![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
chronic low cardiac output often manifests as ___
|
fatigue
|
|
|
Inadequate oxygenation may manifest as ___ and ___ of the fingers / toes as a result of what:
|
central cyanosis
clubbing right to left or extracardiac shunting |
|
|
Heart failure may manifest as ___ in the distal extremities, cool skin, and increased sweating as a result of ___
|
cyanosis
vasoconstriction |
|
|
___ classically manifests as petechiae, Osler's nodes, and Janeway lesions
|
infective endocarditis
|
|
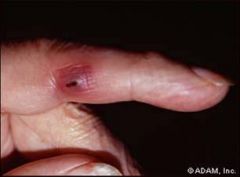
what is this an image of:
this is pathognomonic of what: |
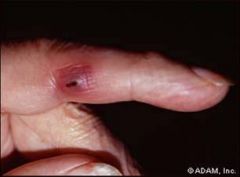
janeway lesion
infective endocarditis |
|
|
what is the description of a janeway lesions: (x4)
|
Non-tender
small (a few millimeters) erythematous or hemorrhagic macular or nodular lesions |
|
|
where do janeway lesions occur:
|
palms or soles of feet
|
|
|
what are janeway lesions:
what are they caused by: |
dermal microabscess with necrosis and inflammatory infiltrate
caused by the deposition of circulating immune complexes in small blood vessels |
|
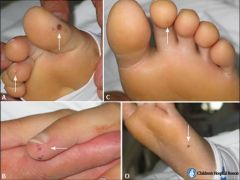
what is this an image of:
what are they caused by: |
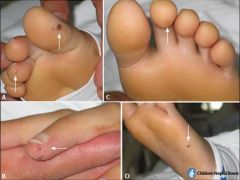
Osler's nodes
immune complex deposition |
|
|
what are Osler's nodes:
|
painful, red, raised lesions on the hands (finger pulps) and feet
|
|
|
Osler's nodes are indicative of what: (x5)
|
subacute infective endocarditis
systemic lupus erythematosus marantic endocarditis disseminated gonococcal infection infected arterial catheter |
|
|
orthostatic hypotension + tachycardia are likely due to
|
hypovolemia
|
|
|
resting tachycardia can be what (x2)
|
hypovolemia or heart failure
|
|
|
for tachypnea consider what:
|
pulmonary venous congestion
|
|
|
what permits visualization of the small vessels:
|
examination of the retina
|
|
|
for optic disk edema, blurred margins, cupping with sharp contours you should consider what: (x2)
|
malignant hypertension
OR thrombosis of central retinal vein |
|
|
what is papilledma: (x2)
|
swelling of the optic disk due to (↑)intracranial pressure
almost always bilateral |
|
|
what is the differential diagnosis for papilledema: (x8)
|
1. brain tumor or abscess
2. cerebral trauma or hemorrhage 3. meningitis 4. arachnoidal adhesions 5. cavernous or dural sinus thrombosis 6. encephalitis 7. idiopathic intracranial hypertension 8. pseudotumor cerebri - elevated CSF pressure and no mass lesion |
|
|
neovascularization of the retina is common in patients with ___:
this is called ___: |
diabetes mellitus
diabetic retinopathy |
|
|
retinal ischemia leads to release of ___ stimulating ___ on retina, optic nerve, or iris
|
a vasoproliferative factor
neovascularization |
|
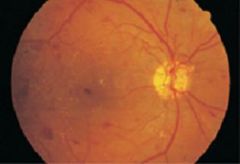
what does this image depict:
|
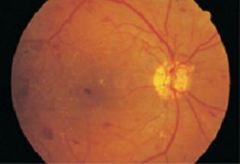
scattered hemorrhages and yellow exudates
|
|
|
when examining the retina, what findings are evident of hypertensive retinopathy: (x5)
|
1. Embolic plaques
2. “nicking” 3. scattered flame-shaped hemorrhages 4. very constricted arterioles 5. cotton-wool spots |
|
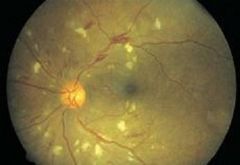
what is the diagnosis:
what do you call the white spots in this image: |
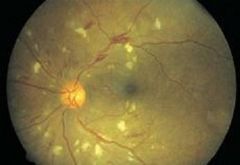
hypertensive retinopathy
cotton wool spots |
|
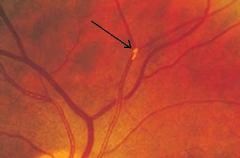
what is the arrow pointing to:
|
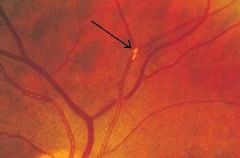
shedding emboli
|
|
|
a pulsatile abdominal mass is indicative of ___
|
abdominal aortic aneurysm
|
|
|
enlarged liver may be indicative of what: (x2)
|
heart failure
pericarditis |
|
|
systolic hepatic pulsations are indicative of ___
|
tricuspid regurgitation
|
|
|
a palpable spleen may be late signs of ___ or can be due to ___
|
severe heart failure
infective endocarditis |
|
|
ascites may occur with ___ and generally responds well to diuretic therapy
consider ___ if ascites is out of proportion to peripheral edema |
heart failure alone
constrictive pericarditis |
|
|
what is ascites:
|
excess fluid in the space between the tissues lining the abdomen and abdominal organs
|
|
|
a continuous murmur heard over the abdomen think ___:
|
arteriovenous fistula
|
|
|
systolic bruit heard over the kidney think ___:
|
renal artery stenosis
|
|
|
what may lead to identification of occlusive arterial lesions:
|
palpation of peripheral pulses in both upper and lower extremities
|
|
|
ischemic tissue damage of the toes presents late in what disease process:
|
peripheral atherosclerosis
|
|
|
___ may produce claudication of the buttock or lower extremities precedes physical exam findings for
|
peripheral atherosclerosis
|
|
|
what is claudication of the buttock:
|
pain or discomfort in a group of muscles, usually in the legs, hips, or buttocks and is worsened by exercise and relieved with rest
|
|
|
bilateral edema in the lower extremity may be a sign of ___ or may be secondary to ___ or ___
|
right sided heart failure
varicose veins thrombophlebitis |
|
|
unilateral lower extremity edema may be caused by: (x3)
|
saphenous vein harvest
DVT thrombophebitis |
|
|
what is the ankle-brachial index (ABI):
|
ratio of the systolic blood pressure at the ankle divided by the higher of the two arm systolic blood pressures
|
|
|
ABI indicates what:
what is an abnormal ABI: |
severity of lower-extremity arterial occlusive disease
ABI<0.9 |
|
|
ABI ___ is consistent with critical ischemia and tissue loss
|
<0.3
|
|
|
pressure is ___ distal to stenotic lesions
|
reduced
|
|
|
___ is a small weak pulse commonly due to what: (x3)
|
pulsus parvus
(↓)left ventricular stroke volume narrow pulse pressure (↑)peripheral vascular resistance |
|
|
when you see a Hypokinetic pulse think ___ (x3)
|
left ventricular failure
restrictive pericardial disease mitral stenosis. |
|
|
what is a hypokinetic pulse:
|
pulse with low volume and amplitude
|
|
|
what is pulsus tardus:
what is it indicative of:(x2) |
delayed systolic peak
(1) Obstruction of left ventricular ejection **(2) Aortic stenosis |
|
|
what kind of pulse is a hyperkinetic pulse:
what is it indicative of: (x8) |
bounding pulse
1. (↑)stroke volume 2. complete heart block 3. anxiety 4. anemia 5. exercise 6. fever 7. patent ductus arteriosus 8. peripheral arteriovenous fistula |
|
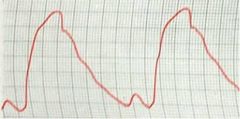
what is depicted in this image:
|
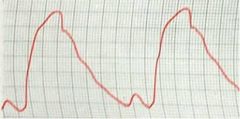
delayed systolic peak
|
|
|
bisferiens pulse is one that has what:
it is indicative of what: (x2) |
two systolic peaks
aortic regurgitation hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
|
|
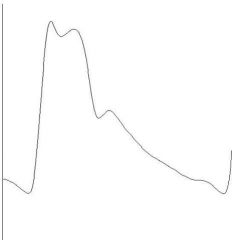
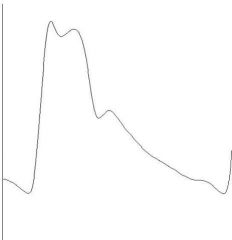
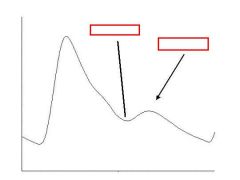
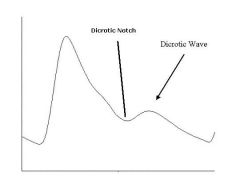
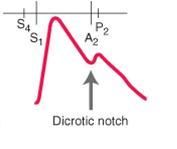
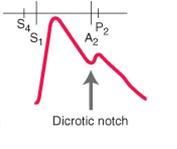
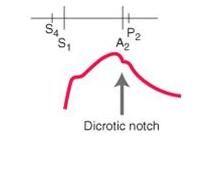
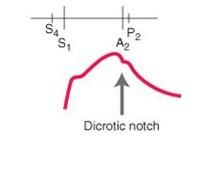
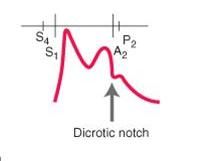
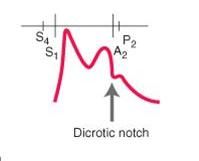
dicrotic pulse is one that has what:
it is indicative of what: (x2) |
one palpable wave one in systole and another palpable wave in diastole
very low stroke volume dilated cardiomyopathy |
|
what does the image depict:
|
pulsus bisferiens
|
|
identify the labeled figure:
|
(see figure)
|
|
identify the type of pulse:
|
normal
|
|
identify the type of pulse:
|
pulsus tardus
|
|
identify the type of pulse:
|
Pulsus bisferiens
|
|
what is the cardiovascular condition associated with this pulse:
|
hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
|
|
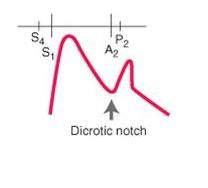
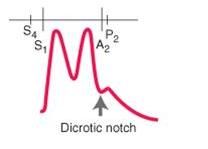
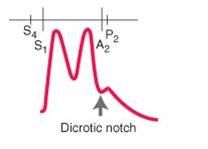
identify the type of pulse:
|
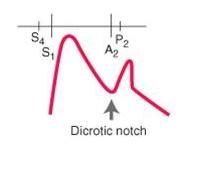
dicrotic pulse - has accentuated diastolic dicrotic wave that follows the dicrotic notch
|
|
|
what is Pulsus alternans:
|
regular rhythm but regular alteration of the pressure pulse amplitude
|
|
|
what is occurring in Pulsus alternans:
Pulsus alternans and loud S3 are associated with what: |
alternating left ventricular contractile force (strong beat/weak beat)
severe left-sided heart failure |
|
|
what pulse is associated with loud S3
|
Pulsus alternans
|
|
|
what is pulsus bigeminus characterized by:
how does it differ from pulsus alternans: |
regular rhythm and regular alteration of pressure pulse amplitude
Premature ventricular contraction (PVC) follows each regular beat |
|
|
what is pulsus paradoxus characterized by: (x2)
|
(1) accentuated inspiratory decrease in systolic arterial pressure beyond the normal/physiologic decrease of <=10 mmHg.
(2) peripheral pulse may completely disappear during inspiration |
|
|
pulsus paradoxus can be indicative of what: (x3)
|
pericardial tamponade
airway obstruction superior vena cava obstruction |
|
|
Radial and femoral arterial pulses should be what:
femoral pulse that is weakened and delayed during simultaneous palpation suggests what: |
virtually coincident
coarctation of the aorta |
|
|
what is coarctation of the aorta:
|
narrowing of the aorta between the upper-body artery branches and the branches to the lower body
|
|
|
what is the technique for inspection of waveform and estimation of the central venous pressure: (x2)
|
use right internal jugular vein
(2) pulsation is greatest when the trunk is inclined by less than 30° (patients with elevated venous pressure may require elevation of 90°) |
|
|
what does the jugular venous pulse reflect:
what does it consist of: |
phasic pressure changes in the right
2 or 3 positive waves and 2 negative troughs |
|
|
what is the dominant wave in the JVP:
what is it produced by: |
the "a" wave
venous distention due to right atrial contraction |
|
|
Right atrium contracting against increased resistance will cause ___ in the "a" wave
|
increase
|
|
|
what is the increasing resistance the causes an increase in the "a" wave: (x3)
|
tricuspid stenosis
pulmonary hypertension pulmonic stenosis |
|
|
atrial fibrillation will cause ___ "a" waves:
|
absent
|
|
|
slide 32
|
slide 32
|

