![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Give 5 reasons why the body needs to produce energy |
- all forms of movement: skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle - moving ions and other molecules against their gradient - biosynthesis - waste disposal - heat-generation |
|
|
Summarise glycolysis |
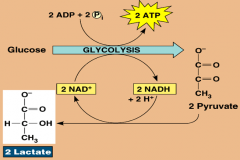
-occurs in the cytosol - glucose is used to produce pyruvate (anaerobic) or lactate (aerobic) - produces 4x ATP and 2x NADH (Nicotinamideadenine dinucleotide) -uses 2x ATP per glucose: net gain is 2x ATP |
|
|
Summarise the link reaction/beta oxidation |
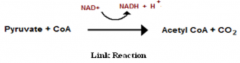
-pyruvate is transported from the cytosol into the mitochondrialmatrix
-pyruvates undergo decarboxylation and then dehydrogenation by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex – producing 1x CO2, 1x NADH and 1xAcetyl CoA -fatty acids can also be used and converted into Acetyl CoA –producing, per pyruvate, 1x Acetyl CoA, 1x NADH and 1x FADH2, also |
|
|
Summarise the citric acid/krebs cycle |
-occurs in the mitochondrial matrix-considered aerobic -begins with Acetyl CoA and ends with the regeneration of oxaloacetate -involves a series of redox(change in oxidation states), dehydration (removal of H2O), hydration(adding of H2O), and decarboxylation (removes carboxyl group)reactions. -products are 1x GTP, 3x NADH, 1x FADH2 and 2x CO2 -purpose is to produce electron carriers and recycle molecules |
|
|
Summarise the electron transport chain (oxidative phosphorylation) |
-occurs in inner membrane of the mitochondria-aerobic -NADH and FADH2 transfer electrons in a series of redox reactions toprotein complexes (I-IV) -hydrogen ions are pumped into the intermembrane space to create agradient -electrons flow back into the matrix through ATP synthase – a typeof motor which turns and produces ATP from ADP and Pi-reaction produces H20, CO2 and ~30 ATP |
|
|
What is an uncoupler? Give an example |
molecules which uncouple electron transport from ATP synthesis, by making the inner mitochondrial membrane permeable to H+. 2,4-dinitrophenol |
|
|
Describe the two reaction involved in protein metabolism |
transamination: conversion of one amino acid to another oxidative deamination: the amino group of an amino acid is lost as ammonia, which can then enter the urea cycle |
|
|
How do you calculate BMI? |
BMI = weight(kg)/height(metres)2 |
|
|
From earliest to latest, what are the major causes of fatigue? |
phosphocreatine depletion phosphocreatine depletion and proton accumulation proton accumulation glycogen depletion |

