![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
... variable is one that which we think will “cause” a change to occur
|
independent
|
|
|
... variable is the outcome. that which we think will change as the result of the independent variable
|
dependent
|
|
|
Smokers have a greater chance of an MI than nonsmokers.
independent variable = ____ dependent variable = ____ |
smoking
myocardial infarction |
|
|
what does this describe:
Confuses the relationship between the independent and dependent variables |
confounding variable
|
|
|
confounding variables have 3 conditions:
1. 2. 3. |
1. Related to the independent variable
2. Related to the dependent variable 3. NOT A CONSEQUENCE of the independent variable |
|
|
smoking is an example of a ...:
People who consume large amounts of Alcohol have a greater incidence of MIs than non-alcohol consumers. (what about those people who smoke too?) |
confounding variable
|
|
|
order the study weakest to strongest:
Case-Control (Retrospective) Case Study Prospective (Cohort) Case Series Randomized Clinical Trial (RCT) |
Case Study
Case Series Case-Control (Retrospective) Prospective (Cohort) Randomized Clinical Trial (RCT) |
|
|
which of these studies uses a comparison group:
Case Study Case Series Case-Control (Retrospective) Prospective (Cohort) Randomized Clinical Trial (RCT) |
Case-Control (Retrospective)
Prospective (Cohort) Randomized Clinical Trial (RCT) |
|
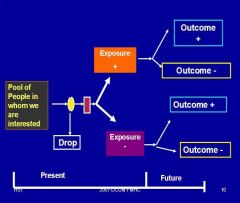
this is an example of what:
|
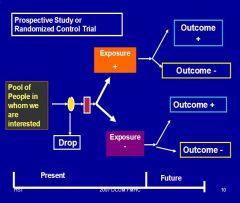
Prospective (Cohort)
|
|
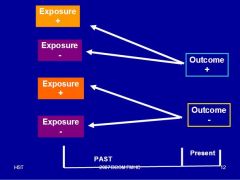
what kind of study does this study represent?
|
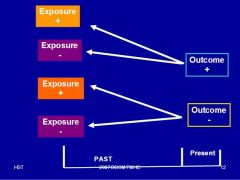
this is Case-Control (Retrospective)
|

