craniopharyngioma
--> hyperphagia |
|
|
|
anterior hypothalamus
vs. posterior hypothalamus |
cooling, pArasympathetic
heating, sympathetic |
|
|
|
posterior hypothalamus is re:
|
heating, sympathetic
|
|
|
|
anterior hypothalamus, think
|
cooling, parasympathetic
A/C "anterior, cooling" |
|
|
|
hypothalamus:
if you zap your lateral nucleus, you... if you zap your medial nucleus, you... |
shrink laterally
grow ventrally and medially |
|
|
|
_ nucleus mediates circadian rhythm
|
suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus
|
|
|
|
thalamus 4 important nuclei
|
VPL
VPM LGN MGN |
|
|
|
thalamus picture. name the nuclei
|
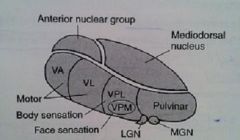
|
|
|
|
VPL input
|
spinothalamic
dorsal columns/medial lemniscus |
|
|
|
VPM input
|
trigeminal
gustatory |
|
|
|
LGN input
|
CN II
|
|
|
|
MGN input
|
superior olive
inferior colliculus of pons |
|
|
|
VPL information
|
pain and temperature
position and proprioception |
|
|
|
VPM information
|
face sensation
taste |
|
|
|
LGN
MGN info |
vvision
hearing "lateral -- light" "medial -- music" |
|
|
|
VPL destination
|
1^ somatosensory cortex
|
|
|
|
VPM destination
|
1^ somatosensory cortex
|
|
|
|
LGN destination
|
calcarine sulcus
|
|
|
|
MGN destination
|
auditory cortex of temporal lobe
|
|
|
|
limbic system includes
|
cingulate gyrus
hippocampus fornix mammillary bodies septal nucleus |
|
|
|
limbic system is responsible for what functions
|
feeding
fleeing fighting feeling fucking |
|
|
|
cerebellum receives _ input from what parts of the brain?
|
contralateral cortical input
via middle cerebellar peduncle ipsilateral proprioceptive info via inferior cerebellar peduncle |
|
|
|
cerebellum input nerves = _
|
climbing and
mossy fibers |
|
|
|
cerebellum provides _ output
|
stimulatory feedback to
contralateral cortex to modulate movement |
|
|
|
output nerves of cerebellum
|
Purkinje fibers-->
deep nuclei of cerebellum--> superior cerebellar peduncle--> cortex |
|
|
|
deep nuclei of cerebellum (lateral to medial) include
|
"Don't Eat Greasy Foods"
dentate emboliform globose fastigial |
|
|
|
lateral cerebellum is re:
|
voluntary movement of extremities
|
|
|
|
medial cerebellum is re:
|
balance
truncal coordination ataxia propensity to fall toward injured (ipsilateral) side |
|
|
|
basal ganglia: important re:
|
voluntary movements
postural adjustments |
|
|
|
basal ganglia receive _ input
provides _ in return |
cortical input
negative feedback to cortex to modulate movement |
|
|
|
direct/excitatory pathway of the basal ganglia
5 steps of stimulation or inhibition |
cortex + striatum;
dopamine from SNc + D1 of the striatum--> GABA, substance P - GPi/SNr - thalamus + cortex |
|
|
|
GPe
GPi SNc SNr |
globus pallidus externus
globus pallidus internus substantia nigra pars compacta substantia nigra pars reticulata |
|
|
|
STN =
|
subthalamic nucleus
|
|
|
|
what dopamine receptors are in the striatum in the
excitatory and inhibitory pathways? |
D1 (excitatory)
D2 (inhibitory) |
|
|
|
dopamine D1 effect on the striatum
|
+
|
|
|
|
dopamine D2 effect on the striatum
|
-
|
|
|
|
two neurotransmitters that modulate the striatum
|
dopamine from substantia nigra pars compacta
ACh from cholinergic interneurons in the striatum |
|
|
|
indirect/inhibitory pathway of the basal ganglia
|
cortex + striatum;
dopamine from SNc - D2 of the striatum--> GABA, enkephalin - GPe - STN + GPi - thalamus + cortex |
|
|
|
striatum =
|
putamen + caudate
|
|
|
|
lentiform =
|
putamen + globus pallidus
|
|
|
|
Parkinson's involves loss of what neurons?
|
dopaminergic neurons
in the substantia nigra |
|
|
|
how does loss of dopamine explain v motion in parkinson's?
|
normally: dopamine stimulates the excitatory pathway by D1 in the striatum
normally, dopamine inhibits the inhibitory pathway by D2 in the striatum loss of dopamine in both, causes v motion |
|
|
|
the chief excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain
chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain |
glutamate
GABA |
|
|
|
parkinson's disease
pathology |
Lewy bodies composed of alpha-synuclein (an intracellular inclusion)
depigmentation of the substantia nigra pars compacta (loss of dopaminergic neurons) |
|
|
|
parkinson's symptoms
|
you are TRAPped in your body
tremor at rest cogwheel Rigidity akinesia or bradykinesia postural instability |
|
|
|
one description of parkinson's tremor
|
pill-rolling remor
|
|
|
|
cogwheel rigidity =
|
muscles respond with cogwheel like jerks to the use of constant force in bending the limb
|
|
|
|
hemiballismus is __
|
sudden, wild flailing of 1 arm +/- leg
|
|
|
|
hemiballismus neurological cause
|
contralateral STN lesion
(e.g. lacunar stroke in a pt. with hx of htn) loss of inhibition of thalamus through globus pallidus |
|
|
|
STN means
|
subthalamic nucleus
|
|
|
|
huntington's disease genetics
|
dominant
trinucleotide repeat disorder expansion of CAG repeats (anticipation) |
|
|
|
huntington's disease is loss of ......
|
caudate loses ACh and GABA
atrophy of striatal nuclei (inhibitors of movement) |
|
|
|
huntington's disease sxs
|
chorea
aggression depression dementia |
|
|
|
mechanism of neuronal death in huntington's
|
neuronal death by
NMDA-R binding and glutamate toxicity |
|
|
|
chorea is movement that is
|
sudden
jerky purposeless |
|
|
|
athetosis is movement that is
|
slow
writhing esp. of fingers |
|
|
|
two movement disorders that occur with basal ganglia lesions
|
chorea
athetosis |
|
|
|
sudden, brief muscle contraction
|
myoclonus
|
|
|
|
sustained, involuntary muscle contractions =
|
dystonia
|
|
|
|
dystonia =
e.g. |
sustained
involuntary muscle contractions e.g. writer's cramp |
|
|
|
myoclonus =
e.g. |
sudden
brief muscular contraction jerks hiccups |
|
|
|
three types of tremors
|
essential/postural tremor
resting tremor intention tremor |
|
|
|
essential/postural tremor
2 comments |
action tremor (worsens when holding posture)
autosomal dominant |
|
|
|
essential/postural tremor
treatment |
beta-blockers
pts. often self-medicate with alcohol, which v tremor |
|
|
|
resting tremor is most notaceable _. example?
|
distally
parkinson's (pill-rolling) |
|
|
|
intention tremor is _
what brain damage? |
slow, zigzag motion when pointing toward something
cerebellar dysfunction |
|
|
|
(3) anterior to the central sulcus is the _
just posterior to it is the _ |
frontal eye fields
premotor area principal motor area principal sensory areas |
|
|
|
where is the primary auditory cortex?
|
just inferior to the Sylvian fissure
|
|
|
|
Broca's area is for _
|
motor speech
|
|
|
|
Wernicke's area is the _
|
associative auditory cortex
|
|
|
|
lesion @ bilateral amygdala
--> |
Kluver-Bucy syndrome:
--hyperorality --hypersexuality --disinhibited behavior |
|
|
|
hyperorality
hypersexuality disinhibited behavior what syndrome what lesion? |
Kluver-Bucy syndrome
bilateral amygdala |
|
|
|
frontal lobe lesion
--> |
disinhibition
deficits in concentration, orientation, judgment reemergence of primitive reflexes |
|
|
|
right parietal lobe lesion -->
|
spatial neglect syndrome i.e.,
agnosia of the contralateral side of the world |
|
|
|
reticular activating synstem (midbrain)
lesion --> |
reduced levels of arousal and wakefulness e.g. coma
|
|
|
|
bilateral lesion of mammillary bodies -->
|
wernicke-korsakoff syndrome
wernicke --confusion --ophthalmoplegia --ataxia korsakoff --memory loss --confabulation --personality changes |
|
|
|
wernicke-korsakoff syndrome =
|
wernicke
--confusion --ophthalmoplegia --ataxia korsakoff --memory loss --confabulation --personality changes |
|
|
|
wernicke (3)
|
confusion
ophthalmoplegia ataxia |
|
|
|
korsakoff (3)
|
memory loss
confabulation personality changes |
|
|
|
basal ganglia lesion -->
|
tremor at rest
chorea athetosis |
|
|
|
cerebellar hemisphere lesion
--> |
intention tremor
limb ataxia ipsilateral deficits fall toward side of lesion |
|
|
|
explain the pathway (in broad terms) that shows that cerebellar lesions cause ipsilateral deficits (5)
|
cerebellum -->
superior cerebellar peduncle--> contralateral cortex--> corticospinal decussation--> ipsilateral body |
|
|
|
cerebellar vermis lesion -->
|
truncal ataxia
dysarthria |
|
|
|
subthalamic nucleus lesion -->
|
contralateral hemiballismus
|
|
|
|
hippocampus lesion -->
|
anterograde amnesia
|
|
|
|
anterograde amnesia =
|
inability to make new memories
|
|
|
|
paramedian pontine reticular formation PPRF lesion -->
|
eyes look away from side of lesion
|
|
|
|
frontal eye fields lesion --> _
|
eyes look toward lesion
|
|
|
|
lesion at
PPRF vs. frontal eye fields |
eyes look away from side of lesion
eyes look toward lesion |
|
|
|
central pontine myelinolysis
sxs |
loss of consciousness
acute paralysis dysarthria dysphagia diplopia |
|
|
|
dysarthria is
|
motor speech disorder
poor articulation |
|
|
|
central pontine myelinolysis cause
|
very rapid correction of hyponatremia
|
|
|
|
very rapid correction of hyponatremia -->
|
central pontine myelinolysis
|
|
|
|
central pontine myelinolysis imaging
|
axial T1-weighted MRI shows
increased signal in the pons |
|
|
|
recurrent laryngeal nerve innervates
|
all laryngeal muscles except cricothyroid
|
|
|
|
aphasia =
|
higher-order inability to speak
|
|
|
|
dysarthria =
|
motor inability to speak
|
|
|
|
broca's aphasia =
|
nonfluent aphasia
intact comprehension |
|
|
|
broca's area
|
inferior frontal gyrus
|
|
|
|
wernicke's aphasia =
|
fluent aphasia
impaired comprehension |
|
|
|
inferior frontal gyrus contains
|
broca's area
|
|
|
|
superior temporal gyrus contains
|
wernicke's area
|
|
|
|
wernicke's area
|
superior temporal gyrus
|
|
|
|
global aphasia
|
nonfluent aphasia
impaired comprehension affects both Broca's and Wernicke's areas |
|
|
|
conduction aphasia
|
poor repetition
fluent speech intact comprehension |
|
|
|
conduction aphasia lesion
|
arcuate fasciculus that connects broca's and wernicke's areas
|
|
|
|
lesion of arcuate fasciculus -->
|
conduction aphasia
|
|
|
|
arteries of the circle of willis
from top down ~ |
anterior cerebral
anterior communicating middle cerebral lateral striate internal carotid posterior communicating posterior cerebral basilar anterior inf. cerebellar a. AICA vertebral posterior inf. cerebellar a. PICA anterior spinal artery |
|
|
|
stroke of anterior spinal artery
--> _ (brief) |
medial medullary syndrome
|
|
|
|
stroke of PICA --> _ (brief)
|
lateral medullary syndrome
aka Wallenberg's |
|
|
|
stroke of AICA --> _ (brief)
|
lateral inferior pontine syndrome
|
|
|
|
wallenberg's syndrome is aka _
caused by stroke of _ artery |
lateral medullary syndrome
PICA |
|
|
|
anterior spinal artery stroke
sxs |
contralateral hemiparesis
(lower extremities) medial lemniscus (v contralateral proprioception) ipsilateral paralysis of hypoglossal nerve |
|
|
|
stroke of PICA
sxs |
loss of pain and temperature
--contralateral body --ipsilateral face trigeminal nucleus (spinal tract and nucleus) ipsilateral Horner's ipsilateral ataxia ipsilateral dysphagia hoarseness v gag reflex vomiting vertigo diplopia nystagmus |
|
|
|
stroke of AICA
sxs |
ipsilateral facial pain and temperature
ipsilateral dystaxia (MCP, ICP) ipsilateral facial paralysis ipsilateral cochlear nucleus vestibular (nystagmus) |
|
|
|
posterior cerebral stroke
sxs |
occipital cortex -->
contralateral hemianopia macular sparing |
|
|
|
middle cerebral stroke
sxs |
contralateral face and arm
--paralysis --sensory loss apasia (dominant sphere) left-sided neglect |
|
|
|
artery in brain that has CVA the most frequently
|
middle cerebral
|
|
|
|
stroke of anterior cerebral
sxs |
leg-foot area
motor and sensory cortices |
|
|
|
anterior cerebral artery supplies _ part of the brain
|
medial surface of the brain
|
|
|
|
stroke of anterior communicating artery
sxs |
visual field defects
|
|
|
|
most common site of circle of Willis aneurysm is
|
anterior communicating artery
|
|
|
|
posterior communicating artery
comments |
common area of aneurysm
causes CN III palsy |
|
|
|
lateral striate atery comes from
|
middle cerebral artery
|
|
|
|
lateral striate artery supplies
|
internal capsule
caudate putamen globus pallidus |
|
|
|
infarct of the posterior limb of the internal capsule
(e.g. fed by _ artery) sxs |
lateral striate
pure motor heiparesis |
|
|
|
watershed zones in the brain are where?
|
between
anterior and middle cerebral middle and posterior cerebral |
|
|
|
watershed zones in the brain
damaged when? sxs |
severe hypotension
upper leg / upper arm weakness defects in higher-order visual processing |
|
|
|
basilar artery infarct -->
|
locked-in syndrome
(CN III is typically intact) |
|
|
|
locked-in syndrome may be caused by
|
basilar artery infarct
|
|
|
|
in general, stroke of anterior circle of Willis
sxs |
general sensory and motor dysfunction
aphasia |
|
|
|
in general, stroke of posterior circle of Willis
sxs |
cranial nerve deficits
--vertigo --visual deficits coma cerebellar deficits --ataxia dominant hemisphere (ataxia) nondominant hemisphere (neglect) |
|
|
|
2 types of brain aneurysms
_ _ |
berry aneurysms
charcot-Bouchard microaneurysms |
|
|
|
berry aneurysms occur where
|
bifurcations in the circle of Willis
most common site: bifurcation of the anterior communicating artery |
|
|
|
rupture of berry aneurysms
--> |
hemorrhagic stroke /
subarachnoid hemorrhage |
|
|
|
berry aneurysms are associated with _ diseases
other risk factors? |
--adult polycystic kidney disease
--Ehlers-Danlos --Marfan advanced age hypertension smoking race (higher in blacks) |
|
|
|
Charcot-Bouchard microaneurysms are associated with _
|
chronic hypertension
|
|
|
|
charcot-bouchard microaneurysms affect
|
small vessels
e.g. in basal ganglia, thalamus |
|
|
|
4 broad types of intracranial hemorrhage
|
epidural hematoma
subdural hematoma subarachnoid hemorrhage parenchymal hematoma |
|
|
|
epidural hematoma happens how?
|
rupture of middle meningeal artery
often 2^ fracture of temporal bone |
|
|
|
middle meningeal artery is a branch of _
|
maxillary artery
|
|
|
|
epidural hematoma
course |
lucid interval
rapid expansion under systemic arterial pressure --> --transtentorial herniation --CN III palsy |
|
|
|
epidural hematoma
CT shows |
"biconvex disk"
not crossing suture lines can cross falx, tentorium |
|
|
|
subdural hematoma
cause |
rupture of bridging veins
|
|
|
|
subdural hematoma
course |
slow venous bleeding(hematoma develops over time)
delayed onset of symptoms |
|
|
|
subdural hematoma is seen in _
|
elderly
alcoholics blunt trauma shaken baby --predisposing factors: brain atrophy shaking whiplash |
|
|
|
subdural hematoma
physical description |
crescent-shaped
crosses suture lines gyri are preserved, since pressure is distributed equally cannot cross falx, tentorium |
|
|
|
epidural hematoma
vs. subdural hematoma they cross _... don't cross _ |
doesn't cross suture lines
can cross falx, tentorium crosses suture lines cannot cross falx, tentorium |
|
|
|
subarachnoid hemorrhage
cause |
rupture of an aneurysm
--usu. berry aneurysm in Marfan's Ehlers-Danlos APCKD or an AVM |
|
|
|
spinal tap in subarachnoid hemorrhage
|
bloody or yellow (xanthochromic)
|
|
|
|
subarachnoid hemorrhage
2-3 days later, there is a risk of... why? treat with __ |
vasospasm
due to blood breakdown products which irritate vessels calcium channel blockers |
|
|
|
parenchymal hematoma
cause |
hypertension
amyloid angiopathy --lobar strokes all ove the brain diabetes mellitus tumor |
|
|
|
parenchymal hematoma
typical location |
basal ganglia
internal capsule |
|
|
|
areas most vulnerable to ischemic brain disease
|
hippocampus
neocortex crebellum watershed areas |
|
|
|
irreversible neuronal injury
pathological progression (5) |
red neurons 12-48 hours
necrosis + neutrophils 24-72 macrophages 3-5 days reactive gliosis + vascular proliferation (1-2 weeks) glial scar (> 2 weeks) |
|
|
|
atherosclerosis --> thrombi--> ischemic stroke
--> |
necrosis
forms cystic cavity with reactive gliosis |
|
|
|
hemorrhagic stroke is often due to _
may also be due to _ |
aneurysm rupture
2^ ischemic stroke followed by reperfusion (^ vessel fragility) |
|
|
|
ischemic stroke
comments |
emboli block large vessels 2^
--atrial fibrillation --carotid dissection --patent foramen ovale --endocarditis lacunar strokes block small vessels --may be 2^ htn |
|
|
|
stroke imaging
|
bright on diffusion-weighted MRI in 3-30 minutes
remains bright for 10 days dark on noncontrast CT in ~ 24 hours bright areas on noncontrast CT indicate hemorrhage |
|
|
|
cerebral veins drainage
|
--> venous sinuses
--> internal jugular vein |
|
|
|
foramina and ventricles
|
lateral ventricles -->
ventricular foramina of monro --> 3rd ventricle --> cerebral aqueduct--> 4th ventricle--> foramina of Luschka (lateral apertures) foramen of Magendie (median aperture) |
|
|
|
CSF from 4th ventricles to absorption
|
4th ventricle-->
lateral apertures (foramina of Luschka) median aperture (foramen of Magendie) --> subarachnoid space --> venous sinus arachnoid granulations |
|
|
|
types of hydrocephalus
|
normal pressure
communicating obstructive ex vacuo |
|
|
|
normal pressure hydrocephalus triad
|
"wet, wobbly, and wacky"
urinary incontinence ataxia dementia |
|
|
|
normal pressure hydrocephalus
physical effects |
does not result in
^ subarachnoid space volume expansion of ventricles distorts the fibers of the corona radiata --> triad of sxs |
|
|
|
communicating hydrocephalus (4)
|
v CSF absorption by arachnoid villi, which can lead to
^ intracranial pressure papilledema herniation |
|
|
|
example of something that can cause communicating hydrocephalus
|
arachnoid scarring post-meningitis-->
v CSF absorption by arachnoid villi |
|
|
|
obstructive hydrocephalus
e.g. |
stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius
|
|
|
|
cerebral aqueduct is aka
|
aqueduct of Sylvius
|
|
|
|
hydrocephalus ex vacuo is at its core
|
appearance of ^ CSF in atrophy
--Alzheimer's --advanced HIV --Pick's disease |
|
|
|
hydrocephalus ex vacuo
manifestations |
pressure is normal
triad is not seen |
|
|
|
vertebral disk herniation is _
usu occurs at what vertebral level? |
nucleus pulposus herniates through annulus fibrosus
between L5 and S1 |
|
|
|
vertebral disk herniation seems to be a problem esp. at
vertebral level _ |
L5-S1
|
|
|
|
in adults, the spinal cord extends to level _
|
lower border of L1-L2
|
|
|
|
subarachnoid space extends to _
|
lower border of S2
|
|
|
|
lumbar puncture is usually performed @
|
L3-L4 or L4-L5 interspaces
at the level of the cauda equina |
|
|
|
the major spinal cord tracts (3)
|
dorsal columns
spinothalamic tract lateral corticospinal tract |
|
|
|
dorsal columns
|
fasciculus cuneatus
--upper body fasciculus gracilis --lower body |
|
|
|
spatial organization of the dorsal columns in the spinal cord
|
organized as a person is:
arms outside (fasiculus cuneatus) legs inside (fasiculus gracilis) |
|
|
|
spatial organization of
lateral corticospinal tract spinothalamic tract in the spinal cord |
Legs are Lateral in both
|
|
|
|
dorsal columns mediate (4) sensations
|
pressure
touch vibration proprioception |
|
|
|
what spinal arteries are there?
|
2 posterior spinal arteries
1 anterior spinal artery |
|
|
|
the intermediate horn in the spinal cord...
made of? found where? |
sympathetics
thoracic only |
|
|
|
_ does not have any choroid plexus
|
cerebral aqueduct
|
|
|
|
remember, ascending tracts _ _
|
synapse and then cross
|
|
|
|
dorsal column pathway
1st-order neuron synapse 1 2nd-order neuron synapse 2 3rd-order neuron |
--sensory nerve ending
--cell body in DRG --ascends ipsilaterally ipsilateral nucleus cuneatus or gracilis (in medulla) --decussates in medulla --ascends contralaterally in medial lemniscus VPL of thalamus sensory cortex |
|
|
|
spinothalamic tract
1st-order neuron synapse 1 2nd-order neuron synapse 2 3rd-order neuron |
--A-delta or C fibers (sensory nerve ending)
-- cell body in DRG ipsilateral gray matter (in spinal cord) --decussates at anterior white commissure --ascends contralaterally VPL of thalamus sensory cortex |
|
|
|
lateral corticospinal tract
1st-order neuron synapse 1 2nd-order neuron synapse 2 3rd-order neuron |
--upper motor neuron
--cell body in 1^ motor cortex --descends ipsilaterally (through internal capsule) --decussates at caudal medulla (pyramidal decussation) --descends contralaterally cell body in anterior horn (spinal cord) lower motor neuron leaves spinal cord neuromuscular junction |
|
|
|
1st-order neuron
of dorsal column |
--sensory nerve ending
--cell body in DRG --ascends ipsilaterally |
|
|
|
synapse 1
of dorsal column |
ipsilateral nucleus cuneatus or gracilis
(in medulla) |
|
|
|
2nd-order neuron
of dorsal column |
--decussates in medulla
--ascends contralaterally in medial lemniscus |
|
|
|
synapse 2
of dorsal column |
VPL of thalamus
|
|
|
|
3rd-order neuron
of dorsal column |
sensory cortex
|
|
|
|
1st-order neuron
of spinothalamic tract |
--A-delta or C fibers
(sensory nerve ending) -- cell body in DRG |
|
|
|
synapse 1
of spinothalamic tract |
ipsilateral gray matter
(in spinal cord) |
|
|
|
2nd-order neuron
of spinothalamic tract |
--decussates at anterior white commissure
--ascends contralaterally |
|
|
|
synapse 2
of spinothalamic tract |
VPL of thalamus
|
|
|
|
3rd-order neuron
of spinothalamic tract |
sensory cortex
|
|
|
|
1st-order neuron
of lateral corticospinal tract |
--upper motor neuron
--cell body in 1^ motor cortex --descends ipsilaterally (through internal capsule) --decussates at caudal medulla (pyramidal decussation) --descends contralaterally |
|
|
|
synapse 1
of lateral corticospinal tract |
cell body in anterior horn
(spinal cord) |
|
|
|
2nd-order neuron
of lateral corticospinal tract |
--lower motor neuron
--leaves spinal cord |
|
|
|
synapse 2
of lateral corticospinal tract |
neuromuscular junction
|
|
|
|
motor neuron signs that UMN lesion shows but LMN lesion does not show
|
^ reflexes
^ tone + babinski + spastic paralysis + clasp knife spasticity |
|
|
|
motor neuron signs that LMN lesion shows but UMN lesion does not show
|
+ atrophy
+ fasciculation v reflexes v tone |
|
|
|
motor neuron signs that UMN and LMN lesions have in common
|
weakness
|
|
|
|
infants' normal Babinski
|
upgoing Babinski is normal in infants
|
|
|
|
poliomyelitis and _ disease have _ lesion
|
werdnig-hoffmann disease
lower motor neuron lesions: destruction of anterior horns |
|
|
|
poliomyelitis and
werdnig-hoffmann disease sxs |
flaccid paralysis
|
|
|
|
UMN or LMN?
polio |
LMN
|
|
|
|
UMN or LMN?
werdnig-hoffmann disease |
LMN
|
|
|
|
werdnig-hoffmann disease
lesion |
lower motor neuron lesions:
destruction of anterior horns |
|
|
|
MS
lesion |
mostly white matter of cervical region
random and assymmetric lesions due to demyelination |
|
|
|
MS
sxs (3) |
scanning speech
intention tremor nystagmus |
|
|
|
UMN or LMN?
ALS |
combined upper and lower
|
|
|
|
ALS lesion
|
both UMN and LMN deficits
no sensory deficit |
|
|
|
complete occlusion of anterior spinal artery
spares _ |
dorsal columns
tract of Lissauer |
|
|
|
a notable watershed area of the spinal cord
|
upper thoracic ASA territory is a watershed area, as
artery of Adamkiewicz supplies ASA below T8 ASA = anterior spinal artery |
|
|
|
tabes dorsalis lesion
|
dorsal roots
dorsal columns |
|
|
|
tabes dorsalis sxs (2)
|
impaired proprioception
locomotor ataxia |
|
|
|
syringomyelia
lesion |
anterior white commissure
of spinothalamic tract (2nd-order neurons) usu C8-T1 can expand and affect other tracts |
|
|
|
syringomyelia
sxs (1) |
bilateral loss of pain and temp
|
|
|
|
syringomyelia is seen with _
|
chiari I
types 1 and 2 |
|
|
|
deficiency of vitamin B12, vitamin E
and Friedreich's ataxia lesion |
demyelination of
--dorsal columns --lateral corticospinal tracts --spinocerebellar tracts |
|
|
|
deficiency of
--vitamin B12 --vitamin E Friedreich's ataxia sxs |
ataxic gait
hyperreflexia impaired position and vibration sense |
|
|
|
spinocerebellar tract
terminates in _ conveys what? |
ipsilateral cerebellum
limb and joint proprioceptive info |
|
|
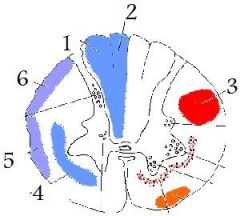
|
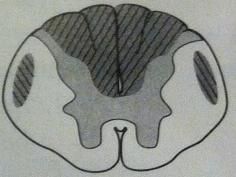
1
fasciculus cuneatus 2 fasciculus gracilis 3 lateral corticospinal tract 4 spinothalamic tract 5, 6 ventral spinocerebellar dorsal spinocerebellar |
|
|
|
fasciculus cuneatus
|
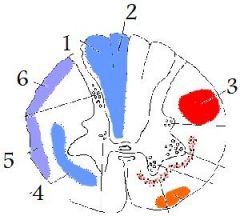
(1)
|
|
|
|
fasciculus gracilis
picture |
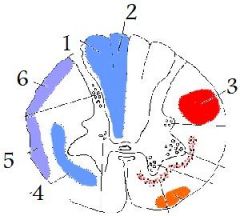
(2)
|
|
|
|
lateral corticospinal tract
picture |
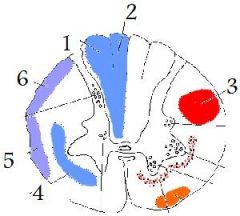
(3)
|
|
|
|
spinothalamic tract
picture |
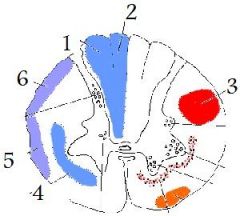
(4)
|
|
|
|
ventral spinocerebellar tract
dorsal spinocerebellar tract picture |
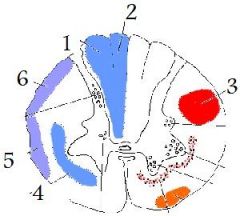
5
6 |
|
|
|
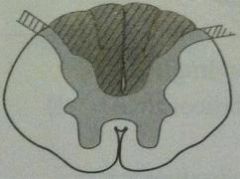
poliomyelitis and werdnig-hoffmann disease
lesion picture lesion description in words |
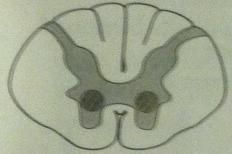
|
LMN lesions
destruction of anterior horns |
|
|
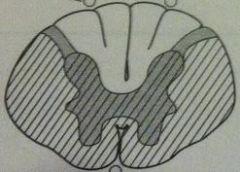
MS
lesion picture lesion in words |
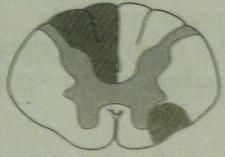
mostly white matter of cervical region
random and asymmetric lesions due to demyelination |
|
|
|
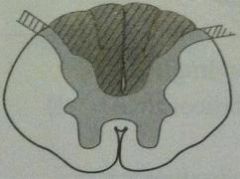
ALS
lesion picture lesion in words |
|
UMN and LMN
no sensory deficit |
|
|
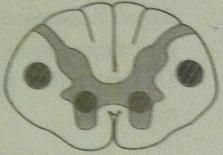
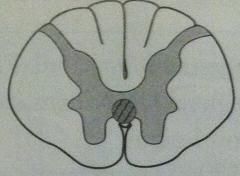
complete occlusion of anterior spinal artery
lesion picture lesion in words |
|
spares
--dorsal columns --tract of Lissauer |
|
|
tabes dorsalis
lesion picture lesion in words |
|
dorsal roots
dorsal columns |
|
|
syringomyelia
lesion picture lesion in words |
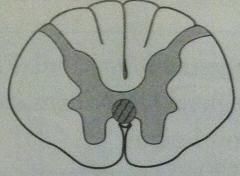
|
anterior white commisure of
spinothalamic tract (2nd-order neurons) usu C8-T1 can expand into other tracts |
|
|
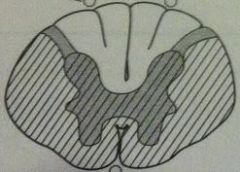
deficiency of
Vitamin B12 Vitamin E Friedreich's ataxia lesion picture lesion in words |
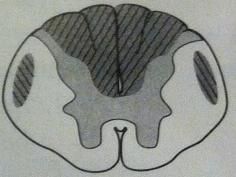
|
demyelination of
--dorsal columns --lateral corticospinal tracts --spinocerebellar tracts |
|
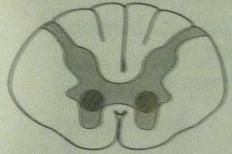
|
poliomyelitis
werdnig-hoffmann disease |
|
|
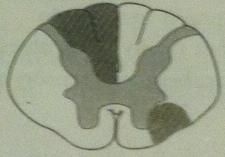
|
MS
|
|
|
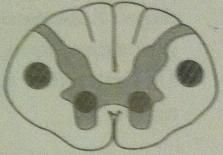
|
ALS
|
|
|
|
complete occlusion of anterior spinal artery
|
|
|
|
tabes dorsalis
|
|
|
|
syringomyelia
|
|
|
|
deficiency:
--vitamin B12 --vitamin E Friedreich's ataxia |
|
|
|
poliomyelitis
transmission |
fecal-oral
|
|
|
|
polio
infection sites in the body |
oropharynx
small intestine then bloodstream CNS |
|
|
|
polio
lesion |
anterior horn
LMN destruction |
|
|
|
polio symptoms (8)
|
malaise
headache fever sore throat nausea abdominal pain LMN lesions, including fibrillation |
|
|
|
polio diagnostic findings
|
CSF
--lymphocytic pleocytosis --slight elevation of protein virus recovered from --stool --throat |
|
|
|
werdnig hoffmann disease is aka
|
infantile spinal muscular atrophy
|
|
|
|
werdnig hoffmann disease
genetics |
recessive
|
|
|
|
something besides botulism, that presents as floppy baby
|
werdnig-hoffmann disease
|
|
|
|
werdnig hoffmann clinical presentation
|
floppy baby
fasciculations |
|
|
|
werdnig hoffmann prognosis
|
death 7 months
|
|
|
|
werdnig hoffmann
lesion |
anterior horns
LMN |
|
|
|
ALS
deficits |
UMN and LMN
no sensory, cognitive, or oculomotor deficits |
|
|
|
ALS genetics
|
can be caused by defect in
superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) |
|
|
|
a defect in SOD1 can cause
|
(superoxide dismutase 1)
ALS |
|
|
|
amylotrophic lateral sclerosis
presentation |
fasciculations
eventual atrophy |
|
|
|
pharmacologic treatment of ALS
|
riluzole
|
|
|
|
riluzole mechanism
|
v presynaptic glutamate release
|
|
|
|
riluzole rx
|
ALS
|
|
|
|
tabes dorsalis sxs (8)
|
impaired proprioception
locomotor ataxia Charcot's joints shooting (lightning) pain Argyll Robertson pupils sensory ataxia at night absence of DTRs positive Romberg |
|
|
|
friedreich's ataxia
molecular genetics |
autosomal recessive
trinucleotide repeat GAA in frataxin gene --> impairment in mitochondrial fxn |
|
|
|
friedreich's ataxia
sxs (8) |
staggering gait
frequent falling nystagmus dysarthria hypertrophic cardiomyopathy --pes cavus --hammer toes --childhood presentation with kyphoscoliosis |
|
|
|
how does friedreich's ataxia affect the heart?
|
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
|
cause of death in friedreich's ataxia
|
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
|
friedreich's ataxia
presentation |
presents in childhood
with kyphoscoliosis |
|
|
|
hemisection of spinal cord is called _ syndrome
|
brown-sequard
|
|
|
|
brown-sequard syndrome
findings (6) |
below lesion:
--ipsilateral UMN signs (corticospinal tract) --ipsilateral loss touch, vibration, and proprioception (dorsal column) --contralateral pain and temperature loss (spinothalamic tract) at level of lesion: --ipsilateral loss of all sensation --LMN signs e.g. flaccid paralysis if lesion occurs above T1, presents with Horner's syndrome |
|
|
|
if brown sequard syndrome lesion occurs above _...
|
if lesion is above T1
presents with Horner's syndrome |
|
|
|
horner's syndrome
sxs |
ptosis
absence of sweating absence of flushing miosis |
|
|
|
horner's syndrome is associated with _
examples? |
lesion of spinal cord above T1
pancoast's tumor brown-sequard [cord hemisection] late-stage syringomyelia |
|
|
|
how does horner's syndrome cause ptosis
|
interference with innervation of
superior tarsal muscle |
|
|
|
oculosympathetic pathway
where are the neuron cell bodies |
1: hypothalamus
2: lateral horn of spinal cord 3: superior cervical ganglion |
|
|
|
oculosympathetic pathway innervates _
|
pupillary dilator
smooth muscle of the eyelids sweat glands of the forehead/face |
|
|
|
the pupillary dilator receives sympathetic fiber via ...
ultimately from the superior cervical ganglion |
superior cervical ganglion
nerve fibers travel with internal carotid artery join up with ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve long ciliary nerve |
|
|
|
C2 dermatome
|
posterior half of a "skull cap"
|
|
|
|
C3 dermatome
|
high turtleneck shirt on the neck
|
|
|
|
C4 dermatome
|
low-collar shirt
|
|
|
|
T4
|
at the nipple
|
|
|
|
T7 dermatome
|
xiphoid process
|
|
|
|
L1 dermatome
|
inguinal ligament
|
|
|
|
L4 dermatome
|
kneecaps
|
|
|
|
S2, S3, S4 dermatomes
|
erection
sensation of penile and anal zones |
|
|
|
_ dermatome is at xiphoid process
|
T7
|
|
|
|
achilles reflex: what nerve root?
|
S1
|
|
|
|
patella reflex: what nerve root?
|
L4
|
|
|
|
triceps reflex: what nerve root?
|
C7
|
|
|
|
biceps reflex: what nerve root?
|
C5
|
|
|
|
babinski reflex is _
|
dorsiflexion of big toe
fanning of other toes |
|
|
|
babinski reflex is a sign of _
|
UMN lesion
|
|
|
|
primitive reflexes include (5)
|
moro
rooting sucking palmar and plantar babinski |
|
|
|
moro reflex (2)
|
abduct/extend limbs when startled
then draw together ("hang on for life") |
|
|
|
primitive reflexes show up when?
|
normally disappear within 1st year
may re-emerge following frontal lobe lesion |
|
|
|
rooting reflex (2)
|
cheek or mouth is stroked-->
move head toward that side (nipple seeking) |
|
|
|
sucking reflex (2)
|
roof of mouth is touched -->
sucking |
|
|
|
pineal gland is responsible for (2)
|
melatonin secretion
circadian rhythm |
|
|
|
superior colliculi (1)
|
conjugate vertical gaze
|
|
|
|
inferior colliculi (1)
|
auditory
|
|
|
|
parinaud syndrome
|
paralysis of conjugate vertical gaze
due to lesion of superior colliculi (e.g. pinealoma) |
|
|
|
paralysis of conjugate vertical gaze
due to lesion of superior colliculi is called _____ caused by e.g. _____ |
perinaud syndrome
pinealoma |
|
|
|
CN IV origin/course in the brain
|
arises dorsally
immediately decussates |
|
|
|
the only CN without thalamic relay to the cortex
|
CN I
|
|
|
|
pupillary constriction is done by what kind of nerve
from what nucleus |
parasympathetic muscarinic
edinger-westphal nucleus |
|
|
|
CN IV innervates
|
superior oblique
|
|
|
|
innervation of salivation
|
VII: submandibular, sublingual
IX: parotid |
|
|
|
what does facial innervate in the ear?
|
stapedius
|
|
|
|
stapedius is innervated by
|
CN VII
|
|
|
|
what muscle does CN IX innervate?
|
stylopharyngeus
|
|
|
|
stylopharyngeus does what?
|
elevates pharynx, larynx
|
|
|
|
parotid is innervated by _
|
CN IX
|
|
|
|
swallowing is innervated by _
|
CN IX
CN X |
|
|
|
CN IX elevates _
CN X elevates _ |
pharynx, larynx
palate |
|
|
|
vagus is responsible for innervating
(8) |
taste from epiglottic region
swallowing palate elevation midline uvula talking coughing thoracoabdominal viscera aortic arch chemo- and baroreceptors |
|
|
|
cranial nerve nuclei are located where?
|
tegmentum portion of brain stem
(between dorsal and ventral portions) |
|
|
|
midbrain has what CN nuclei?
|
3,4
|
|
|
|
pons has what CN nuclei?
|
5-8
|
|
|
|
medulla has what CN nuclei?
|
9-12
|
|
|
|
lateral CN nuclei (3)
|
sensory
(alar plate) sulcus limitans |
|
|
|
medial CN nuclei (2)
|
motor
(basal plate) |
|
|
|
cranial nerve reflexes include (5)
|
corneal
lacrimation jaw jerk pupillary gag |
|
|
|
corneal reflex
innervations |
afferent
--V1 ophthalmic (nasociliary branch) efferent --VII temporal branch (orbicularis oculi) |
|
|
|
lacrimation reflex
innervations |
afferent: V1
efferent: VII |
|
|
|
loss of lacrimation reflex...
|
does not preclude emotional tears
|
|
|
|
pupillary reflex
innervations |
afferent: II
efferent: III |
|
|
|
gag reflex
innervations |
afferent: IX
efferent: IX, X |
|
|
|
vagal nuclei include
|
nucleus solitarius
nucleus ambiguus dorsal motor nucleus |
|
|
|
nucleus solitarius
what functions? |
(Solitarius Sensory)
visceral sensory information (taste, baroreceptors, gut distention) |
|
|
|
nucleus ambiguus
what functions? |
(aMbiguus Motor)
motor innervation of pharynx, larynx, upper esophagus (swallowing, palate elevation) |
|
|
|
dorsal motor nucleus
functions |
parasympathetic fibers to
heart lungs upper GI |
|
|
|
nucleus ambiguus: what CNs
|
9, 10, 11
|
|
|
|
nucleus solitarius: what CNs
|
7, 9, 10
|
|
|
|
which CNs in the middle cranial fossa?
|
II - VI
|
|
|
|
which CNs in the posterior cranial fossa?
|
VII-XII
|
|
|
|
the CNs in the middle cranial fossa are _
and they traverse the _ bone |
2-6
sphenoid |
|
|
|
the CNs in the posterior cranial fossa are _
and they traverse the _ bone |
7-12
temporal or occipital |
|
|
|
optic canal transmits
|
CN II
ophthalmic artery central retinal vein |
|
|
|
superior orbital fissure transmits
|
III, IV, V1, VI
ophthalmic vein sympathetic fibers |
|
|
|
foramen rotundum transmits
|
V2
|
|
|
|
foramen ovale transmits
|
V3
|
|
|
|
foramen spinosum transmits
|
middle meningeal
|
|
|
|
V1, V2, V3 are transmitted by
|
divisions of CN V exit due to Standing Room Only
Superior orbital fissue Rotundum Ovale |
|
|
|
5 important tunnels in the sphenoid bone
|
optic canal
superior orbital fissue foramen rotundum foramen ovale foramen spinosum |
|
|
|
internal auditory meatus transmits
|
CN 7, 8
|
|
|
|
jugular foramen transmits
|
CN 9, 10, 11
jugular vein |
|
|
|
CN XII is transmitted by
|
hypoglossal canal
|
|
|
|
foramen magnum transmits
|
spinal roots of CN XI
brain stem vertebral arteries |
|
|
|
the midbrain has two parts
|
tectum
tegmentum |
|
|
|
the cranial nerves that pass through the cavernous sinus, from top to bottom
|
III
IV VI V1 V2 |
|
|
|
besides cranial nerves, _ passes through the cavernous sinus
|
internal carotid artery
with postganglionic sympathetics |
|
|
|
blood from (2) --> cavernous sinus --> _
|
eye
superficial cortex internal jugular vein |
|
|
|
cavernous sinus syndrome (e.g. due to _)
sxs: |
mass effect
ophthalmoplegia sensory loss: --ophthalmic --maxillary |
|
|
|
CN V lesion -->
|
jaw deviates toward side of lesion
|
|
|
|
this jaw muscle is special...
|
lateral pterygoid has
bilateral cortical input |
|
|
|
CN X lesion -->
|
uvula deviates away from lesion
|
|
|
|
facial nerve
LMN lesion (2) |
ipsilateral paralysis
upper and lower face |
|
|
|
facial nerve
UMN lesion (3) |
contralateral paralysis
lower face only |
|
|
|
upper face re: facial nerve
|
upper face receives bilateral UMN innervation
so it is paralyzed if there's a unilateral LMN lesion |
|
|
|
bell's palsy
is _ |
destruction of the facial nucleus
or its branchial efferent fibers (facial nerve proper) |
|
|
|
bell's palsy
sxs |
ipsilateral facial paralysis (upper and lower face)
inability to close eye on involved side |
|
|
|
bell's palsy is seen as a complication in _
|
the problem is your STD, not your HLA
Sarcoidosis Tumors Diabetes Herpes simplex Lyme disease AIDS |
|
|
|
sounds to test different CNs
|
Kuh-- palate elevation (CN X)
La-- tongue (CN XII) Mi-- lips (CN VII) |
|
|
|
what muscles open the jaw?
|
lateral pterygoid
|
|
|
|
the "posterior chamber" of the eye is where?
|
behind iris
in front of lens |
|
|
|
anterior chamber is in front of _
|
iris
|
|
|
|
retinitis (3)
|
retinal necrosis
edema --> atrophic scar |
|
|
|
iritis is _ e.g.
|
systemic inflammation e.g. Reiter's
|
|
|
|
for seeing near vision what does the eye do?
|
ciliary muscle contracts -->
zonular fibers relax--> lens relaxes --> more convex |
|
|
|
aging affects the eye how? (2)
|
sclerosis and
v elasticity --> lens shape to change |
|
|
|
retinal artery occlusion
sxs and findings |
acute
painless monocular loss of vision pale retina cherry-red macula (it is supplied by the choroid artery) |
|
|
|
macula is supplied by _
|
choroid artery
|
|
|
|
pupillary dilator is aka _
pupillary sphincter is aka |
radial muscle
circular muscle constrictor muscle |
|
|
|
pupillary sphincter contracts on signal through _ receptors
|
M3
|
|
|
|
pupillary dilator contracts on signal through _ receptors
|
alpha 1
|
|
|
|
what produces aqueous humor?
what receptor? |
ciliary process
beta |
|
|
|
accommodation is done by _ muscle
what receptor? |
ciliary muscle
M3 |
|
|
|
glaucoma gist
|
impaired flow of aqueous humor -->
^ intraocular pressure --> optic disk atrophy with cupping |
|
|
|
open / wide angle glaucoma is a problem where?
|
obstructed outflow e.g. canal of Schlemm
|
|
|
|
open/wide angle glaucoma
sxs |
"silent"
painless |
|
|
|
open/wide angle glaucoma is associated with
|
myopia
^ age African-Americans |
|
|
|
which type of glaucoma is more common?
|
open/wide angle
|
|
|
|
closed/narrow angle glaucoma
affects what anatomy? |
obstruction of flow between iris and lens
--> pressure buildup behind iris |
|
|
|
closed/narrow angle glaucoma
sxs |
very painful
v vision rock-hard eye frontal headache |
|
|
|
do not give _ drug to people with _ glaucoma
|
epinephrine
closed/narrow angle glaucoma |
|
|
|
cataracts are
|
painless
bilateral opacification of lens--> v in vision |
|
|
|
cataracts risk factors (9)
|
age
smoking EtOH sunlight classic galactosemia galactokinase deficiency diabetes (sorbitol) trauma infection |
|
|
|
papilledema is (3)
|
^ intracranial pressure -->
elevated optic disk with blurred margins bigger blind spot |
|
|
|
papilledema can be seen in _ condition
|
hydrocephalus
|
|
|
|
_ structure is right below the inferior rectus
|
infraorbital nerve
|
|
|
|
_ structure is with the optic nerve, and is actually
R, L, above, below... |
ophthalmic artery
above |
|
|
|
CN III damage -->
|
eye looks down and out
ptosis pupillary dilation loss of accommodation |
|
|
|
CN IV damage -->
|
eye drifts upward causing vertical diplopia
problems reading newspaper or going down stairs |
|
|
|
the superior oblique does what?
|
abducts
intorts depresses while the eye is adducted |
|
|
|
pupillary constriction is ultimately from what pathway
|
edinger-westphal nucleus
CN III ciliary ganglion |
|
|
|
innervation of pupillary dilation
|
T1 preganglionic sympathetic
superior cervical ganglion postganglionic sympathetic long ciliary nerve |
|
|
|
pupillary light reflex
pathway |
CN II
pretectal nuclei in midbrain which activate bilateral Edinger Westphal nuclei pupils contract bilaterally (consensual reflex) |
|
|
|
pupillary light reflex at its simplest...
|
illumination of 1 eye -->
bilateral pupillary constriction |
|
|
|
a specific named defect in the pupillary light reflex
|
Marcus Gunn pupil
|
|
|
|
Marcus Gunn pupil is what?
|
afferent pupillary defect -->
v bilateral pupillary constriction when light is shone in affected eye |
|
|
|
Marcus Gunn pupil can be caused by e.g.
|
optic nerve damage
retinal detachment |
|
|
|
CN III has some strange anatomy about the never itself...
|
center: output to ocular muscles
periphery: parasympathetic output |
|
|
|
center of CN III is affected...
|
primarily by vascular disease
e.g. diabetes: glucose --> sorbitol due to ^ diffusion to interior |
|
|
|
periphery of CN III is affected...
|
affected 1st by compression e.g.
--PCA berry aneurysm --uncal herniation |
|
|
|
mnemonic for the structure of CN III
|
Parasympathetics on the
Periphery |
|
|
|
retinal detachment pathophys
|
separation of neurosenosry layer of retina
from pigment epithelium --> degeneration of photoreceptors --> vision loss |
|
|
|
retinal detachment may be 2^
|
trauma
diabetes |
|
|
|
the macula is notably affected by _ disease
|
age related macular degeneration
|
|
|
|
age-related macular degeneration
sxs |
loss of central vision (scotomas)
|
|
|
|
age related macular degeneration
types time course what causes them |
"dry"/atrophic
--slow --fat deposits "wet" --rapid --neovascularization |
|
|
|
cutting the right optic nerve -->
|
right anopia
|
|
|
|
cutting the optic chasm -->
why? |
(destruction of nasal fibers)-->
bitemporal hemianopia |
|
|
|
cutting right optic tract -->
why? |
(destruction of L nasal fibers)
(destruction of R temporal fibers) left homonymous hemianopia |
|
|
|
cutting the right meyer's loop -->
|
left upper quadrantic anopia
|
|
|
|
cutting right dorsal optic radiation -->
|
left lower quadratic anopia
|
|
|
|
the optic tract reaches _ and bifurcates into _
|
lateral geniculate body
dorsal optic radiation --parietal lobe meyer's loop --temporal lobe |
|
|
|
_ can cause lesion of meyer's loop
|
temporal lesion
MCA |
|
|
|
_ can cause lesion of dorsal optic radiation
|
parietal lesion
MCA |
|
|
|
MCA can interfere with what parts of the vision circuit?
|
meyer's loop
dorsal optic radiation |
|
|
|
lesion of the visual pathway at the right visual cortex -->
|
left hemianopia
with macular sparing |
|
|
|
why does lesion of right visual cortex--> left hemianopia with macular sparing?
|
because the macula -->
bilateral projection to occiput |
|
|
|
when an image hits the 1^ visual cortex, it is ...
|
upside down and
left-right reversed |
|
|
|
meyer's loop contains fibers from _
therefore, |
inferior retina
lesion --> superior quadrant vision loss |
|
|
|
dorsal optic radiation contains fibers from _
therefore, |
superior retina
lesion --> inferior quadrant vision loss |
|
|
|
dorsal optic radiation goes through _
meter's loop goes through _ |
internal capsule
loops around inferior horn of lateral ventricle |
|
|
|
lesion in the medial longitudinal fasciculus
--> |
medial rectus palsy
on attempted lateral gaze nystagmus in abducting eye |
|
|
|
what is normal in MLF lesion?
|
convergence
|
|
|
|
lesion of the visual pathway at the right visual cortex -->
|
left hemianopia
with macular sparing |
|
|
|
internuclear ophthalmoplegia is lesion of _
and it's seen in _ |
medial longitudinal fasciculus
multiple sclerosis |
|
|
|
why does lesion of right visual cortex--> left hemianopia with macular sparing?
|
because the macula -->
bilateral projection to occiput |
|
|
|
looking to the left done by a patient with right MLF damage
--> |
patient's right eye doesn't adduct
patient's left eye abducts but has right-beating nystagmus |
|
|
|
when an image hits the 1^ visual cortex, it is ...
|
upside down and
left-right reversed |
|
|
|
meyer's loop contains fibers from _
therefore, |
inferior retina
lesion --> superior quadrant vision loss |
|
|
|
dorsal optic radiation contains fibers from _
therefore, |
superior retina
lesion --> inferior quadrant vision loss |
|
|
|
dorsal optic radiation goes through _
meter's loop goes through _ |
internal capsule
loops around inferior horn of lateral ventricle |
|
|
|
lesion in the medial longitudinal fasciculus
--> |
medial rectus palsy
on attempted lateral gaze nystagmus in abducting eye |
|
|
|
what is normal in MLF lesion?
|
convergence
|
|
|
|
internuclear ophthalmoplegia is lesion of _
and it's seen in _ |
medial longitudinal fasciculus
multiple sclerosis |
|
|
|
looking to the left done by a patient with right MLF damage
--> |
patient's right eye doesn't adduct
patient's left eye abducts but has right-beating nystagmus |
|

