![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The superior laryngeal artery and internal laryngeal nerve pierce the ...
|
Thyrohyoid Membrane
|
|
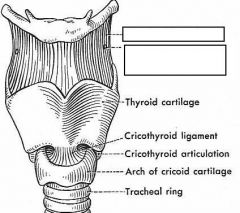
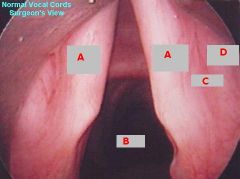
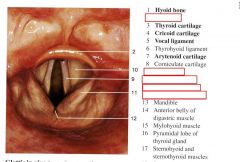
identify the labeled structures:
|
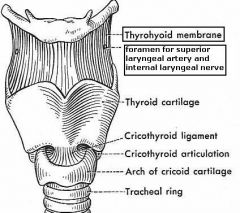
(see figure)
|
|
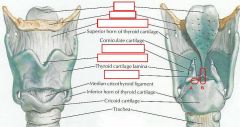
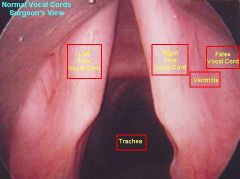
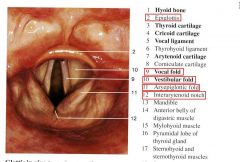
identify the labeled structures:
identify a and b: |
(see figure)
a. sinovial joint b. glottis |
|
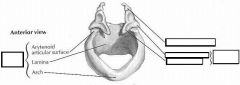
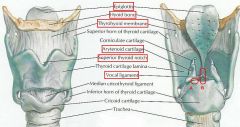
identify labeled structures:
|
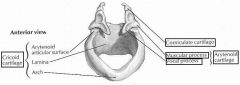
(see figure)
|
|
|
the cricoid cartilage is at the level of ... vertebral body
|
C6
|
|
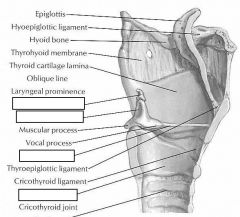
identify the labeled structures:
|
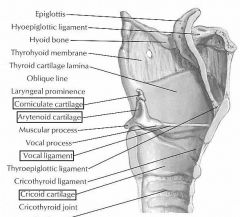
(see figure)
|
|
|
there is a ... joint between each arytenoid and cricoid cartilage
|
synovial
|
|
|
the arytenoid cartilage is capable of moving:
|
in three planes: med/lat, ant/post, and rotation.
|
|
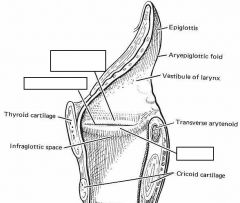
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
|
describe airflow when you speak:
|
you are pushing air up through your trachea
|
|
|
what structure lies underneath the vocal fold:
|
vocal ligament
|
|
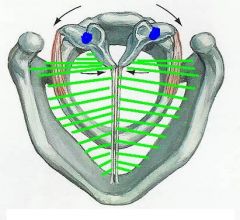
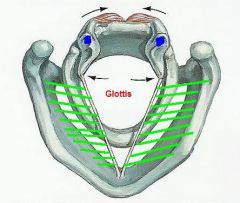
1. what is the name of the muscle near the arrows?
2. what is the function of this muscle? |
1. lateral cricoarytenoid
2. closes glottis - adduction of vocal ligaments |
|
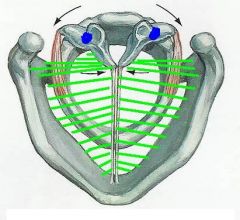
1. what is the name of the muscle near the arrows?
2. what is the function of this muscle |
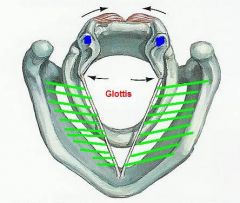
1. posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
2. opens glottis (abduction of vocal ligaments) |
|
|
what is the most important skeletal muscle in your body:
|
posterior cricoarytenoid
|
|
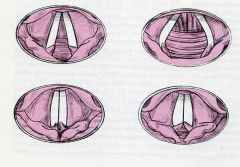
match the glottal opening with the correct term:
1. whispering 2. full glottal opening 3. normal speech 4. full glottal stop |
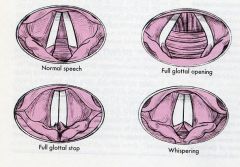
(see figure)
|
|
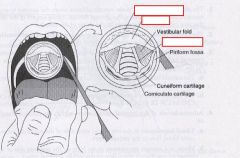
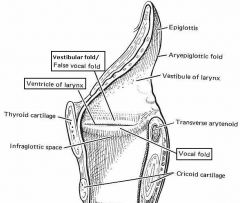
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
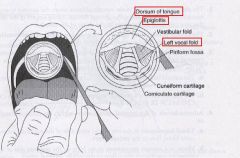
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
|
there are 3 main functional laryngeal muscle groups, what do they do:
1. 2. 3. |
1. tense or relax the vocal folds
2. open or close the glottis 3. modify the laryngeal aditus |
|
|
what are the muscles the tense or relax the vocal folds:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. cricothyroid
2. thyroarytenoid 3. vocalis 4. posterior cricoarytenoid |
|
|
what are the muscles that open or close the glottis:
1. 2. 3. |
1. posterior cricoarytenoid
2. lateral cricoarytenoid 3. transverse arytenoids |
|
|
what are the muscles that modify the laryngeal aditus:
1. 2. |
1. oblique arytenoid
2. aryepiglotticus |
|
|
the cricoarytenoids ... the vocal ligaments by pulling the thyroid cartilage ...
|
increase tension/lengthen
forward |
|
|
what happens if you damage the external laryngeal nerve (cricothyroid)
|
flaccid vocal cords, monotone voice
|
|
|
what muscle is this:
Lower fibers attach to the arytenoid. Upper fibers continue into the aryepiglottic folds as the thyro-epiglotticus. Contraction shortens and relaxes the Vocal ligament |
Thyroarytenoids
|
|
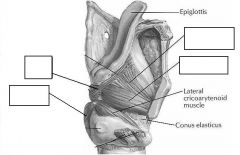
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
|
what is the function of the thyroepiglottic muscle:
|
opens the larynx
|
|
|
... are the most important skeletal muscle in the body because they are the only muscles that open the ...
|
Posterior Cricoarytenoids
glottis |
|
|
Contraction of the Posterior Cricoarytenoids pulls the muscular processes ... rotating the arytenoids ... and (ab/ad)-ducting the vocal folds.
|
medially
laterally abducting |
|
|
Lateral Cricoarytenoids pulls the muscular process ... rotating the arytenoids ... and (ab/ad)-ducting the vocal ligaments.
|
forward
medially adducting |
|
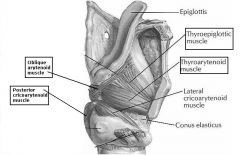
identify the labeled structures
|
(see figure)
|
|
|
During swallowing the ... close the Aryepiglottic Folds and pull the ... forward to contact the epiglottis thus closing the ...
The Transverse Arytenoids close the ... |
Oblique Arytenoids
arytenoids laryngeal inlet posterior part of the glottis |
|
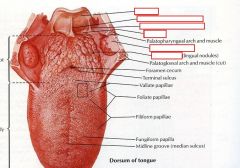
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
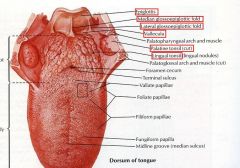
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
|
what does the following describe:
the two mucosal folds that run from the arytenoid to lateral edges of the epiglottis that contain muscles fibers – the aryepiglotticus. |
Aryepiglottic Folds
|
|
|
the Aryepiglottic folds form the lateral edges of the entrance to the larynx that is called the ...
|
the laryngeal additus or inlet
|
|
|
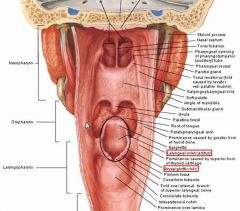
The piriform fossa lies between the ... and the ... – lined by internal laryngeal nerves.
|
aryepiglottic folds
inferior pharyngeal mucosa |
|
|
what is the function of the Aryepiglotticus Muscle
|
closes laryngeal inlet
|
|
|
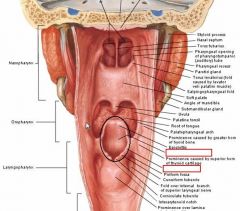
there are two lateral and one median glossepiglottic folds running from the back of the tongue to ... On either side of the median fold are two spaces – the ...
|
epiglottis
valleculae |
|
fill in the missing iformation:
|
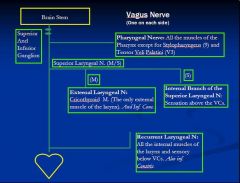
(see figure)
|
|
|
Pharyngeal Nerve innervates all the muscles of the
Pharynx except for ... and ... |
Stylopharyngeus (9)
Tensor Veli Palatini (V3) |
|
|
External Laryngeal nerve innervates the ...
|
Cricothyroid Muscle
inferior constrictor |
|
|
what is special about the Cricothyroid muscle:
|
the only external muscle of the larynx
|
|
|
Internal Branch of the
Superior Laryngeal Nerve does Sensation ... |
above the vocal chords
|
|
|
Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve innervates ... and sensory ... also innervates ...
|
all the internal muscles of the larynx
below vocal chords inferior constrictor |
|
|
Superior Laryngeal Nerve splits into ... and
|
internal laryngeal
external laryngeal |
|
|
internal laryngeal runs with the ... and pierces the ...
|
superior laryngeal A.
thyrohyoid membrane |
|
|
external laryngeal nerve runs with the ...
|
superior thyroid artery
|
|
identify the labeled structures:
|
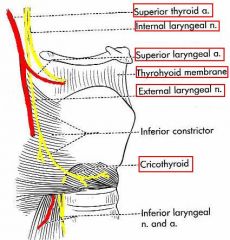
(see figure)
|
|
|
... carries preganglionic secretomotor parasympathetic fibers to the larynx
|
internal laryngeal nerve
|
|
|
the gag reflex is controlled by ... and ...
|
cn9 in (sensory input)
cn10 out (gagging) |
|
|
right recurrent laryngeal nerve loops behind the ... On the left it loops behind the ...
|
subclavian artery
aortic arch |
|
|
recurrent laryngeal nerve ascends between ... and ... along with ... it enters the larynx beneath the ...
If damaged on one side, ... If both, ... |
trachea
esophagus inferior thyroid artery inferior constrictor fixed vocal cord and hoarseness asphyxiation possible |
|
|
Left Rec. Laryngeal N. is more
susceptible to damage because it enters ... and can be damaged by ... |
superior mediastinum
aortic arch aneurysm |
|
|
... and ... provide blood to the larynx
|
superior thyroid artery
inferior laryngeal branch of the inferior thyroid artery |
|
|
Swollen nodes palpable to the upper tracheal rings suggest ...
|
Cancer of larynx
|
|
|
Contraction of the abdominal and thoracic wall muscles, along with forced closure of the glottis is called the ... and is necessary part of several human functions:
1. 2. 3. |
Valsalva Maneuver
1. urination 2. defecation 3. childbirth |
|
|
Thyroidectomy may result in damage to ... nerves
|
recurrent laryngeal
|
|
|
Cricothyrotomy is ...
|
Emergency Airway opening
|
|
|
in a ... the incision is made through the skin and cricothyroid membrane
|
Cricothyrotomy
|

