![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the 3 ways we take up glucose from the blood stream (think tissue and think receptor):
1. 2. 3. |
1. glut 1 & 3 (rbc & brain)
2. glut 2 (liver) 3. glut 4 (muscle/adipose) |
|
|
which of the glucose transport proteins are non-hormonal responsive:
|
glut 1 & 3
|
|
|
which of the glucose transport proteins are the sensors:
|
glut 2
|
|
|
which of the glucose transport proteins are:
1. high affinity 2. low affinity |
1. glut 4
2. glut 2 |
|
|
1. high Km =
2. low Km = |
1. low affininty
2. high affinity |
|
|
what is normal blood fasting glucose:
|
80-90 mg/dl
|
|
|
glycogen stores serve different funcitons in the muscle and liver, what are they:
1. muscle 2. liver |
1. fuel source
2. source of blood glucose |
|
|
what is glycogenolysis:
|
break down of glycogen
|
|
|
which of the glucose transporter proteins are sensitive to insulin:
|
glut 4
glut 2 |
|
|
which of the glucose transporter proteins are hormone independent:
|
glut 1 & 3
|
|
|
how is glucose trapped inside of a cell:
|
phosphate from ATP is transfered to carbon 6 of glucose
|
|
|
what enzymes add phosphate to glucose and where are they found:
|
glucokinase (liver)
hexokinase (other tissue) |
|
|
what does hexokinase work on:
|
glucose and other alternate sugars
|
|
|
when blood glucose rises, the glut 2 tranporters in the pancreas sense it and secrete ...
|
insulin
|
|
|
which of the glucose transporter proteins gets stimulated by insulin:
|
glut 2 and glut 4
|
|
|
hexokinase is hormone (dependent/independent)
|
independent
|
|
|
what trapping enzyme is induced by insulin:
|
glucokinase
|
|
|
what will inhibit the hexokinase reaction:
|
glucose-6-phosphate
|
|
|
glucose-6-phosphate inhibits (glucokinase/hexokinase)
|
hexokinase
|
|
|
which has the higher affiniity:
glucokinase or hexokinase |
hexokinase
|
|
|
what is the function of UDP-glucose (uridinediphosphoglucose):
|
activates glucose; carrier of glucose; earmarks for sugar production
|
|
|
what is the function of glycogen synthase:
|
puts glucose on in 1,4 linkages and makes straight chain
|
|
|
glycogen synthesis happens in what world:
|
insulin
|
|
|
most of the biosynthesis takes place in what world:
|
insulin
|
|
|
how are branches made in the production of glycogen
|
via 4:6 transferase (branching enzyme)
|
|
|
what is the funciton of glycogen phosphorylase:
|
breaks 1,4-linkages
|
|
|
if i want to mobilize my glycogen stores by making glucose, glucose ... must be converted to glucose...
|
glucoss-1-phosphate
glucose-6-phosphate |
|
|
what does the debranching enzyme do:
|
breaks the 1,6-linkages
|
|
|
where is glucose-6-phosphatase found and what does it do:
|
found only in the liver
takes phosphate off of glucose so it can go into the blood stream and be used by other tissues |
|
|
what is the function of phosphoglucomutase:
|
facilitates the intraconversion of glucose 1-phosphate and glucose 6-phosphate
|
|
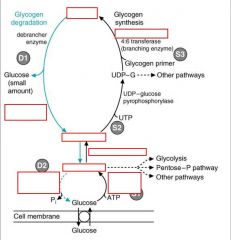
identify the labeled structures:
|
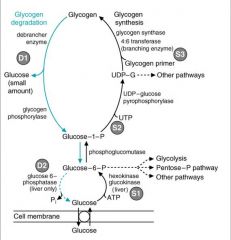
(see figure)
|
|
|
what 2 enzymatic activities does the branching enzyme have:
1. 2. |
1. alpha-1,4-glucosidase (breaks apart the 1,4-linkages in glycogen)
2. alpha-1,4:alpha-1,6 transferase: (moves over the branch and makes the 1,6 linkage) |
|
|
what are the 2 enzymatic activities of the debranching enzyme:
|
1st: alpha-1,6 glucosidase
2nd: alpha-1,4:alpha-1,4 transferase |
|
|
which of the 2 worlds is phosphorylated and which is dephosphorylated:
|
insulin: dephosphorylated
glucagon: phosphorylated |
|
|
glycogen synthase is (off/on) in the insulin world and is (dephosphorylated/phosphorylated) in that world
|
on
dephosphorylated |
|
|
glycogen phosphorylase is (off/on) in the insulin world and is (dephosphorylated/phosphorylated) in that world
|
off
dephosphorylated |
|
|
glycogen synthase is (off/on) in the glucagon world and is (dephosphorylated/phosphorylated) in that world
|
off
phosphorylated |
|
|
glycogen phosphorylase is (off/on) in the glucagon world and is (dephosphorylated/phosphorylated) in that world
|
on
phosphorylated |
|
|
in the (glucagon/insulin) world, what enzyme dephosphorylates everything:
|
insulin
protein phosphatase |
|
|
in the (glucagon/insulin) world, what enzyme phosphorylates everything:
|
protein kinase
|
|
|
glucagon and epinephrine bind to beta receptor in ... and start ... where ... phosphorylates what 2 glucagon world enzymes (indicate active or inactive):
1. 2. |
liver
phosphorylation cascade cAMP dependent protein kinase 1. glycogen phosphorylase (active) 2. glycogen synthase (inactive) |
|
|
alpha receptor is more abundant in liver and binds ... and is g-protein mediated. you get phosphorylation cascade as a result of activating:
1. 2. |
epinephrine
phopholipase C protein kinase C |

