![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
fatty acids are the major source of fuel when:
1. 2. 3. |
1. in between meals
2. when fasting (e.g. overnight) 3. periods of physical exertion |
|
|
fatty acids are a fuel source for what kind of tissue:
1. 2. 3. |
skeletal muscle
cardiac muscle liver |
|
|
fatty acids generate (more/less) fuel compared to glucose
|
more
|
|
|
dietary fatty acids are transported from intestine in the form of lipoprotein particles ... and ...
|
chylomicrons
VLDL |
|
|
when fatty acids reach their target cells, they are cleaved from VLDL and the free fatty acid diffuses across the cell membrane where 2 things can happen:
1. 2. |
1. used immediately for energy
2. converted into fatty acyl CoA |
|
|
fatty acyl CoA combines with ... to from ... so it can be stored for later use as fuel for the body
|
glycerol-3-phosphate
triglyceride |
|
|
excess glucose can be converted into ... and ...
this is stimulated by the hormone ... |
acetyl CoA
glycerol-3-phosphate insulin |
|
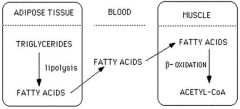
look at the figure and use a ↑ or ↓ to indicate what is going on with the below listed hormones and enzymes:
glucagon / (insulin) cAMP levels in adipocytes protein kinase A (PKA) hormone-sensitive lipase |
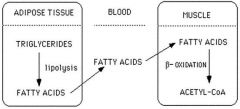
↑ glucagon (↓insulin)
↑ cAMP levels in adipocytes ↑ protein kinase A (PKA) ↑ hormone-sensitive lipase |
|
|
put the following in the correct order:
↑ cAMP levels in adipocytes ↑ glucagon (↓insulin) ↑ hormone-sensitive lipase ↑ protein kinase A (PKA) fasting |
fasting
↑ glucagon (↓insulin) ↑ cAMP levels in adipocytes ↑ protein kinase A (PKA) ↑ hormone-sensitive lipase |
|
|
what are the function of lipases:
|
to relase fatty acids from triglycerides
|
|
|
lipases are ... sensitive
|
hormone
|
|
|
free fatty acids diffuse out of adipose cell and into the bloodstream where they travel attached to ...
|
albumin
|
|
|
glycerol derived from lipolysis enters bloodstream and can be used by the liver for ...
|
gluconeogenesis
|
|
|
Fatty acids enter cells through two routes:
1. 2. |
diffusion
transport via fatty acid binding protein (FaBP) |
|
|
where is the fatty acid binding protein located:
|
plasma membrane
|
|
|
fatty acids are ultimately oxidized to ... and ...
|
CO2
H2O |
|
|
acetyl-CoA produced through β-oxidation of fatty acids in the liver can be:
1. 2. |
1. converted to ketone bodies
2. enter the TCA Cycle. |
|
|
where does β-oxidation of fatty acids occur:
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
in β-oxidation of fatty acids, free fatty acids are converted into ... before they cross the outer membrane of the mitochondria
|
fatty acyl CoA
|
|
|
... shuttles fatty acyl CoA across the ... membrane
|
carnitine
mitochondrial inner |
|
|
what is the enzyme the catalyzes the following reaction:
fatty acid --> fatty acyl CoA |
acyl CoA synthetase + ATP
|
|
|
what can we use fatty acyl CoA for:
1. 2. 3. |
1. energy
2. membrane lipids 3. storage |
|
|
carnitine comes from ... or can be synthesized in the ... from ... and
|
red meats/dairy
liver lysine |
|
|
synthesis of carnitine requires ... and ...
|
vitamin C
S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) |
|
|
... is on the outer mitochondrial membrane and is the rate-limiting enzyme (inhibited by malonyl CoA)
transfers the fatty acyl group to carnitine, forming fatty acylcarnitine, which is then translocated into the mitochondrial matrix |
Carnitine Palmitoyl Transferase I (CPT I)
|
|
|
... on the inner mitochondrial membrane
transfers the fatty acyl group back to CoASH (re-forming the fatty acyl CoA) and releases the carnitine for recycling |
Carnitine Palmitoyl Transferase II (CPT II)
|
|
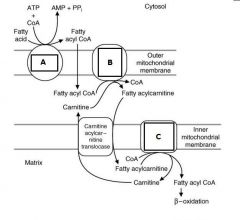
identify the 3 enzymes labeled a, b, and c
|
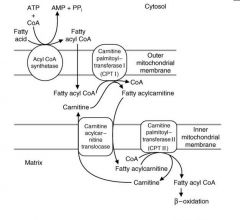
(see figure)
|
|
|
what are the 3 most common diseases associated with carnitine metabolism:
1. 2. 3. |
1. Carnitine or carnitine uptake deficiency
2. CPT I deficiency 3. CPT II deficiency |
|
|
what happens in persons with carnitine deficiencies:
|
inability to transport fatty acids into the mitochondria
|
|
|
who is afflicted with carnitine deficiences:
|
occurs in newborns (particularly pre-term infants), patients undergoing hemodialysis, patients with organic acidemia
|
|
|
what are the symptoms in carnitine deficiencies:
|
muscle weakness, muscle cramping, cardiomyopathy, hepatomegaly, encephalopathy, sudden death
|
|
|
CPT I Deficiency is a (sex-linked/autosomal) (dominant/recessive) defect in CPT I gene that primarily affects ... in the liver
|
autosomal
recessive fatty acid oxidation |
|
|
the symptoms of CPT I Deficiency usually present after a period of ... or after a ... illness:
the symptoms include: 1. 2. 3. 4. |
fasting
gastrointestinal 1. hypoketosis and hypoglycemia 2. lethargy 3. seizures 4. coma |
|
|
CPT II Deficiency is a (sex-linked/autosomal) (dominant/recessive) defect in CPT II gene and has ...(number) subtypes
|
autosomal
recessive 3 |
|
|
the 3 subtypes of CPT-II deficiency are:
1. 2. 3. |
1. myopathic CPT-II deficiency (most common)
2. hepatic CPT-II deficiency (similar to CPT I) 3. multiorgan |
|
|
what are the symptoms of myopathic CPT-II deficiency:
1. 2. 3. |
1. adolescence or adulthood onset
2. recurrent muscle pain, fatigue, and myoglobinuria (particularly following exercise) 3. often misdiagnosed (fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue) |
|
|
The β-Oxidation Spiral is where ... are sequentially cleaved from ...
|
2-carbon acetyl CoA units
fatty acyl group |
|
|
what are the 4 repeating steps in fatty acid oxidation:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. oxidation
2. hydration 3. oxidation 4. cleavage |
|
|
what are the 4 repeating steps in fatty acid synthesis:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. condensation
2. reduction 3. dehydration 4. reduction |
|
|
what is the most important (rate-limiting) step in fatty acid oxidation and what is the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction:
|
1st oxidation
aceyl CoA dehydrogenase |
|
|
in oxidation, a ... is inserted into the fatty acid
|
double bond
|
|
|
there are several acyl CoA dehydrogenases, each works on a specific chain length. the most important is ... because it is most involved in pathologies and it works on fatty acids that are ... carbons in length
|
MCAD - medium chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase
6-12 |
|
|
what are the most frequently diagnosed of the fatty acid oxidation disorders
|
MCAD Deficiency
|
|
|
what accounts for about 1 in 100 SIDS deaths
|
MCAD Deficiency
|
|
|
... usually presents clinically between second month and second year of life following a period of fasting (even overnight fasting) or illness
|
MCAD Deficiency
|
|
|
how do you prevent Deficiency symptoms:
|
frequent feedings, high-carb/low-fat diet
|
|
|
...% of MCAD Deficiency patients will die with their first episode of illness
|
20-25
|
|
|
how would you manage MCAD Deficiency:
1. 2. 3. |
1. eat regularly, avoid fasting
2. diet high in carbs, low in medium and long chain fatty acids 3. oral carnitine |
|
|
where is the energy coming from in β-oxidation
|
FADH2 and NADH from the 2 oxidation steps in the β-oxidation spiral
|
|
|
the most common fatty acids used in β-oxidation are:
1. 2. 3. 4. and they are the most common becuase: |
1. palmitate
2. stearate 3. oleate 4. linoleate most common dietary fatty acids and also commonly synthesized in humans |

