![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what does xylem do?
|
assist in water going up
|
|
|
what does phloem do?
|
assist in sugar doing down
|
|
|
what is vascular tissue?
|
the plant tissue called xylem and phloem it is specialized for
the transport of water and nutrients |
|
|
example of a protected gamete in a land plant
|
pollen
|
|
|
what is the order for the origin of plants?
|
green algae
early vascular plants seed plants flowering plants |
|
|
what is charophytea?
|
green algae -- from paleozoic era
|
|
|
what are bryophytes?
|
mosses -- from paleozoic era
they have NO VASCULAR TISSUE |
|
|
what are ferns and horectalia?
|
early seedless vascular plants-- from paleozoic era
|
|
|
what are gymnosperms?
|
first seed plants (conifers) -- from paleozoic era
|
|
|
what are angiosperms?
|
flowering plants -- from the MESOZOIC era
|
|
|
what does moss need to live?
|
a wet habitat
|
|
|
Mosses lack these three things
|
vascular tissue
thick cuticle or stomata |
|
|
how do mosses reproduce?
|
male sperm swims from male gametophyte; therefore ...
no water, no swim, no mo' moss. |
|
|
what is the thallus?
|
main plant body o' moss
it's not organized into roots or shoots |
|
|
what food does the thallus look like?
|
corn flakes
|
|
|
who has sporangia?
|
both moss and ferns
|
|
|
how do liverworts (marchantia) reproduce?
|
sexually or asexually
|
|
|
3 examples of seedless vascular plants?
|
ferns
club mosses horsetail |
|
|
what are the three most important things that seedless vascular plants have?
|
vascular tissue
lignified tissue depend on water for fertilization |
|
|
what are the most common and successful seedless vascular plants
|
ferns!
|
|
|
what are fronds?
|
leaves of ferns
|
|
|
what does sporangia do?
|
produce spores
|
|
|
what are sori?
|
spots on the bottom of ferns that contain the sporangia
|
|
|
what's a rhizome?
|
a fern root--
it's like a stem, runs along/under ground |
|
|
what are carboniferous forests?
|
vast swamp eras in the paleozoic era
now they are coal! |
|
|
what happens when coal is burned?
|
carbon is released into the atmosphere as CO2
contributes to greenhouse effect |
|
|
what types of plants dominate most landscapes?
|
seed plants
|
|
|
what did pollen eliminate the need for?
|
water for fertilization
|
|
|
what are the two groups of plants?
|
gymnosperms and angiosperms
|
|
|
what kind of seed do gymnosperms have?
|
naked
|
|
|
what are conifers?
|
cone bearing plants-- evergreens
|
|
|
what are needle-shaped leaves adapted for?
|
dry conditions
|
|
|
what are three types of conifers?
|
redwoods
Bristlecone (Methusaleh is 4600 y. old) Pacific Yew (Taxol used for breast cancer treatment) |
|
|
two other gynosperms
|
cycads- palm-like
ginko biloba |
|
|
tell me about ginko biloba
|
it is a common city tree
smelly female treees-- better to plant males |
|
|
what is coevolution?
|
when two species evolve to benefit each other mutually-- mutualism
|
|
|
what is mutualism?
|
both benefit
|
|
|
how did insects coevolve with flowers?
|
they see yellow and blue flowers
|
|
|
how did birds coevolve with flowers?
|
they see red flowers and use tubular shapes or strong landing platforms for their beaks
|
|
|
how did moths coevolve with flowers?
|
they see white flowers
|
|
|
why do angiosperms produce fruits and flowers?
|
they help them reproduce
it is an evolutionary adaptation |
|
|
what are the major parts of a flower's anatomy?
|
anther, carpel, ovule, petal
pollen sepal stamen |
|
|
what does the flower's anther do?
|
produce pollen
|
|
|
what is the stigma
|
pollen tube
|
|
|
examples of flowers made up of many flowers
|
dandelion, sunflower
|
|
|
what phylum are angiosperms?
|
anthophyta
|
|
|
how do conifers limit self-pollination?
|
the male have cones are on the outside
the female have cones on inside |
|
Five qualities of dinoflagellates
|
1. Unicellular,
2. marine, 3. flagella, 4. toxins, 5. red tides (blooms) |
|
|
1.All live in water,
2.auto or heterotroph, 3.uni or multicellular, 4. sessile or motile 5. free or parasite, 6. 60,000 species |
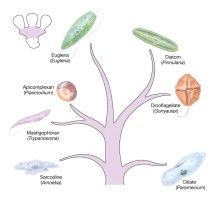
6 qualities of kingdom protista
|
|
|
Stuff a paramecium has
|
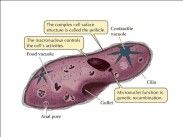
Anal pore,
food vacuole, contractile vacuole, macro and micronucleus, pellicle, gullet, trichocysts CILIA! |
|
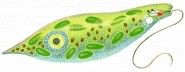
Euglena!
|
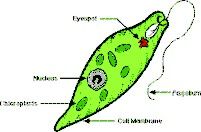
Motile (swims w/flagella)
photosynthetic, photoautotroph or heterotroph (mixotroph |
|
|
PSP—Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning
|

What can the bioaccumulation of dinoflagellates in shellfish cause?
|
|
|
Many genera produce toxins, may become abundant (bloom/red tide), can harm fish and people
|

Why dinoflagellate is called terrible
|
|
|
Can dinoflagellates do any good in the world? If so, what?
|

They can light up surface water! Bioluminescence!
|
|
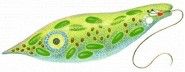
Stuff inside the wild Euglena!
|
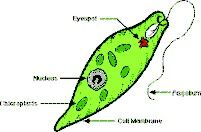
Flagellum, nucleolus, nucleus, chloroplasts, stored polysaccharaides from photosynthesis, contractile vacuole, photoreceptor, pigment shield
|
|
|
Three bad protests!
|
Plasmodium, giardia, trypanosoma
|
|
|
2.3 billion at risk; 3-500 million infected; 120 million cases; 1.5- 3 million die (one child every 20 sec)
|
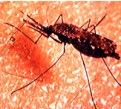
The tragedy of malaria
|
|
|
Furry animal-like protests
|

Ciliates
|
|
|
Extremely cool diatom qualities
|

Unicellular, marine, SILICA FRUSTULES!
|
|

Trypanosoma
|

Protist carried by tsetse fly, causes African sleeping sickness
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|

If dinoflagellates build up in shellfish like oysters, clams, and muscles, what is it called?
|
|
|
5 qualities of protozoa
|

Animal-like protests; unicellular; heterotrophic; free living or parasites; motile
|
|
|
Unicellular, multicellular or colonial; autotrophic; plant-like protests
|

3 qualities of algae in general
|
|
|
Example of a ciliate
|
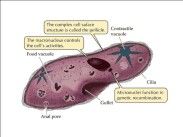
Paramecium
|
|
|
Diatoms and dinoflagellates are both:
|
Phytoplankton; unicellular; photoautotrophs; marine; algae
|
|
|
Two important phytoplankton
|
Diatoms and dinoflagellates
|
|
|
Four kingdoms of domain eukaryia
|
Protista, plantae, fungi, animalia
|
|
|
Asexually
|
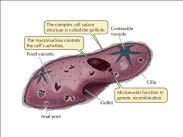
How do paramecium reproduce?
|
|
|
Flagellated protist of malaria
|

Plasmodium
|
|
|
Intestinal parasite protist from contaminated water, ingested in cyst stage
|
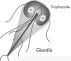
Giardia
|
|
|
4 things an amoeba has
|
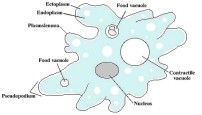
Plasma membrane, plasmagel, plasmasol, pseudopod
|
|
|
How amoebas eat
|
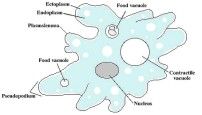
Phagocytosis
|
|
|
Whassa pseudopod?
|
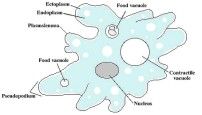
What amoeba uses to move
|
|
|
Malaria vector
|
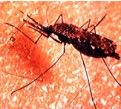
Anapholes mosquito
|
|
|
Algae seaweed types
|
Brown – phaeophyta
Red- rhodophyta Green- chlorophyta |
|
|
7500 species
uni & multicellular filamentous colonial (volvox) or sheet like (ulva) |

Chlorophyta (green) algae
|
|
|
Deep water
Warmer water People eat it—Nori, sushi seaweed! |

Rhodophyta (red)
|
|
|
Cold water kelp, rock weed (focus)
|

Phaephyta (brown)seaweed
|

