![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the relative intracellular/extracellular ion concentrations or the following ions:
K+ Na+ Cl- Ca++ proteins |
K+ → (↑)intracellular; (↓)extracellular
Na+ → (↓)intracellular; (↑)extracellular Cl- → (↓)intracellular; (↑)extracellular Ca++ → (↓)intracellular; (↑)extracellular proteins → (↑)intracellular; (↓)extracellular |
|
|
what does the Nernst equation describe:
|
the membrane potential established by a concentration difference for a single ion across a semipermeable membrane
|
|
|
what is membrane potential
|
the electrical potential difference (voltage) across a cell's plasma membrane.
|
|
|
what is the resting membrane potential of a cell (in terms of relative charge):
|
there is excess negative charge inside the cell compared to outside
|
|
|
Membrane Conductance can be thought of as what:
|
a measure of permeability
|
|
|
if you (↑)conductance → effect: (polarization/flux)
K+ Cl- Na+ Ca++ |
(↑)conductance → effect
K+ hyperpolarize, efflux Cl- hyperpolarize, influx Na+ DEPOLARIZE, INFLUX Ca++ DEPOLARIZE, INFLUX |
|
|
where do you find cardiac fast response action potentials: (x2)
|
(1) atrial and ventricular myocytes
(2) conducting fibers of the Purkinje system |
|
|
where do you find cardiac slow response action potentials: (x2)
|
(1) sinoatrial node
(2) atrioventricular node |
|
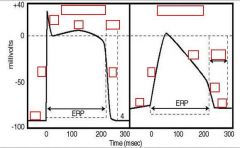
what are the type of action potentials depicted:
identify each phase: |
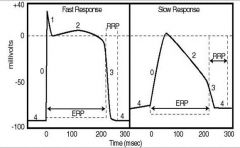
(see figure)
RRP = relative refractory period |
|
|
what are the phases of the cardiac action potential and what is going on in each phase:
|
Phase 0 fast upstroke of depolarization
Phase 1 rapid partial repolarization Phase 2 plateau depolarization Phase 3 repolarization to resting membrane potential Phase 4 resting membrane potential |
|
|
what is the resting membrane potential in the cardiac cell:
|
-90 mV
|
|
|
how do the cardiac action potential phases differ in the slow from the fast responses: (x4)
|
(1) no phase 1
(2) lower amplitude (3) phase 2 is less flat (less of a plateau) (4) relative refractory period extends into a larger fraction of the resting potential |
|
|
how long is the duration of the ventricular muscle action potential and therefore its effective refractory period:
What is the consequence of this phenomenon with regards to cardiac cells: |
approximately as long as the mechanical event
tetany will not occur because very difficult to achieve summation → due to long effective refractory period |
|
|
what is effective refractory period:
|
During a cardiac cycle, once an action potential is initiated, there is a period of time that a new action potential cannot be initiated
|
|
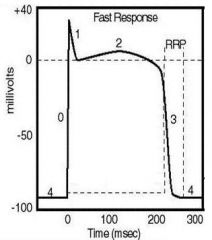
identify the effective refractory period:
|
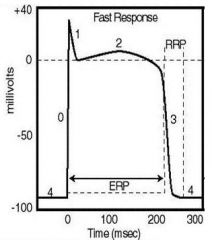
(see figure)
|
|
|
what are the different types of potassium channels in cardiac muscle: (x4)
(what type of stimulus do they respond to) |
voltage regulated
and those that respond to: neurotransmitter hormone intracelular metabolsim (such as [ATP]) |
|
|
During phase 4 there is an (efflux/influx) of potassium through a voltage-gated channel which tends to ___ the cell, referred to as the what:
|
efflux
hyperpolarize inwardly rectifying K+ current (iK1) |
|
|
for other electrically excitable cells, ___ concentration has a large effect on resting membrane potential
|
extracellular potassium
|
|
|
as the extracellular K+(↑), what happens to:
resting membrane potential: |
decreases
|
|
|
why does the [K+] have more of an effect on membrane potential than [Na+]:
|
K+ has a higher conductance than Na+
|
|
|
Extracellular sodium concentration has almost no effect on ___ but has a large effect on the ___
|
resting membrane potential
action potential amplitude |
|
|
the cardiac cell resting potential is about ___
the threshold is about ___ |
-90 mV
-65 mV |
|
|
The upstroke, phase 0, occurs when sufficient ___ channels are opened
|
fast sodium
|
|
|
what type of channels are responsible for the phase 0 rapid depolarization:
|
Na+ channels
|
|
|
what are the fast sodium channel activation gates:
|
m gates
|
|
|
what are the fast sodium channel inactivation gates:
|
h gates
|

