![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
209 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
epithelial cell junctions
|
zona occludens
zona adherens macula adherens gap junction hemidesmosome |
|
|
tight junction aka
|
zona occludens
|
|
|
zona occludens aka
|
tight junction
|
|
|
zona adherens aka
|
intermediate junction
|
|
|
intermediate junction aka
|
zona adherens
|
|
|
macula adherens aka
|
desmosome
|
|
|
desmosome aka
|
macula adherens
|
|
|
zona occludens aka
role composition |
tight junction
prevents diffusion across paracellular space claudins occludins |
|
|
zona occludens proteins
|
claudins
occludins |
|
|
zona adherens aka
proteins |
intermediate junction
cadherins connect to actin |
|
|
cadherins are __
|
calcium-depdendent adhesion molecules
|
|
|
cadherins are __
|
calcium-depdendent adhesion molecules
|
|
|
cadherins are __
|
calcium-depdendent adhesion molecules
|
|
|
cadherins are __
|
calcium-depdendent adhesion molecules
|
|
|
macula adherens aka
proteins |
desmosome
cadherins link cells desmoplakin keratin (intermediate filaments) |
|
|
macula adherens aka
proteins |
desmosome
cadherins link cells desmoplakin keratin (intermediate filaments) |
|
|
macula adherens aka
proteins |
desmosome
cadherins link cells desmoplakin keratin (intermediate filaments) |
|
|
pemmphigus vulgaris pathophys in 1 phrase
|
autoantibodies against desmosome
|
|
|
gap junction allows adjacent cells to communicate for ...
|
electric and metabolic functions
|
|
|
cadherins are __
|
calcium-depdendent adhesion molecules
|
|
|
macula adherens aka
proteins |
desmosome
cadherins link cells desmoplakin keratin (intermediate filaments) |
|
|
pemmphigus vulgaris pathophys in 1 phrase
|
autoantibodies against desmosome
|
|
|
pemmphigus vulgaris pathophys in 1 phrase
|
autoantibodies against desmosome
|
|
|
what causes the unhappy triad knee injury?
|
football
force from the lateral side |
|
|
gap junction protein
|
connexon (forms a channel)
|
|
|
what causes the unhappy triad knee injury?
|
football
force from the lateral side |
|
|
pemmphigus vulgaris pathophys in 1 phrase
|
autoantibodies against desmosome
|
|
|
gap junction allows adjacent cells to communicate for ...
|
electric and metabolic functions
|
|
|
gap junction allows adjacent cells to communicate for ...
|
electric and metabolic functions
|
|
|
macula adherens aka
proteins |
desmosome
cadherins link cells desmoplakin keratin (intermediate filaments) |
|
|
gap junction protein
|
connexon (forms a channel)
|
|
|
pemmphigus vulgaris pathophys in 1 phrase
|
autoantibodies against desmosome
|
|
|
autoantibodies against desmosome --->
against hemidesmosome --> |
pemphigus vulgaris
bullous pemphigoid |
|
|
autoantibodies against desmosome --->
against hemidesmosome --> |
pemphigus vulgaris
bullous pemphigoid |
|
|
pemphigus vulgaris vs.
bullous pemphigoid pathophys |
autoantibodies:
against desmosome against hemidesmosome |
|
|
gap junction allows adjacent cells to communicate for ...
|
electric and metabolic functions
|
|
|
integrin role
|
maintains "integrity" of BM
binds to laminin in BM |
|
|
gap junction allows adjacent cells to communicate for ...
|
electric and metabolic functions
|
|
|
unhappy triad/knee injury (3)
|
medial collateral ligament
anterior cruciate ligament lateral meniscus |
|
|
pemmphigus vulgaris pathophys in 1 phrase
|
autoantibodies against desmosome
|
|
|
what causes the unhappy triad knee injury?
|
football
force from the lateral side |
|
|
gap junction protein
|
connexon (forms a channel)
|
|
|
anterior and posterior in ACL and PCL refer to...
|
sites of tibial attachment
|
|
|
pemphigus vulgaris vs.
bullous pemphigoid pathophys |
autoantibodies:
against desmosome against hemidesmosome |
|
|
_ indicates torn ACL
_ indicates torn MCL |
positive anterior drawer sign
abnormal passive abduction |
|
|
_ indicates torn ACL
_ indicates torn MCL |
positive anterior drawer sign
abnormal passive abduction |
|
|
_ indicates torn ACL
_ indicates torn MCL |
positive anterior drawer sign
abnormal passive abduction |
|
|
_ indicates torn ACL
_ indicates torn MCL |
positive anterior drawer sign
abnormal passive abduction |
|
|
abnormal passive abduction indicates _
|
a torn MCL
|
|
|
abnormal passive abduction indicates _
|
a torn MCL
|
|
|
abnormal passive abduction indicates _
|
a torn MCL
|
|
|
abnormal passive abduction indicates _
|
a torn MCL
|
|
|
positive anterior drawer sign indicates
|
torn ACL
|
|
|
positive anterior drawer sign indicates
|
torn ACL
|
|
|
positive anterior drawer sign indicates
|
torn ACL
|
|
|
pemphigus vulgaris vs.
bullous pemphigoid pathophys |
autoantibodies:
against desmosome against hemidesmosome |
|
|
what causes the unhappy triad knee injury?
|
football
force from the lateral side |
|
|
positive anterior drawer sign indicates
|
torn ACL
|
|
|
integrin role
|
maintains "integrity" of BM
binds to laminin in BM |
|
|
besides an epidural, to relieve pain of delivery...
|
pudendal nerve block
|
|
|
besides an epidural, to relieve pain of delivery...
|
pudendal nerve block
|
|
|
besides an epidural, to relieve pain of delivery...
|
pudendal nerve block
|
|
|
besides an epidural, to relieve pain of delivery...
|
pudendal nerve block
|
|
|
autoantibodies against desmosome --->
against hemidesmosome --> |
pemphigus vulgaris
bullous pemphigoid |
|
|
landmark for pudendal nerve block
|
ischial spine
|
|
|
landmark for pudendal nerve block
|
ischial spine
|
|
|
landmark for pudendal nerve block
|
ischial spine
|
|
|
landmark for pudendal nerve block
|
ischial spine
|
|
|
pemphigus vulgaris vs.
bullous pemphigoid pathophys |
autoantibodies:
against desmosome against hemidesmosome |
|
|
integrin role
|
maintains "integrity" of BM
binds to laminin in BM |
|
|
pemphigus vulgaris vs.
bullous pemphigoid pathophys |
autoantibodies:
against desmosome against hemidesmosome |
|
|
unhappy triad/knee injury (3)
|
medial collateral ligament
anterior cruciate ligament lateral meniscus |
|
|
integrin role
|
maintains "integrity" of BM
binds to laminin in BM |
|
|
unhappy triad/knee injury (3)
|
medial collateral ligament
anterior cruciate ligament lateral meniscus |
|
|
cadherins are __
|
calcium-depdendent adhesion molecules
|
|
|
what causes the unhappy triad knee injury?
|
football
force from the lateral side |
|
|
unhappy triad/knee injury (3)
|
medial collateral ligament
anterior cruciate ligament lateral meniscus |
|
|
integrin role
|
maintains "integrity" of BM
binds to laminin in BM |
|
|
what causes the unhappy triad knee injury?
|
football
force from the lateral side |
|
|
macula adherens aka
proteins |
desmosome
cadherins link cells desmoplakin keratin (intermediate filaments) |
|
|
unhappy triad/knee injury (3)
|
medial collateral ligament
anterior cruciate ligament lateral meniscus |
|
|
_ indicates tearing of ACL
|
anterior drawer sign
|
|
|
_ indicates torn MCL
|
abnormal passive abduction
|
|
|
__ causes unhappy triad knee injury
|
football. force from the lateral side
|
|
|
anterior and posterior in ACL and PCL refer to _
|
sites of tibial attachment
|
|
|
besides epidural, think of _ nerve block to relieve pain of delivery
|
pudendal nerve block
|
|
|
pudendal nerve block landmark
|
ischial spine
|
|
|
pitching injury think _
|
infraspinatus
|
|
|
upper trunk is lesioned by _
|
trauma
|
|
|
C7 root is lesioned by _
|
cervical disk lesion
|
|
|
cause of lower trunk injury
|
cervical rib
pancoast tumor of lung |
|
|
lower trunk injury leads to _
|
klumpke's palsy
|
|
|
radial nerve injury. what causes it?
(3) |
compressed in axilla by a crutch
in spiral groove: midshaft fracture of humerus deep branch below elbow: stretched by subluxation of radius |
|
|
axillary nerve injury:
cause? |
fracture of surgical neck
humerus dislocation intramuscular injections |
|
|
median nerve injuries
|
recurrent branch: superficial laceration
at elbow: --supracondylar fracture of humerus --pronator teres syndrome at wrist, compressed in --carpal tunnel syndrome --dislocated lunate |
|
|
ulnar nerve injuries
|
elbow:
--repeated minor trauma --humerus medial epicondyle fracture hand: --trauma to heel of hand --fracture of hook of hamate |
|
|
fracture of hook of hamate may injure _ nerve
|
ulnar nerve
|
|
|
dislocated lunate may injure _ nerve
|
median nerve
|
|
|
fracture of medial epicondyle of humerus may injure
|
ulnar nerve
|
|
|
supracondylar fracture of humerus may injure
|
median nerve
|
|
|
subluxation of radius may injure
|
deep branch of radial nerve
(a little below elbow) |
|
|
_ thenar muscle is innervated by ulnar
|
adductor pollicis
|
|
|
_ branch of median nerve that does not go through the carpal tunnel
_ branch of median nerve that innervates thenar muscles |
palmar cutaneous branch
recurrent branch |
|
|
waiter's tip is aka
|
erb's palsy
|
|
|
total claw hand is aka
|
klumpke's palsy
|
|
|
klumpke's palsy is aka
|
total claw hand
|
|
|
erb's palsy is aka
|
waiter's tip
|
|
|
upper trunk injury -->
|
waiter's tip (Erb's palsy)
|
|
|
lower trunk injury -->
|
total claw hand (Klumpke's palsy)
|
|
|
injury of posterior cord of brachial plexus -->
|
wrist drop
|
|
|
injury of long thoracic nerve -->
|
winged scapula
|
|
|
injury of axillary nerve-->
|
deltoid paralysis
|
|
|
injury of radial nerve -->
|
saturday night palsy (wrist drop)
|
|
|
injury of musculocutaneous -->
|
difficulty flexing elbow
variable sensory loss |
|
|
injury of median nerve -->
|
v thumb function ("ape hand")
|
|
|
injury of ulnar nerve -->
|
intrinsic muscles of hand
claw hand ("Pope's blessing") |
|
|
axillary
radial median ulnar musculocutaneous what C levels? |
56
58 61 81 57 |
|
|
axillary c levels
|
56
|
|
|
radial c levels
|
58
|
|
|
median c levels
|
61
|
|
|
ulnar c levels
|
81
|
|
|
musculocutaneous c levels
|
57
|
|
|
saturday night palsy is __
affects what nerve? |
extended compression of axilla by back of chair or crutches
affects radial nerve |
|
|
median motor deficits
proximal lesion distal lesion |
lateral finger flexion
wrist flexion opposition of thumb |
|
|
median sensory deficit
proximal lesion vs distal lesion |
both:
dorsal and palmar aspects of lateral 3 1/2 fingers proximal: also includes thenar eminence |
|
|
ulnar nerve distal lesion is __
occurs how? |
fracture of hook of hamate
falling onto outstretched arm |
|
|
ulnar nerve proximal lesion
motor deficit |
medial finger flexion
wrist flexion |
|
|
lateral finger flexion
medial finger flexion what nerve deficit? |
median nerve, proximal lesion
ulnar nerve, proximal lesion |
|
|
wrist flexion is affected by what nerve lesion?
|
proximal lesion of either median or ulnar
|
|
|
ulnar nerve distal lesion lesion
motor deficit |
interossei
--abduction of fingers --adduction of fingers adductor pollicis lumbricals --extension of 4th and 5th fingers |
|
|
musculocutaneous nerve is injured how?
|
upper trunk compression
|
|
|
musculocutaneous lesion
motor deficit |
bicepts
brachialis coracobrachialis |
|
|
ulnar nerve proximal lesion
sign |
radial deviation of wrist upon wrist flexion
|
|
|
ulnar nerve distal lesion
|
ulnar claw hand (when asked to straighten fingers)
aka Pope's blessing |
|
|
waiter's tip is caused by what injury?
how? |
upper trunk injury 2^
blow to shoulder trauma during delivery |
|
|
waiter's tip findings
|
limb hangs by side
(paralysis of abductors) mediallly rotated (paralysis of lateral rotators) forearm is pronated (loss of biceps) |
|
|
thoracic outlet syndrome is _
|
cervical rib
compress subcclavian artery and inferior trunk |
|
|
thoracic outlet syndrome features
|
atrophy
--thenar and hypothenar --interossei sensory deficits medial side of forearm and hand moving head toward a side--> disappearance of radial pulse |
|
|
distortions of the hand:
4 types |
ulnar claw
median claw "ape hand" klumpke's total claw |
|
|
lumbricals action
|
flex MCP joints
extend DIP and PIP joints |
|
|
ulnar claw
|
distal ulnar nerve lesion-->
loss of medial lumbrical fxn 4th and 5th digits are clawed (cannot extend them) |
|
|
pope's blessing is seen when?
|
distal ulnar nerve lesion (4th and 5th fingers clawed) when trying to extend the hand
or making fist with proximal median nerve lesion (can't flex lateral digits) |
|
|
median claw
|
distal median nerve lesion
loss of lateral lumbrical function 2nd and 3rd digits are clawed (cannot extend) |
|
|
"ape hand"
|
proximal median nerve lesion
loss of opponens pollicis function unopposable thumb |
|
|
klumpke's total claw
|
lesion of lower trunk -->
loss of function of all lumbricals leaving forearm finger flexors and finger extensors unopposed |
|
|
long thoracic nerve c___
|
57
|
|
|
thenar muscles innervated by median nerve
hypothenar muscles innervated by ulnar nerve |
opponens pollicis
abductor pollicis brevis flexor pollicis brevis opponens digiti minimi abductor digiti minimi flexor digiti minimi |
|
|
dorsal interossei vs. palmar inerossei do what?
|
dorsal abduct D AB
palmar adduct P AD |
|
|
lumbricals do what?
|
flex at the MCP joint
|
|
|
golf elbow is where?
tennis elbow is where? |
medial epicondylitis
lateral epicondylitis |
|
|
lower extremity nerves LS
|
obturator: 24
femoral: 24 common peroneal: 42 tibial: 42 superior gluteal: 41 inferior gluteal: 52 |
|
|
obturator LS
|
24
|
|
|
femoral LS
|
24
|
|
|
common peroneal LS
fibial LS |
42
42 |
|
|
superior gluteal
inferior gluteal LS |
41
52 |
|
|
obturator nerve
cause of injury |
anterior hip dislocation
|
|
|
femoral nerve cause of injury
|
pelvic fracture
|
|
|
common peroneal nerve
cause of injury |
trauma to lateral leg
or fibula neck fracture |
|
|
tibial nerve
cause of injury |
knee trauma
|
|
|
superior gluteal
cause of injury |
posterior hip dislocation
polio |
|
|
inferior gluteal
cause of injury |
posterior hip dislocation
|
|
|
posterior hip dislocation can injure _ nerve
|
superior gluteal
inferior gluteal |
|
|
obturator nerve
motor deficit |
thigh adduction
|
|
|
common peroneal LS
fibial LS |
42
42 |
|
|
superior gluteal
inferior gluteal LS |
41
52 |
|
|
obturator nerve
cause of injury |
anterior hip dislocation
|
|
|
femoral nerve cause of injury
|
pelvic fracture
|
|
|
common peroneal nerve
cause of injury |
trauma to lateral leg
or fibula neck fracture |
|
|
tibial nerve
cause of injury |
knee trauma
|
|
|
superior gluteal
cause of injury |
posterior hip dislocation
polio |
|
|
inferior gluteal
cause of injury |
posterior hip dislocation
|
|
|
posterior hip dislocation can injure _ nerve
|
superior gluteal
inferior gluteal |
|
|
obturator nerve
motor deficit |
thigh adduction
|
|
|
femoral nerve
motor deficit |
thigh flexion
leg extension |
|
|
common peroneal nerve
motor deficit |
foot eversion and dorsiflexion
toe extension foot drop foot slap steppage gait |
|
|
tibial nerve
motor deficit |
foot inversion and plantarflexion
toe flexion |
|
|
foot inversion is by
foot eversion is by |
tibial
common peroneal |
|
|
superior gluteal motor deficit
|
thigh abduction
|
|
|
trendelenburg sign is __
indicates injury to _ nerve |
hip drops when standing on opposite foot
deficit in thigh abduction due to superior gluteal nerve injury |
|
|
inferior gluteal nerve
motor deficit |
can't jump
climb stairs rise from seated position push inferiorly (downward) |
|
|
obturator nerve
sensory deficit |
medial thigh
|
|
|
femoral nerve
sensory deficit |
anterior thigh
medial leg |
|
|
common peroneal nerve
sensory deficit |
anterolateral leg
dorsal foot |
|
|
tibial nerve
sensory deficit |
sole of foot
|
|
|
mnemonic for peroneal
|
PED
Peroneal Everts and Dorsiflexes if injured, foot dropPED |
|
|
dorsiflexion =
|
extend foot
|
|
|
mnemonic for tibial nerve
|
TIP
Tibial Inverts and Plantarflexes if injured, can't stand on TIPtoes |
|
|
sciatic nerve LS
|
42
|
|
|
sciatic nerve splits into _ nerves
|
common peroneal
tibial |
|
|
muscle contraction:
nerve steps |
1. action potential depolarization opens Ca++ channels
--> neurotransmitter release 2. postsynaptic ligand binding --> muscle cell depolarization in motor end plate depolarization travels down the T-tubule |
|
|
muscle contraction:
depolarization of the T tubule then what? (till calcium is released) |
4. depolarization of voltage sensitive dihydropyridine receptor
coupled to the ryanodine receptor on the sarcoplasmic reticulum --> Ca++ release from SR |
|
|
once calcium is released from the SR... then
|
5. Ca++ binds troponin C -->
conformational change that moves tropomyosin out of the myosin-binding groove on actin filaments myosin releases bound ADP and is displaced on the actin filament (power stroke) |
|
|
muscle contraction results in shrinkage of _ but not _
|
H zone and I band
not A band (A band is Always the same length) |
|
|
sarcomere =
|
z line to z line
|
|
|
sarcomere
|
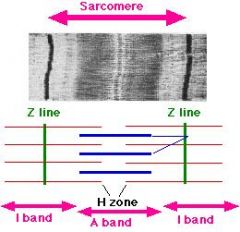
|
|
|
3 sizes of muscle "fibers"
|
fascicle
fiber myofiber |
|
|
type 1 vs. type 2 muscle fibers
|
"One Slow Red Ox"
type 1 --slow twich --red ^ mitochondria ^ myoglobin for oxidative phosphorylation type 2 --fast twitch --white v mitochondria v myoglobin because ^ glycolysis |
|
|
myosin power stroke state... then what?
|
ADP release,
ATP binding--> release of actin ffilament, allowing cross-bridge cycling and shortening to occur |
|
|
myosin...
hydrolysis of ATP --> |
moves the myosin head into cocked state
|
|
|
4 states of muscle contraction
|
1. cocked state (caused by ATP hydrolysis)
Ca++ facilitates (2) 2. cross-bridged state (bound to filament) 3. power stroke state (then releases ADP) 4. released state (has ATP) |
|
|
Ca++'s crucial role in muscle contraction
|
binds troponin C -->
conformational change that moves tropomyosin out of the myosin-binding groove on actin filaments |
|
|
smooth muscle contraction
|
action potential
smooth muscle membrane depolarization voltage gated Ca++ channels open ^ Ca++ in cytoplasm Ca++ binds calmodulin activates myosin light-chain kinase (MLCK) |
|
|
smooth muscle contraction apparatus
|
myosin light chain kinase MLCK -->
myosin P + actin = cross bridge formation with contraction |
|
|
smooth muscle relaxation apparatus
|
myosin light chain phosphatase -->
myosin + actin --> relaxation |
|
|
how does nitric oxide cause smooth muscle relaxation?
|
NO -->
guanylate cyclase --> cGMP --> inhibition of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) |
|
|
endochondral ossification
|
cartilaginous model is first made by chondrocytes
osteoclasts and osteoblasts later replace with woven bone and remodel to lamellar bone |
|
|
membranous ossification involves what bones?
|
skull
facial bones axial skeleton |
|
|
axial skeleton
|

|
|
|
membranous ossification
|
woven bone formed directly, without cartilage
later remodeled to lamellar bone |

