![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
produces niacin, heat sensative catalase, non-white person
|
mycobacterium tuberculosis
|
|
|
Tb test came back positive about 11 mm, who is population probably made of?
|
IV drug abusers, people living in poverty or immigrants from high TB area
|
|
|
Tb test came back positive: 5 mm in size, who is the population made of?
|
HIV+ or anyone with recent TB exposure
|
|
|
Granuloma with central caseous necrosis
|
Tuberculosis Granuloma: primary tuberculosis
|
|
|
Granuloma without central caseous necrosis
|
Sarcodosis
|
|
|
Side effects:
Isoniazid |
peripheral neuropathy
|
|
|
Side effects:
Ethambutol |
eye complications
|
|
|
Side Effects:
pyrazinamide |
Orange Urine
|
|
|
Side Effects:
Rifampin |
Orange Urine, Hepatitis
|
|
|
Side Effects:
Streptomycin |
autotoxicity
|
|
|
photochromogenic; forms yellow pigmented colonies in the presence of light. Along with cough, fever, etc
|
Mycobacterium Kansasii
|
|
|
sx: progressive weight loss, night sweats, diarrhea
|
Mycobacterium Avium
|
|
|
Tx: MAC + ethambutol for AIDs patients with a CD of at least 50.
|
Mycobacterium Avium
|
|
|
produces yellow colonies in light or dark within 2 weeks. Common cause of granulomatous cervical lymphadenitis in kids.
|
Mycobacterium Scrofulaceum
|
|
|
chinese letter patterns, tinsdale agar and Loeffler’s serum.
|
corynebacterium diphtheriae
|
|
|
pseudomembrane- grayish white membrane
|
corynebacterium diphtheriae
|
|
|
Exotoxins inhibit the protein synthesis of the host cell and thereby causing death of the cells
|
corynebacterium diphtheriae
|
|
|
grows best on chocolate agar medium and satellite colony
|
Hemophilus influenza pneumonia
|
|
|
requires hematin (X factor) and NAD (nicotine adenamide diphosphate, V factor) for growth in culture
|
hemophilus influenza pneumonia
|
|
|
requires hematin (X factor) and NAD (nicotine adenamide diphosphate, V factor) for growth in culture
|
epiglottitis and pneumonia
|
|
|
tx: start with third generation cephalosporin, but usually already vaccinated against.
|
H. influenza
|
|
|
prevented by giving DTaP
|
whooping cough
|
|
|
Special charcoal medium, Regan-low
|
bordetella pertussis
|
|
|
what is this stage of whooping caugh called:
profuse and mucoid rhinorrhea for 1 to 2 weeks; most communicable at this stage. |
catarrhal- stage 1
|
|
|
what is this stage of whooping caugh called:
lots of coughing for 2-4 weeks, marked lymphocytosis |
Paroxysmal- stage 2
|
|
|
what is this stage of whooping caugh called:
coughing subsides |
convalescent- stage 3
|
|
|
Name the toxin and associated bacteria:
A-B toxin and has a binding component (B) and an active component (A)—increasing cAMP levels |
Pertussis toxin
B. Pertussis |
|
|
Name the toxin and its associated bacteria:
catalyzes the conversion of host cell ATP to cAMP increased cAMP levels (increased mucus production), |
Adenylate toxin
B. Pertussis |
|
|
Name the toxin and its associated bacteria:
fragment of cell wall peptidoglycan. Produces NO which causes death of ciliated cell. |
Tracheal cytotoxin
|
|
|
which toxin produces a cytokine that may cause fever? what cytokine is that?
|
Tracheal Cytotoxin; IL-1
|
|
|
during catarrhal phase, what medium is best to test for B. pertussis?
|
blood chocolate agar with cephalosporin (to inhibit growth of normal flora)
|
|
|
During paroxysmal phase, what is the best diagnostic test?
|
Direct flourescent antibody technique
|
|
|
what is the best treatment during catarrhal phase?
|
erythromycin or clarithromycin
|
|
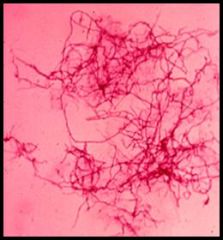
What kind of stain is this? what is it for?
|
AFB- for nocardia
|
|

what kind of stain is this and what is it identifying?
|
AFB and M. tuberculosis
|
|
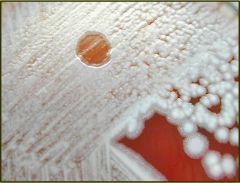
what is identified here?
|
bascillis anthracis
|
|
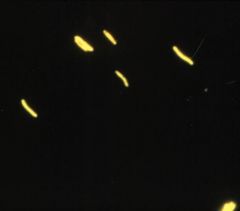
what kind of stain is this and what is it identifying?
|
Auramine Rhodamine staining; mycobacterium
|
|
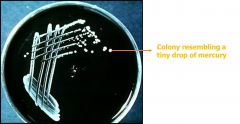
what kind of medium is this and what is it identifying?
|
chocolate agar; B. pertussis
|
|
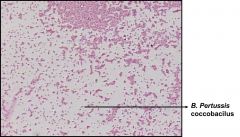
what kind of stain is this and what is it identifying?
|
Gram staining; B. pertussis
|
|

what kind of agar is this and what is it identifying?
|
Cysteine- Tellurite blood agar; Corynebacterium Diphtheriae
|
|
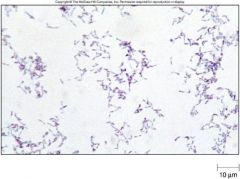
What is this?
|
Corynebacterium Diphtheria
|
|
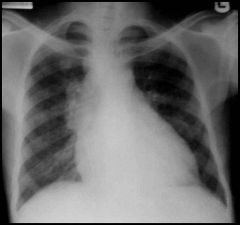
what is the diagnosis?
|
hilar lymphadenopathy
|
|
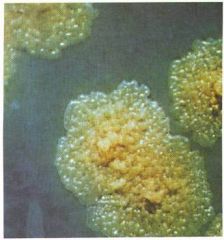
what kind of medium is this and what is it identifying?
|
Lowenstein- jensen; Mycobacterium tuberculosis
|
|
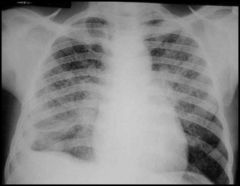
what is the diagnosis?
|
millary TB
|
|
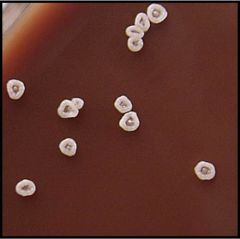
what kind of medium is this and what is it identifying?
|
Chocolate agar, norcadia asteroides
|
|
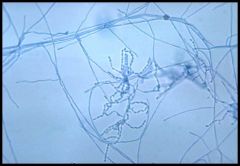
what kind of stain is this and what is it identifying?
|
Gram staining; nocardia
|
|
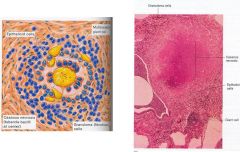
diagnosis
|
primary tuberculosis granuloma formation
|
|
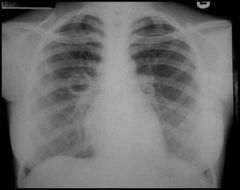
diagnosis?
|
Pulmonary TB with cavity formation
|
|
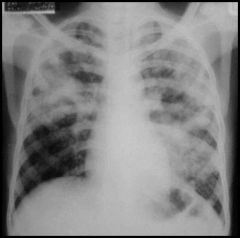
diagnosis?
|
pulmonary TB
|
|
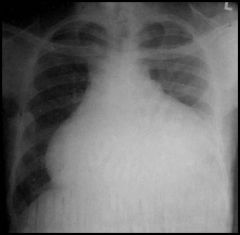
diagnosis
|
TB pericarditis
|
|
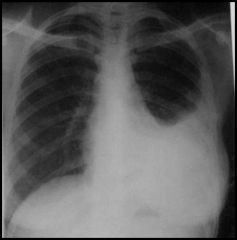
diagnosis?
|
Tuberculous plueral effusion
|

