![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
vector means the same thing as …
|
replicon
|
|
|
|
DNA cloning means the same as …
|
molecular cloning
|
|
|
|
foreign DNA means the same as … or … DNA
|
insert
target |
None
|
|
|
what are the 4 essential steps in cell-based cloning?
|
1. Formation of recombinant DNA
2. Transformation 3. Amplification to produce numerous cell clones 4. Isolation of recombinant DNA clones |
None
|
|
|
how do you form a recombinant DNA?
|
separately digest purified DNA and vector DNA and with restriction endonuclease and then ligate together
|
|
|
|
describe step 2 - transformation:
|
introduce recombinant DNA into bacterial cells … the cells only take up one recombinant DNA
|
|
|
|
describe step 3 - amplification:
|
the transformed bacterial cells are plated and then individual colonies are picked up and grown in nutrient media
|
|
|
|
what is the 4th step in DNA cloning in bacterial cells?
|
isolation of recombinant DNA clones
|
|
|
|
… cleaves DNA at a recognition sequence
|
restriction enzyme/endonuclease
|
|
|
|
restriction enzyme recognition sequences have the properties of being …
|
palindromic
usually 4-6 bp in length |
None
|
|
|
the frequency of restriction sites on a DNA molecule depends on the …
|
length of the recognition site
|
|
|
|
DNA cleavage by restriction enzymes can produce either … or … ends
|
blunt
sticky |
None
|
|
|
what are the 2 properties that a cleaved DNA has due to the sequence being palindromic:
|
cleaved ends are complimentary
two strands have same nucleoide sequence running 5' to 3' |
None
|
|
|
a. EcoRI
b. SmaI |
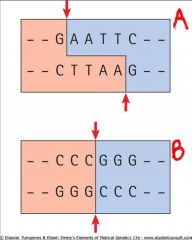
identify the restriction enzyme belonging to the identified recognition site:
a. b. |
|
|
|
what is the function of DNA ligases?
|
rejoins sticky or blunt ends by reforming the phosphodiester bond
|
|
|
|
a restriction enzyme with a recognition site that is 4 bps long will cut every … bases
|
4^4 (258)
|
|
|
|
a restriction enzyme with a recognition site that is 6 bps long will cut every … bases
|
4^6 (4096)
|
|
|
|
… is used to separate digested DNA according to it's size
|
gel electrophoresis
|
|
|
|
migration through the gel matrix in an electric field is influenced by … and … and …
|
size
charge shape |
None
|
|
|
the overall charge of DNA is …
|
negative
|
|
|
|
larger DNA fragments will migrate (faster/slower) than smaller fragments in gel electrophoresis
|
slower
|
|
|
|
what is the base pair difference that gel electrophoresis can detect?
|
1 bp
|
|
|
|
positive
negative |
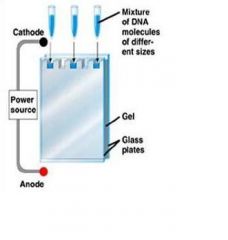
Anode: an electrode from which electrons flow out of create a … charge
Cathode: an electrode in which electrons flow into creating a ... charge |
None
|
|
|
vector DNA is also know as a …
|
plasmid
|
|
|
|
plasmids are extrachromosomal elements that:
|
a. incorporate themselves in host DNA
b. replicate autonomously |
None
|
|
|
the larger the insert size of the DNA the (lower/higher) the overall yield
|
lower
|
|
|
|
the hybrid - the combination of the vector and the insert (foreign) DNA is also known as …
|
recombinant DNA
|
|
|
|
heat shock is a method used for … (used to temporarily disrupt the cell membrane of the host bacteria
|
transformation
|
|
|
|
competence is …
|
the ability of a cell to take up DNA from the environment
|
|
|
|
PCR stands for …
|
polymerase chain reaction
|
|
|
|
what are the 4 ingrediants for PCR?
|
1. DNA sample to be amplified
2. complementary primars for 3' flanking regions of your target DNA (in excess) 3. Deoxyribonucleotides (in excess) 4. Heat-stable DNA polymerase |
None
|
|
|
which DNA polymerase lacks 3' to 5' exonuclease activity and has a low fidelity?
|
taq (thermus aquaticus)
|
|
|
|
which DNA polymerase has 3' to 5' exonuclease activity and has a high fidelity?
|
pfu (pyrococcus furiosus)
|
|
|
|
PCR has 3 series of successive reactions, what are they?
|
1. denaturation of DNA
2. annealing of primer 3. DNA synthesis |
|
|
|
why would one want to clone a PCR product?
|
the amount of DNA from PCR reaction is limited
|
|
|
|
what is T-A cloning?
|
taq leaves a 3' 'A' overhang in PCR products and the products can be ligated into vectors with 5' 'T' overhangs
|
|
|
|
pfu creates (sticky/blunt) end clones
|
blunt
|
|
|
|
briefly describe a southern blot:
|
DNA is electorphoresed and transferred to a membrane. DNA clone is then used as a hybridization probe against target DNA from gel
|
|
|
|
briefly describe a northern blot:
|
RNA is electorphoresed and transferred to a membrane. a hybridization probe is then used to detect target RNA.
|
|
|
|
briefly describe a western blot:
|
proteins are size fractionated on a polyacrylamide gel and then probed with an antibody
|
|
|
|
a working form of a hybridization probe must be ... stranded and must be ...
|
single
labeled (radioactive or fluorescence) |
|
|
|
put the following steps in order:
a. Separate DNA digests by electrophoresis b. Expose membrane to x-ray film c. Digest with restriction endonuclease d. Transfer DNA from gel to membrane e. Hybridize membrane with probe |
c, a, d, e, b
|
|

