![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the steps to the gram stain:
|
1. stain with crystal violet
2. add iodine soln 3. decolorize with alcohol 4. counterstain with safranin |
|
|
what does alcohol do to the crystal violet in gram negative cells:
|
extracts it
|
|
|
the thick peptidoglycan layer of (Gram-positive/Gram-negative) cells becomes dehydrated by the alcohol. The pores in the peptidoglycan close up and the ... complex remains inside the cell
|
Gram-positive
crystal violet-iodine |
|
|
why is safranin used in gram staining:
|
to visualize gram-negative cells
|
|
|
1. what is the type of cell wall do mycobacteria have:
2. and what happens with gram staining: |
1. typical Gram-positive cell wall structure
2. mycolic acid bound to the outside of the peptidoglycan interferes with the staining procedure |
|
|
what kind of bacteria stain with acid fast:
|
Mycobacterium
|
|
|
what 2 organisms discussed in class are too small to be seen with a brightfield microscope and therefore cannot be gram stained:
|
Mycoplasma
Treponema |
|
|
..., ... and ... are gram-negative, however, since they are obligate intracellular parasites, the Gram stain is not useful here
- what would you use to stain these organisms: |
Chlamydia
Chlamydiophila Rickettsia Other sensitive stains, such as fluorescent antibodies |
|
|
what are the gram positive bacilli:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. |
1. Bacillus
2. Clostridium 3. Corynebacterium 4. Listeria 5. Propionibacterium |
|
|
what are the gram positive cocci:
1. 2. 3. |
1. Enterococcus
2. Staphylococcus 3. Streptococcus |
|
|
what are the gram positive filamentous organisms:
1. |
1. Actinomyces
|
|
|
what are the gram negative cocci:
1. 2. |
1. Moraxella
2.Neisseria |
|
|
what are the gram negative curved or spiral organisms:
1. 2. |
1. Campylobacter
2. Helicobacter |
|
|
what are the gram negative spirochete:
1. 2. |
1. Borrelia
2. Leptospira |
|
|
what are the non-gram staining bacilli:
1. 2. |
1. Mycobacterium
2. Rickettsia |
|
|
what are the non-gram staining cocci:
1. 2. |
1. Chlamydia
2. Chlamydiophila |
|
|
what are the non-gram staining filamentous organisms:
1. |
1. Mycoplasma
|
|
|
what are the non-gram staining spirochetes:
1. |
1. Treponema
|
|
|
what are the steps to acid fast staining:
|
1. stain with carbol fushin
2. decolorize with acid-alcohol 3. counterstain with methylene blue |
|
|
Acid-fast organisms are stained ... all others are stained ...
|
pink to red
blue |
|
|
what makes acid fast organisms resistant to acid-alcohol decolorizing:
|
mycolic acids
|
|
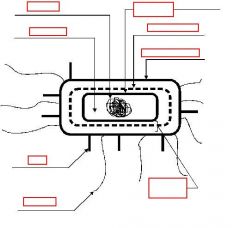
identify the labeled structures:
what does this figure depict: |
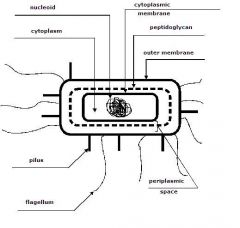
(see figure)
Structure of a Gram-negative Bacterium |
|
|
the cytoplasmic membrane is also called the:
1. 2. |
inner membrane
plasma membrane |
|
|
Phospholipids of inner membranes have a hydrophilic group that faces the ... or ...
|
cytoplasm
periplasm |
|
|
The fatty acids in the plasma membranes of gram positive and gram negative bacteria are typically ... to ... carbons long and have ...(number) or ...(number) double bonds
|
16
18 zero one |
|
|
In additions to phospholipids, the cytoplasmic membrane of gram positive and gram negative bacteria contains molecules called ... which are similar to the sterols found in eukaryotes and serve to make the membrane more ... and about 1/2 of the membrane mass comes from ...
|
hopanoids
rigid protein |
|
|
what are the functions of the cytoplasmic membrane of gram positive and gram negative bacteria:
1. 2. 3. |
1. barrier separating the cytoplasm from the periplasm
2. transport 3. respiration |
|
|
... compounds can diffuse across the membrane to some degree which can be dangerous to the cell, so one function of the ... of the cell envelope is to protect the cytoplasmic membrane from these compounds
|
hydrophobic
outer layers |
|
|
how many layers does the gram-negative cell wall have:
gram-positive: |
2
1 |
|
|
identify the layers of the gram-negative cell wall:
|
peptidoglycan
outer layer |
|
|
what is the shape and composition of the peptidoglycan layer of the gram-negative cell wall:
1. 2. |
1. peptidoglycan layer is a single sheet
2. composed of two sugars, N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic |
|
|
The peptidoglycan chains in the gram-negative cell wall are held together by crosslinks between the ... acids and are composed of ...
|
N-acetylmuramic
short chains of amino acids |
|
|
Gram-negative bacteria, and some Gram-positive bacteria, have the unusual amino acid ... in the peptide crosslink of the peptidoglycan
|
meso-diaminopimelate
|
|
|
what is the function of the peptidoglycan layer:
|
provide rigidity to the cell and to prevent it from exploding due to the higher pressure inside the cell than outside it
|
|
|
The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria is a ... composed of an outer ... layer and an inner ... layer
|
lipid bilayer
lipopolysaccharide (LPS) phospholipid |
|
|
the LPS has 2 portions, what are they:
|
phospholipid (lipid A)
chains of polysaccharides |
|
|
what portion of the LPS is toxic to humans and what is the toxin called:
|
lipid A
endotoxin |
|
|
what is the function of the sugar side chains of the LPS:
|
prevent diffusion of hydrophobic compounds into the cell
|
|
|
The core polysaccharide of the LPS contains 9 to 12 sugar residues and includes the unusual sugar ... while the ... is a 4 to 7 residue polysaccharide that is repeated 50 to 100 times and is called the ... antigen
|
KDO (keto-deoxy-octanoate)
O-specific polysaccharide O |
|
|
what are porins:
|
proteins that form pores and allow small hydrophillic compounds to enter the cell
|
|
|
where are porins located:
|
outer membrane of gram negative bacteria
|
|
|
can you use vancomycin against gram negative bacteria?
|
no, too large to get through porin
|
|
|
what is the relationship between antibiotic resistance and porins:
|
a lot of antibiotic resistance due to smaller pores in porin
|
|
|
space between the outer membrane and the cytoplasmic membrane in Gram-negative bacteria is called the ... space
|
periplasmic
|
|
|
what do hydrolytic enzymes do and where are they found in gram negative bacteria:
in gram positive bacteria: |
break down large complex nutrients
found in the periplasmic space within mesh of peptidoglycan and the surrounding medium |
|
|
... is found in the periplasm and breakdowns ... antibiotics such as ... and is also secreted into the ...
|
β-lactamase
β-lactam penicillin surrounding medium |
|
|
do gram positive or gram negative have a periplasmic space or both:
|
gram negative
|
|
|
how does the peptidoglycan layer of gram positive bacteria differ to that of gram negative bacteria:
|
thicker - can be as many as 25 sheets
in the peptide crosslinks the meso-diaminopimelate is often replaced with L-lysine in some Gram-positive bacteria, a string of glycines connect the amino acid strands in the crosslinks |
|
|
The cell walls of many Gram-positive bacteria contain highly negatively charged polysaccharides called ... that stick out from the peptidoglycan into the medium and help prevent diffusion of ... compounds into the cell
|
teichoic acids
hydrophobic |
|
|
If the teichoic acids are bound to the cytoplasmic membrane, they are known as ...
|
lipoteichoic acids
|
|
|
Teichoic acids are common surface antigens that distinguish ... These are important ... factors Lipoteichoic acids are also shed into the environment and cause a weak ... reaction
|
serotypes
virulence endotoxin-like |
|
|
where are Teichoic acids and lipoteichoic acids NOT found:
|
gram negative bacteria
|
|
|
Gram-positive cells lack an ... membrane, so the only barrier to many compounds is the ... membrane, also the peptidoglycan is often the ... layer of the cell
|
outer
cytoplasmic outermost |
|
|
the bond between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetylglucosamine can be broken by ... causing the formation of a protoplast.
the above is true for gram-positive or gram negative bacteria: |
lysozyme
gram-positive |
|
|
... is found in tears and saliva and is active only against Gram-positive cells
|
Lysozyme
|
|
|
lysozyme is effective against gram-negative or gram positive bacteria:
|
gram-positive
|
|
|
why isn't lysozyme effective against gram-negative bacteria:
|
lysozyme can’t get through the Gram-negative outer membrane to get at the peptidoglycan
|

