![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Requires special charcoal containing medium for growth. Uses silver staining and DFA techniques. Requires L-cysteine for it to grow on a medium.
|
Legionella pneumophila
|
|
|
Francisella, brucella, legionella, and pasteurella.
|
bacteria requiring cysteine for growth
|
|
|
usually a waterborne pathogen
|
Legionella pneumophila
|
|
|
headache, dry cough, 25% of cases have abdominal symptoms (diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting)
|
Legionnaires disease
|
|
|
how does L. pneumophila invade macrophages?
|
2 ways: 1) Porins on the surface of L. pneumophila bind with C3b (which aids in phagocytosis) allowing the cell to go undetected into the macrophage. 2) L. pneumophila has a surface protein named Macrophage invasion potentiator (Mip) which aids in entry into the macrophages.
|
|
|
best diagnostic tools: DFA + BCYE culture; how effective is DFA by itself?
|
Legionnaires disease; not effective-- positive in only 25-50% culture positive cases.
|
|
|
how do you treat Legionnaires Disease?
|
erythromycin and rifampin
|
|
|
cough, low grade fever, medical student
|
Mycoplasmal pneumonia
|
|
|
Produces mulberry shaped colony in a sterile content media.
|
mycoplasma pneumoniae colony
|
|
|
14 weeks of shedding, cytadhesins, bronchial epithelial cells
|
mycoplasma pneumoniae
|
|
|
cold-agglutin test
|
diagnostic for mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
|
|
|
how do you treat m. pneumoniae pneumonia?
|
eryrthomycin and tetracycline or azithromycin and quinolones
|
|
|
#2 pathogen to cause pneumonia in alcoholics
|
klebsiella pneumonia
|
|
|
non-motile, large capsule, enterobacteria, mucoid colony
|
klebsiella pneumonia
|
|
|
jumping gene
|
Klebsiella pneumonia
|
|
|
Red gelantinous sputum
|
Klebsiella pneumonia
|
|
|
forms lung abscesses, interferes with phagocytosis, leaves residue behind on CT even after treatment
|
Klebsiella pneumonia
|
|
|
How do you treat Klesiella pneumonia?
|
Tx: ciprofloxacin or combo of cephalosporin and aminoglucosides.
|
|
|
Fruity odor and striking green color
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
oxidase positive distinguishing it from enterobacteriaceae
|
pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
alignate and mutates LPS and porin proteins
|
pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
Two most popular underlying diseases to contract p. aeruginosa
|
CF and burn victims.
|
|
|
what does alignate serve as?
|
microbial barrier
|
|
|
what is the tx for P. aeruginosa?
|
B-lactam antibiotics specifically anti-pseudomonal penicillins: carbenicillin, piperacillin, ticracillin.
|
|
|
#1 cause of PID
|
Chlamydia pneumoniae
|
|
|
has an elementary body as the infective form and a reticular body as the intracellular form.
|
Chlamydia
|
|
|
Tx for chlamydia pneumonia
|
Tx: macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin), tetracycline (doxycycline), and levofloxacin.
|
|
|
what pathogen is associated with atherosclerosis?
|
C. pneumoniae
|
|
|
spenomegaly, birds, and pneumonia
|
C. Psittaci
|
|
|
How do you tx: C. Psittaci Pneumonia?
|
Tx: macrolide and tetracycline.
|
|

What is the pathogen?
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
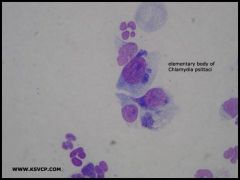
what is this? what pathogen does it belong to?
|
elementary body of C. psittaci
|
|

what is it? what pathogen does it belong to?
|
elementary bodies of Chlamydia pneumoniae
|
|

what is it? what kind of agar is it on?
|
Klebsiella Pneumoniae on Macconkey agar
|
|

what is it and what medium is it on?
|
L. pneumophila on BCYE agar
|
|

what is the name of this pathogen? what is it stained with?
|
L. pneumophila stained with Direct Flourescent antibody.
|
|

diagnosis
|
mycoplasma pneumonia pneumonia
|
|

what is this pathogen?
|
mycoplasma pneumoniae
|
|

what is this pathogen? where is it located?
|
P. aeruginosa in the blood
|

