![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
sx: fever, inflammatory edema of nasal mucosa, initially clear secretions.
|
rhinitis
|
|
|
|
sore throat, red and swollen pharynx, exudates and/or petechial hemorrhagic spots
|
pharyngitis and tonsillitis
|
|
|
|
sore throat, red and swollen pharynx, exudates and/or petechial hemorrhagic spots + vesicles and ulcers on pharyngeal mucosa.
what is the critter (s) that causes this? |
HSV and pharyngeal candidiasis
|
|
|
|
pseudomembrane in oral cavity.
what critter causes this? |
pharyngeal diphtheria
|
|
|
|
Multiple ulcers on oral mucosa extending to tongue lips and face.
|
stomatitis
|
|
|
|
single or multiple painful ulcers with irregular margin in the oral cavity. Recur in relation to stress, menses, local trauma and other non-specific stimuli.
|
aphthous stomatitis
|
|
|
|
severe gangrenous type of URTI that progresses beyond the mucus membrane to involve soft tissue, skin, and sometimes bone
|
Noma or cancrum oris
|
|
|
|
in what population is noma usually found?
|
immunocompromised
|
|
|
|
what is the etiology of noma?
|
fusobacterium, bacteroids, and p.aeruginosa
|
|
|
|
local pain (hard to swallow), tonsillar asymmetry with 1 tonsil usually displaced medially by the abscess
|
peritonsillar and retrotonsillar abcesses
|
|
|
|
what population is peritonsillar abscess most commonly found?
|
children above 5 years age and adults
|
|
|
|
Sx: pain, change in phonation, extended neck.
|
retropharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal abcesses
|
|
|
|
most commonly affect is infants and children under 5 years of age and may arise as a complication of pharyngitis.
|
retropharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
|
|
|
|
what do you always do first when presented with an abscess?
|
drain the abscess
|
|
|
|
what do you treat S. pyogenes infection with?
|
penicillin
|
|
|
|
how do you treat peritonsillar and retrotonsillar abscesses?
|
with antimicrobials
|
|
|
|
throat and neck pain, inspiratory stridor, muffled phonation, difficulty in swallowing.
|
epiglottitis.
|
|
|
|
fever, inspiratory stridor, hoarse phonation, harsh barking cough. (brassy cough).
|
laryngitis and croup
|
|
|
|
sputum and bubbling ronchi, cough, and fever
|
Bronchitis or tracheobronchitis
|
|
|
|
critters to blame for laryngitis and croup?
|
Viruses to blame: Parainfluenza viruses, influenza viruses, adenoviruses, and RSV
|
|
|
|
more common in people who have an underlying lung condition. Lack functional integrity and are susceptible to infections with members of oropharyngeal flora.
|
chronic bronchitis
|
|
|
|
two most common causes of chronic bronchitis
|
S. pneumonia and H. influenza
|
|
|
|
what is the main cause of acute bronchitis in kids?
|
B. pertusis
|
|
|
|
what is the appropriate medium for B. pertusis?
|
chocolate blood agar
|
|
|
|
what is the cut off point between URTI and MRTI?
|
epiglottis
|
|
|
|
3 ways a LRTI may result from
|
may result from aspiration of pathogens, hematogenous spread from a distant site, extension of MRTI.
|
|
|
|
fever, cough, productive purulent sputum.
|
acute pneumonia
|
|
|
|
what critter is to blame for 2/3 of community acquired pneumonia?
|
streptococcus P
|
|
|
|
what two pathogens cause acute pneumonia in immunocompromised individuals?
|
candida albicans and pneumocystis
|
|
|
|
what pathogen is #1 in AIDS patients for causing acute pneumonia?
|
pneumocystis
|
|
|
|
Sx: fever, night sweats, sleeplessness, dyspnea, sputum-long term.
|
chronic pneumonia
|
|
|
|
what are the two common pathogens for chronic pneumonia?
|
mycobacterium Tb and mycobacterium Nocardia
|
|
|
|
purulent infection of pleural space (either from infected lung or abdominal infection).
|
empyema
|
|
|
|
what pathogens cause empyema?
|
anaerobes and S. aureus
|
|
|
|
sx: fever, cough, foul-smelling sputum.
|
lung abscess
|
|
|
|
what does true sputum show?
|
an abundance of inflammatory cells and no squamous epithelial cells
|
|
|
|
what does saliva usually show?
|
squamous eipthelial cells and mixed bacterial population.
|
|
|
|
what is the causative organism for strep throat?
|
streptococcal pyogenes
|
|
|
|
a hazy zone with green discoloration around the colony-
name this -lysis |
alpha-hemolysis
|
|
|
|
Grows best in enriched media. Identified as a clear zone surrounding the colony.
|
B-hemolytic streptococci
|
|
|
|
Morphology: gram positive oval cells growing in chains. Non acid Fast, not spore forming, nonmotile
|
streptococcal pyogenes
|
|
|
|
what two pathogen categories produce superantigen? what does this cause?
|
staph and strep. Induces polyclonal T cell activation which leads to DIC, hypovolemia, MOF.
|
|
|
|
what is the bacitracin sensitive?
|
group A streptococcus
|
|
|
|
sx: strawberry tongue
|
scarlet fever
|
|
|
|
Result of infection with s. pyogenes strain that is itself infected with a bacteriophage.
|
scarlet fever
|
|
|
|
complication of untreated streptococcus pyogenes. Usually begins 3 weeks post infection.
|
rheumatic fever
|
|
|
|
Major criteria: carditis, arthritis, chorea, erythema marginatum.
|
rheumatic fever
|
|
|
|
what are the clinical values for ESR, CPR, and ASO for rheumatic fever?
|
Clinical values: Increased ESR, CPR, and ASO (antistreptolysine) titer.
|
|
|
|
how do you treat the infection, pain and inflammation, and chorea of rheumatic fever?
|
penicillin (ten day or single injection of Pencillin-G), aspirin for pain and inflammation, and diazepam or haloperidol for chorea.
|
|
|
|
what is a complication that may arise from S. pyogenes infection?
|
acute glomerulonephritis
|
|
|
|
Sx: runny nose, fever with shaking chills, sputum that is rust colored.
|
Pneumococcal pneumonia
|
|
|
|
what is the pathogen associated with alcohols who contract pneumococcal pneumonia? what type of pneumonia is presented here?
|
Streptococcus Pneumonia; lobar pneumonia
|
|
|
|
what is the #1 pathogen for adults that can cause meningitis?
|
S. pneumoniae
|
|
|
|
what medium is used to determine the pathogen associated with pneumococcal pneumonia? what is a rapid test that can be done?
|
optochin disc; bile solubility: clear is positive, cloudy is negative.
|
|
|
|
what is the tx for pneumococal pneumonia? what is the S. pneumoniae is resistant to all other antibiotics?
|
penicillin and its derivatives; use ketolides.
|
|
|
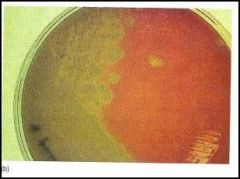
what type of hemolysis is this an example of?
|
alpha
|
|
|
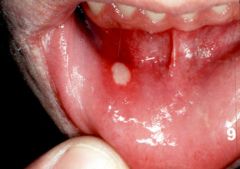
what is this an example of?
|
aphthous somatitis
|
|
|
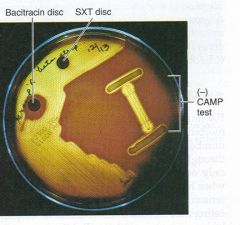
what is this test? what is it for?
|
Bacitracin sensitive; testing for Group A streptococcus
|
|
|

what type of hemolysis is this?
|
Beta
|
|
|
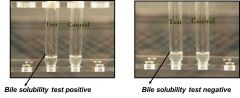
what will this test prove?
|
rapid test of pneumococcal pneumonia via Streptococcal pneumonia
|
|
|
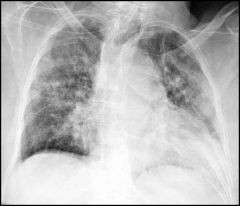
diagnosis?
|
bronchopneumonia
|
|
|

diagnosis?
|
Cancrum oris
|
|
|

what is this an example of?
|
GAS rapid method test
|
|
|
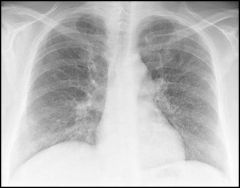
diagnosis?
|
interstitial pneumonia
|
|
|
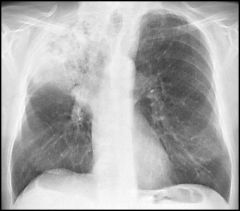
diagonsis?
|
lobar pneumonia
|
|
|
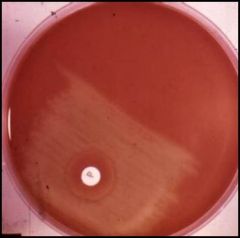
what is this disc? what is it testing for?
|
Optochic disc for s. pneumonia
|
|
|
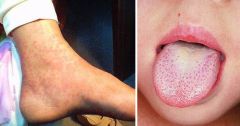
diagnosis
|
scarlet fever
|
|
|
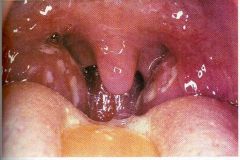
diagnosis?
|
streptococcal pharyngitis and tonsilitis
|
|
|
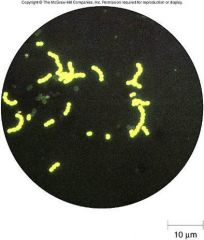
what is this a culture of?
|
streptococcal pyogenes
|
|
|
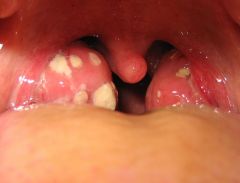
Sx: tonsillar asymmetry with one tonsil usually displaced medially by the abcess, can cause sever hemorrhage; local pain
|
peritonsillar and retrotonsillar abscesses
Next: common in ___. Most common bug |
children over 5
S pyogenes |

