![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
GFR measure by ?
|
Inulin clearance
|
|
|
INULIN is renally Filtered, Reabsorbed, or Secreted?
|
only Filtered
|
|
|
GFR decrease causes what serum concentration changes?
|
BUN increase
Creatinine increase |
|
|
In Pre-Renal Azotemia, what is the ratio of BUN:Creatinine?
What does this ratio imply? |
> 20:1
implies decreased GFR |
|
|
Aging causes what changes to GFR?
This change in GFR causes what changes to serum [creatinine]? |
Aging decreases GFR
[Creatinine] unchanged due to decrease in muscle mass. |
|
|
GFR implies the Filtration across what?
|
Glomerular Capillaries
|
|
|
What is the driving force for GFR?
|
Net Ultrafiltration Pressure
(across glomerular capillaries) |
|
|
Filtration Fraction (FF) is the fraction of ____ across _________.
|
Renal Plasma Flow (RPF)
Glomerular capillaries |
|
|
FF equation ?
FF is normally what numerical value? |
= GFR / RPF
~ = 0.2 |
|
|
If the FF is 0.2, then what does that mean?
What happens to the 0.8 part? What does 0.8 part become? |
0.2 = 20% RPF filtered across GC
0.8 = 80% RPF leaves GC via EA Then becomes the PTCC (PTCC = PeriTubular Capillary Circulation) |
|
|
Increased FF means what for the RPF in the PTCC?
(causing what concentration change) What does this ultimately cause physiologically & where? |
Less RPF to the PTCC (via EA)
(thus increasing [protein] in PTCC) Increased Reabsorption @ PT |
|
|
Decreased FF means what for the RPF in the PTCC?
(causing what concentration change) What does this ultimately cause physiologically & where? |
More RPF to the PTCC (via EA)
(thus decreasing [protein] in PTCC) Decreased Reabsorption @ PT |
|
|
GFR equation in terms of Starlings
Renally, Filtration is always ______? |
Kf [(Pgc - Pbs) - (PPgc - PPbs)]
Favored |
|
|
Kf (Filtration Coefficient) is based on what structure?
|
Glomerular Capillary BARRIER
|
|
|
Glomerular Capillary Barrier is lined with what?
Why is this clinically significant? |
NEGATIVE Anion Glycoproteins
Plasma Proteins are also negatively charged, so they are restricted by the negative barrier. |
|
|
Loss of Negative charge (as seen in glomerular Dz's) on the glomerular capillary barrier manifests what Sign/Sx?
|
Proteinuria
|
|
|
Glomerular Capillary Hydrostatic Pressure (Pgc) is increased with what change to the AFFERENT Arteriole?
|
AA Dilation
(thus increasing GFR) |
|
|
Glomerular Capillary Hydrostatic Pressure (Pgc) is increased with what change to the EFFERENT Arteriole?
|
EA Constriction
(thus increasing GFR) |
|
|
Bowman's Space Hydrostatic Pressure (Pbs) increases with what vessel change?
(such change seen in what pathology?) |
Ureter Constriction
(as seen in Ureteral stones) |
|
|
What Starling variable is constant across the length of the glomerular capillary?
What Starling variable is increasing along the length of the glomerular capillary? why? |
Pgc (hydrostatic of GC)
PPgc (oncotic of GC) as more is filtrated out, the [protein] increases at capillary blood |
|
|
What Starling variable is usually ZERO?
|
Bowman's Space Oncotic Pressure (PPbs)
(b/c only small amt of protein is ever filtered) |
|
|
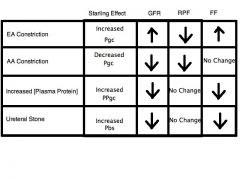
EA constriction (e.g. - via Angiotensin II) has what effect on (GC), GFR, RPF, and FF?
This FF change causes what @ PT? |
(Pgc increases, thus)
GFR increase RPF decrease thus FF increases Increases Reabsorption @ PT |
|
|
AA constriction (e.g. - via Angiotensin II) has what effect on (GC), GFR, RPF, and FF?
This FF change causes what @ PT? |
(Pgc decreases, thus)
GFR decrease RPF decreases also thus, FF UNCHANGED Reabsorption UNCHANGED @ PT |
|
|
Increased [Plasma Protein] has what effect on (Pressure), GFR, RPF, and FF?
This FF change causes what @ PT? |
(increases PPgc, thus)
GFR decreases RPF UNCHANGED thus FF decreases Decreases Reabsorption @ PT |
|
|
Ureteral Stones has what effect on (Pressure), GFR, RPF, and FF?
This FF change causes what @ PT? |
(Increases Pbs, thus)
GFR decreases RPF UNCHANGED thus FF decreases Decreases Reabsorption @ PT |
|
|
Filtered Load = ?
|
GFR x [Plasma]
|
|
|
Excretion Rate = ?
|
Volume x [Urine]
|
|
|
Reabsorption rate = ?
|
Filtered Load - Excretion Rate
|
|
|
Secretion rate = ?
|
Excretion Rate - Filtered Load
|
|
|
Net Secretion criteria in terms of Filtered Load?
|
Filtered Load > Excretion Rate
|
|
|
Net Reabsorption criteria in terms of Filtered Load?
|
Filtered Load < Excretion Rate
|
|
|
GLUCOSE is Filtered, Reabsorbed, or Secreted?
|
Filtered and Reabsorbed
|
|
|
PAH is Filtered, Reabsorbed, or Secreted?
|
Filtered and Secreted
|
|
|
Glucose is reabsorbed via what mechanism?
where? |
Na+/Glucose COTransporter
PT |
|
|
PAH is secreted via what mechanism?
where? |
Carrier transporter
PT |
|
|
ALL glucose is reabsorbed if.....?
Thus, at this level, the excretion of glucose is? |
Plasma [Glucose] < 250 mg/dL
Zero excretion |
|
|
Na+/Glucose Cotransporter starts losing affinity for glucose when?
This point at which this starts to happen is called what? |
Plasma [Glucose] > 250 mg/dL
Threshold for glucose ( = 250 mg/dL) |
|
|
Glucose will CEASE to Reabsorb if...?
This point at which this starts to happen is called what? |
Plasma [Glucose] > 350 mg/dL
Transport Maximum (Tm) |
|
|
What is Splay?
(include specific numerical values) |
(shaded) Region of Glucose Reabsorption curve between Threshold (250 mg/dL) and Tm (350 mg/dL)
|
|
|
Once plasma glucose exceeds Tm, all additional increases in [Glucose] will ?
|
be excreted
|
|
|
SATURATION of Na+/Glucose Cotransporter occurs when plasma [Glucose] reaches what?
What is the value of this? |
Tm (Transport Maximum)
350 mg/dL |
|
|
PAH secretion occurs where on the renal tubules?
|
PT
|
|
|
Prior to PAH Tm, @ Low plasma [PAH], what character is the secretion rate?
|
Any increases in plasma [PAH] will also cause Secretion rate increases
|
|
|
Beyond PAH Tm, what is the character for PAH secretion rate?
|
No more secretion
(even with increased plasma [PAH]) |
|
|
|
|
|
Weak Acid excretion can be increased by?
|
Alkalinizing urine
|
|
|
Weak base excretion can be increased by?
|
Acidifying the urine
|
|
|
PAH excretion = ?
|
Filtration Load + Secretion
(rem: PAH is Filtered & Secreted) |
|
|
Once the Tm for PAH is exceeded, the Excretion slope = ?
|
Filtration slope
|

