![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
in cellular ion gradients, which ion is the only one with higher concentrations inside the cell? (all the others have higher concentrations outside the cell)
|
k⁺
|
|
|
which side of a cell is typically more negative?
|
the inside
|
|
|
what does this describe:
spontaneous movement of molecules from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration (“downhill”, movement along a concentration gradient) |
simple diffusion
|
|
|
what are the molecules involved in simple diffusion:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. |
1. O2
2. CO2 3. H20 4. ethanol 5. steroid hormones 6. hydrophobic vitamins |
|
|
the following describes what:
transmembrane protein creates a water-filled pore through which ions and other small hydrophilic molecules can pass by diffusion |
facilitated diffusion
|
|
|
in facilitated diffusion transmembrane proteins have channels that are regulated or ... to control amount of diffusion allowed across membrane
|
“gated”
|
|
|
the below describes what:
small signaling molecule (or ligand) binds to a channel, creating a conformational change that “opens” the channel |
ligand-gated ion channels
|
|
|
... is an extracellular ligand that opens Na+ channels in neurons to initiate a nerve impulse
|
Acetylcholine
|
|
|
... is an extracellular ligand that opens Cl- channels to inhibit creation of a nerve impulse
|
GABA
|
|
|
examples of intracellular ligands are:
1. 2. 3. |
1. cAMP (olfaction)
2. cGMP (vision) 3. ATP opens Cl- and HCO3- channels |
|
|
stereocilia of hair cells in the cochlea get distorted or bent by sound waves which
opens Na+ channels to create nerve impulse that brain interprets as a sound this is an example of ... |
mechanically-gated ion channels
|
|
|
Stretch receptors in tendons and muscles are examples of ...
|
mechanically-gated ion channels
|
|
|
in ... some channels open in response to local changes in charge across the plasma membrane
2 types of cells that do this are: 1. 2. |
voltage-gated ion channels
muscle neuron |
|
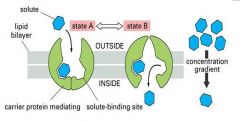
what kind of transport is this and what is happening with the transport protein?
|
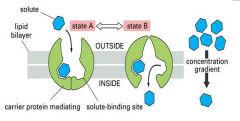
passive transport
conformational change |
|
|
... transport is against the concentration gradient and requires ...
|
active
ATP |
|
|
what are the following:
Na+/K+ ATPase H+/K+ ATPase Ca2+ ATPase |
transmembrane transporters that possess ATPase activity
|
|
|
... is found in almost every cell and uses ⅓ of the cell’s supply of ATP. it pumps out ... Na+ for every ... K+ it pumps in
|
Na+/K+ ATPase
3 2 |
|
|
why is Na+/K+ ATPase important?
1. 2. 3. |
1. establishes a net charge across the plasma membrane called
2. helps to maintain osmotic balance 3. gradient of Na+ ions harnessed to provide energy to drive several secondary active transporters |
|
|
the interior of the cell being more negatively charged with respect to the exterior is known as ...
|
resting membrane potential
|
|
|
... uses the downhill flow of one ion to pump some other molecule or ion against its concentration gradient
driving ion is usually ... the pumped molecule can move in same direction ... as ... or opposite direction ... as ... |
coupled or secondary active transport
Na+ symport Na+ antiport Na+ |
|
|
where would you find Na+/glucose transporter (a symport) and why?
|
in intestinal epithelium and kidney tubules ensures glucose is transported back into the bloodstream
|
|
|
where would you find amino acid symporters.
|
kidneys and in synaptic clefts
|
|
|
special term used to describe the diffusion of water through a cell membrane is known as ...
|
osmosis
|
|
|
osmosis can include facilitated diffusion through water channels called ...
|
aquaporins
|
|
|
... solutions have a concentration of water that is greater outside the cell due to lower solute concentration
|
Hypotonic
|
|
|
... solutions have a concentration of water that is lower outside the cell due to higher solute concentration
|
Hypertonic
|
|
|
... solutions are where concentration of water and total solute are equal inside and outside the cell
|
Isotonic
|
|
|
when a cell shrinks and shrivels it is called ...
|
crenation
|
|
|
cystic fibrosis is a ... channel disease where there is a mutation in ... that results in defective ... ion transport
|
Chloride
CFTR gene (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator) Cl- |
|
|
CF is the most common lethal inherited disease of ... (1 in 2500) where the average life expectancy is 37 years.
lung disease responsible for ... of mortality and the incidence of heterozygous carriers: 1 in ... |
Caucasians
95% 25 |

