![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Phylum Annelida
|

Segmented worms.
Specialized digestive & excretory system. |
|
|
Septa
|
In segmented worms, separate body segments.
|
|
|
Setae
|

Hair-like or hook-like extensions made of chitin.
|
|
|
Annelid classes
|
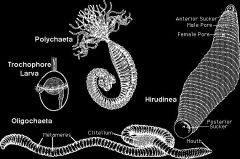
Class Oligochaeta.
Class Polychaeta. Class Hirudinea. |
|
|
Class Oligochaeta
|

Earthworms.
|
|
|
Class Polychaeta
|

Marine worms.
Most have complex segmentation, with parapodia & elaborate setea. |
|
|
Class Hirudinea
|
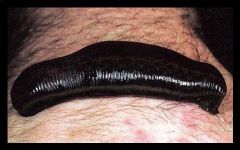
Leeches.
Mostly freshwater & terrestrial. Parasites that connect & extract blood with hirudin. Once common in medical treatment, still sometimes used. |
|
|
Hirudin
|
Anti-coagulate used to extract blood.
|
|
|
Phylum Arthropoda
|
Crabs, insects, spiders, centipedes, lobsters.
Nearly 1 Million species! |
|
|
Phylum Arthropoda Anatomy
|
Segmentation: head, thorax, abdomen.
Exoskeleton: protects & provides sites for muscle attachment. Jointed appendages: specialized for variety of uses. |
|
|
Arachnida
|
Spider, scorpions, ticks, horeshoe crabs.
Book lungs. |
|
|
Chelicerates
|
In Arachnida, fang-like chelicerae are modified appendages.
|
|
|
Insecta
|
Have many complex organ systems
|
|
|
Crustacea
|
Crabs, lobsters, shrimp, krill.
|
|
|
Phylum Echinodermata
|
Sea stars (asteroidea); brittle stars (ophiuridae); sea cucumbers, sea urchins.
Approx 7,000 species, all marine. |
|
|
Phylum Echinodermata Anatomy
|
Radial symmetry .
Water vascular system with tube feet. Some able to regenerate lost appendages. |

