![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
fatty acids are synthesized mainly in the ... but can also be synthesized and ... tissue or ... tissue
|
liver
adipose mammary |
|
|
dietary ... serves as the major source of ...
|
glucose
carbon |
|
|
glucose must first be converted to ... which provides the 2-carbon units that condense to form a fatty acid chain
|
acetyl CoA
|
|
|
a. pyruvate dehydrogenase
b. acetyl CoA c. citrate d. citrate e. citrate lyase f. acetyl CoA |
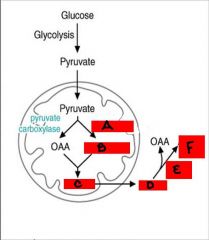
identify the following:
a. (enzyme) b. (product) c. (product) d. (product) e. (enzyme) f. (product) |
|
|
... cannot cross mitochondrial membrane and must be converted into ... first
|
citrate
|
|
|
... continuously synthesized and transported out of mitochondria into cytosol through ... regulation
|
citrate
reciprocal |
|
|
citrate is formed by the condensation of ... and ... this condensation reduces the levels of ... in the mitochondria, thus driving pyruvate dehydrogenase to make more ...
|
acetyl-CoA
OAA acetyl-CoA acetyl-CoA |
|
|
describe the recycling of oxaloacetate after citrate is cleaved into acetyl-CoA and OAA:
|
OAA is converted into malate and then finally back to pyruvate
|
|
|
NADPH is required for fatty acid synthesis and is generated through 2 pathways:
1. 2. |
pentose phosphate pathway
by malic enzyme during the recycling of OAA |
|
|
insulin activates ... which drives mitochondrial formation of acetyl CoA
|
pyruvate dehydrogenase
|
|
|
insulin induces synthesis of ... and ... both increase NADPH levels
|
malic enzyme
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase |
|
|
insulin induces ... which increases cytosolic levels of acetyl CoA and recycles oxaloacetate
|
citrate lyase
|
|
|
cytosolic acetyl CoA converted to ... which serves as the immediate donor of 2-carbon units that are added to the growing fatty acid chain
|
malonyl CoA
|
|
|
conversion of acetyl CoA to malonyl CoA requires:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
acetyl CoA carboxylase
biotin CO2 ATP |
|
|
the conversion of acetyl CoA to malonyl CoA is heavily ... and is a rate ... step
|
regulated
limiting |
|
|
... sequentially adds 2-carbon units from malonyl CoA to the growing fatty acyl chain to form ... (C16:0)
|
fatty acid synthase
palmitate |
|
|
fatty acid synthase complex involves ... derived from the vitamin ... and ...
|
phospho-pantetheine
pantothenic acid an acyl carrier protein (ACP) |
|
|
fatty acid synthase is a single enzyme consisting of a ... of 2 large polypeptide chains containing several functional domains
|
homodimer
|
|
|
acetyl and malonyl attach to the ACP phosphopantetheinyl sulfhydral group, then condense to form a 4 carbon ... chain.
|
alpha-keto acyl
|
|
|
in the fatty acid synthase reaction, ... provided the reducing equivalents to drive this elongation of the original acetyl group by 2 carbons.
|
NADPH
|
|
|
in the fatty acid synthase reaction after reduction, in each subsequent round of elongation, a new ... group attaches to the FAS complex and condenses with the newly forming fatty acid chain.
|
malonyl
|
|
|
the elongation of fatty acid chain occurs via 4 recurring reactions:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. condensation
2. reduction 3. dehydration 4. reduction |
|
|
the end product of the fatty acid synthase (FAS) complex is ...
|
palmitate (C16:0)
|
|
|
palmitate is activated forming ...
|
palmityl CoA
|
|
|
palmityl CoA is then used, along with ... and ... to form longer chain fatty acids within the ...
|
malonyl CoA
NADPH endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
desaturation of fatty acids most commonly involves the placement of a double bond between carbons ... and ... and requires:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
9
10 1. O2 2. NADH 3. cytochrome b5 4. desaturase enzyme |
|
|
there are three main families of unsaturated fatty acids:
1. 2. 3. |
omega 3
omega 6 omega 9 |
|
|
omega fatty acids are named by the double bonds are in association with the ... end
|
methyl
|
|
|
... is an omega-6 essential fatty acid
|
linoleic acid
|
|
|
... is an omega-3 essential fatty acid
|
alpha-linolenic acid
|
|
|
these fatty acids are essential because mammals lack the ability to introduce double bonds in fatty acids beyond carbon ... and ... because they lack the ... enzyme
|
9
10 desaturase |
|
|
essential fatty acids are converted into ... and other ...
|
prostaglandins
eicosanoids |
|
|
the omega-6 fatty acids ... and ... are precursors for prostaglandins and other eicosanoids and are essential for ...
|
linoleic acid
arachidonic acid development brain, eyes, dermal support, renal function and parturition |
|
|
omega-6 fatty acids from from ... oils
|
plant
|
|
|
omega-6 fatty acids are (pro/anti) -inflammatory agents and omega-3 fatty acids are (pro/anti) -inflammatory agents
|
pro
anti |
|
|
identify some sources for omega-3 fatty acids:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. |
Cold water fish (like salmon)
Flaxseed Eggs Walnuts Grass-fed animals |
|
|
name 3 omega-3 fatty acids:
1. 2. 3. |
alpha-linolenic acid (ALA, 18:3)
eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, 20:5) docosahexanoic acid (DHA, 22:6) |
|
|
omega 3 fatty acids decrease risk of ... improve ... and learning and raise ...DL and lower ...DL
|
heart disease
memory H L |
|
|
symptoms of omega-6 fatty acid deficiency:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
growth retardation
skin lesions reproductive failure fatty liver |
|
|
symptoms of omega-3 fatty acid deficiency:
1. 2. 3. |
learning deficiencies
impaired visual acuity depression |
|
|
the first step in synthesis of triglycerides is generation of ... from ... via ...
|
glycerol 3-phosphate
glucose dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) |
|
|
step 2 in triglyceride synthesis is ... with ATP and ... forming a fatty acyl CoA
|
fatty acid activation
fatty acyl CoA synthetase |
|
|
step 3 in triglyceride synthesis: ... reacts with fatty acyl CoA forming ... which then dephosphorylates forming ...
|
glycerol 3-phosphate
phosphatidic acid diacylglycerol (DAG) |
|
|
the 4th step in triglyceride synthesis involves the addition of a third and final fatty acyl CoA, forming a ...
|
triacylglycerol
|
|
|
in step 5 in triglyceride synthesis, the triglyceride incorporated into ... particles or stored as adipose
|
VLDL
|
|
|
VLDL stands for ...
|
Very Low Density Lipoprotein
|
|
|
fatty acids for VLDL synthesis in the liver, are obtained form ... or synthesized from ...
|
blood
glucose |
|
|
the function of the VLDL is to transport ... to ... and ...
|
triglycerides
muscle adipose |

