![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the midgut gives rise to ... and is supplied by branches of ...
and receives sympathetic innervation from ... and receives parasympathetic innervation from ... |
duodenum (distal to opening of bile duct) to proximal 2/3 of transverse colon
SMA (Superior Mesenteric Artery) superior mesenteric ganglion vagus nerve |
|
|
the hindgut gives rise to ... and is supplied by branches of ...
and receives sympathetic innervation from ... and receives parasympathetic innervation from ... |
distal 1/3 of transverse colon to upper part of anal canal
IMA (Inferior Mesenteric Artery) inferior mesenteric ganglion pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2,3,4) |
|
|
what kind of mesentery do the mid and hind gut have ...
|
dorsal only
|
|
|
what are the 3 parts of the small intestine?
1. 2. 3. |
1. duodenum
2. jejunum 3. ileum |
|
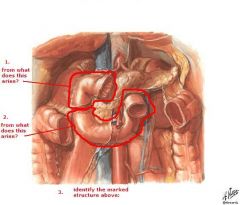
(see figure)
|
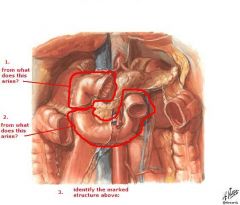
1. foregut
2. midgut 3. duodenum |
|
|
where are the 3 parts of the intestine in relation to one another and how long is each part:
|
1st: duodenum - 10 inches
2nd: jejunum - 8 feet 3rd: ileum - 12 feet |
|
|
which of the following are intraperitoneal:
duodenum jejunum ileum |
jejunum
ileum |
|
|
where does the jejunum begin and the ileum end:
|
jejunum begins at duodenojejunal flexure
ileum ends at ileocecal juncuntion |
|
|
what are the jejunum and ileum held by:
|
mesentery
|
|
|
together the jejunum and ileum measure about ... meters with the proximal ...(fraction) being jejunum, and the distal ...(fraction) being ileum
|
6
2/5 3/5 |
|
|
coils of jejunum occupy the ... part of abdominal cavity
while coils of ileum occupy the ... part of abdominal cavity and some extend into the ... |
upper left
lower right pelvis |
|
|
what are the functions of the small intestine:
1. 2. |
1. digestion of nutrients
2. absorption of nutrients |
|
|
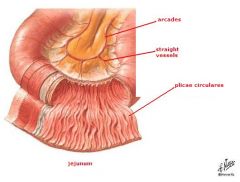
Plicae circulares are ... that are largest in the ... and small in the ...
|
large circular folds
jejunum ileum |
|
|
villi are ... that are longest in the ... and smaller in the ...
|
microscopic, finger like projections
jejunum ileum |
|
|
Peyer’s patches are ... and are commonly seen in the ... and only occasionally seen in the ...
|
collections of B-cell and T-cell lymphocytes
ileum jejunum |
|
|
what is the function of Peyer’s patches and where are they mostly located:
|
protect against bacteria
commonly seen in ileum |
|
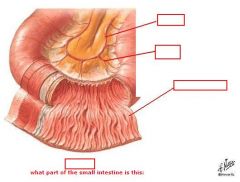
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
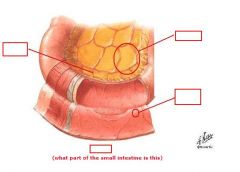
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
|
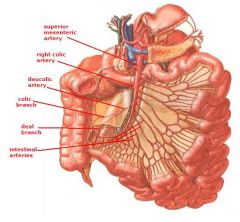
the ...artery supplies the midgut which consists of:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. |
superior mesenteric
1. Jejunum 2. Ileum 3. Cecum & Appendix 4. Ascending colon 5. Proximal 2/3 of transverse colon |
|
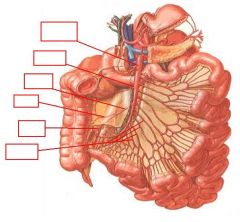
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
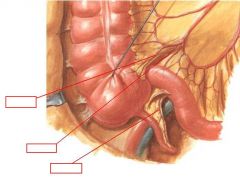
identify the labeled structures
|
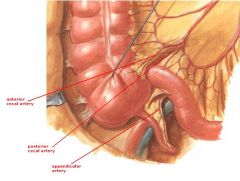
(see figure)
|
|
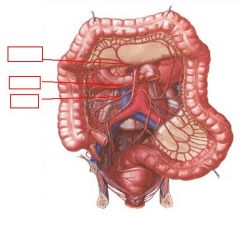
identify the labeled structures:
|
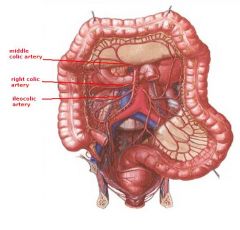
(see figure)
|
|
|
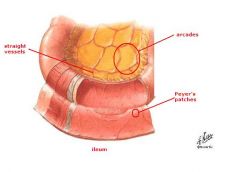
what does the following describe:
Few arcades (arches of anastomosing arteries) Long vasa recta Tall plicae circulares |
Jejunum
|
|
|
what does the following describe:
More arcades Shorter vasa recta few, shallow plicae circulares Peyer’s patches, becoming more abundant distally |
Ileum
|
|
|
how often does Ileal (Meckel’s) Diverticulum occur and who does it affect the most:
|
2-4% of the population
males |
|
|
Ileal (Meckel’s) Diverticulum represents a remnant of the ... and typically appears as a finger-like pouch, 3 to 6 cm long, that arises from ... border of ..., 40 to 50 cm from ... junction
|
proximal part of vitelline duct (yolk stalk)
antimesenteric ileum ileocecal |
|
|
26% of the time an Ileal (Meckel’s) Diverticulum may be connected to the ... by ...
|
umbilicus
fibrous cord |
|
|
Ileal (Meckel’s) Diverticulum contains all layers of ... and may contain small patches of ... and ... tissues and may become inflamed and cause symptoms that mimic ...
|
ileum
gastric pancreatic appendicitis |
|
|
what are the functions of the large intestine:
1. 2. |
1. Store feces for disposal
2. Absorption of water and electrolytes |
|
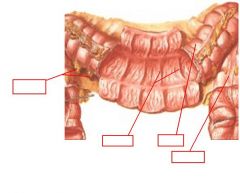
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
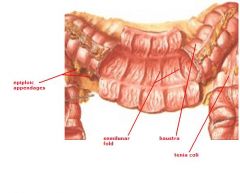
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
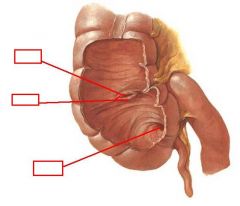
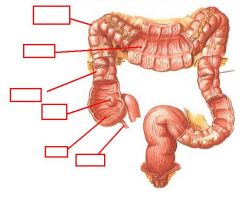
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
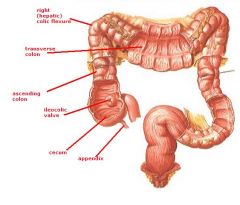
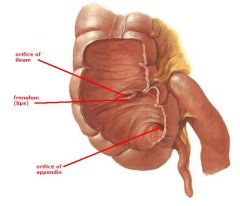
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
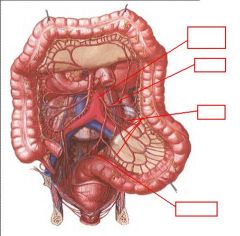
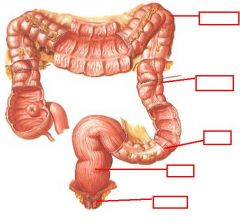
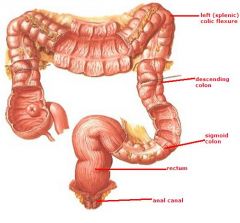
identify the labeled structures:
|
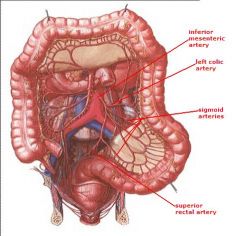
(see figure)
|
|
|
... supplies the hindgut which consists of:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
inferior mesenteric artery
1. Last 1/3 of transverse colon 2. Descending colon 3. Sigmoid Colon 4. Part of blood supply to rectum |

