![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what makes an enzyme an ABC enzyme:
|
ATP utilization
Biotin is a required cofactor C is for carboxylation |
|
|
pyruvate carboxylase catalyzes the reaction ...
|
pyruvate --> oxaloacetate
|
|
|
in the insulin world ... is used to make fatty acids and it is pulled out of the tca cycle which makes a build up of ... this build up turns ... (enzyme) 'off' and ... (enzyme) 'on' which puts ... back into the system
|
citrate
acetyl CoA pyruvate dehydrogenase pyruvate carboxylase 4C molecule |
|
|
in the glucagon world, we have ... from fatty acid breakdown and this turns 'off' ... and turns 'on' ...
we do gluconeogenesis and get the precursor ... from the tca cycle |
acetyl CoA
pyruvate dehydrogenase pyruvate carboxylase malate |
|
|
in gluconeogenesis, where do we get the pyruvate from?
|
amino acids
|
|
|
what does the following describe:
An enzyme-catalyzed chemical reaction that recharges the supply of intermediate molecules in various metabolic reactions such as the citric acid cycle. |
anaplerotic pathway/reaction
|
|
|
tca cycle (is/is not) under hormonal regulation:
|
is not
|
|
|
the first irreversible step in the tca cycle is ... and is regulated by:
1. 2. 3. |
isocitrate --> alpha-ketoglutarate via isocitrate dehydrogenase
1. ADP (+) 2. NADH (-) 3. Ca2+ (+) |
|
|
if i am in an energy poor state i have plenty of ...
if i am in an energy rich state i have plenty of ... |
ADP
NADH |
|
|
when you have decarboxylation you are generating ...
|
NADH
|
|
|
what are the 5 cofactors for pyruvate dehydrogenase:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. |
1. NADH
2. FADH (riboflavin) 3. lipoate/lipoic acid 4. thiamine (B1) 5. CoASH/Coenzyme A (panthothenic acid) |
|
|
1. NADH
2. FADH (riboflavin) 3. lipoate/lipoic acid 4. thiamine (B1) 5. CoASH/Coenzyme A (panthothenic acid) are coenzymes for pyruvate dehydrogenase and ... |
alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
|
|
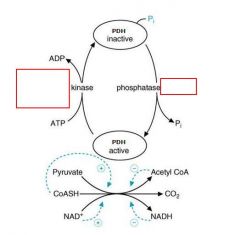
1. what activates pyruvate dehydrogenase? 2. and what inactivates pyruvate dehydrogenase?
|
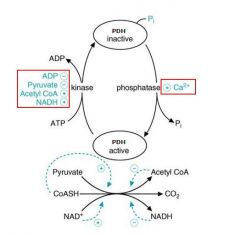
1. Ca++, ADP, pyruvate
2. acetyl CoA, NADH |

