![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the three layers (tunics) of the eye:
1. 2. 3. |
1. fibrous (external) tunic
2. vascular (middle) tunic or uvea. 3. nervous tunic (retina) |
|
|
the fibrous tunic consists of:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. sclera
2. limbus 3. cornea 4. conjunctiva |
|
|
the conjunctiva consists of 2 parts. what are they and what do they cover:
1. 2. |
1. bulbar - covers the front, external eyeball
2. palpebral -lines the under surface of the eyelids |
|
|
what kind of muscles insert into the sclera?
|
Extraocular skeletal muscles
|
|
|
the sclera consists of a vascularized dense regularly arranged connective tissue, what is its functions:
|
maintains the size and form of the eye.
|
|
|
what is the blood supply to the cornea?
|
it has no direct blood supply
|
|
|
the outermost layer of the cornea is called the ... and is a stratified squamous, nonkeratinized epithelium
|
Anterior epithelium
|
|
|
underneath the anterior epithelium of the cornea is ... - a basement membrane network of irregular fine fibrils of collagen.
|
Bowman's membrane
|
|
|
the largest cornea layer is the ... and it constitutes the bulk of cornea, consists of many orthogonal laminae of highly ordered, uniform collagen fibrils with fibroblasts between the laminae.
|
stroma
|
|
|
just beneath the stroma layer lies ... an acellular, homogenous basement membrane, made of an atypical form of collagen. and just beneath that is the final layer,
... that forms the posterior surface of cornea and is a single layer of squamous to cuboidal cells. |
Descemet's membrane
Endothelium (mesenchymal epithelium) |
|
|
the junction between transparent cornea and opaque sclera is called the ...
|
corneoscleral junction or limbus
|
|
|
the vascular tunic consists of:
1. 2. 3. |
1. choroid
2. ciliary body 3. iris |
|
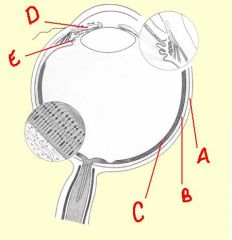
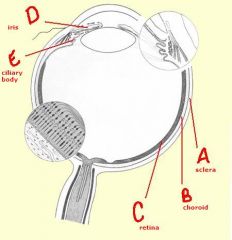
identify the labeled structures:
|
(see figure)
|
|
|
the ... lies just beneath the sclera and is heavily vascularized and contains many pigment-containing cells in stroma.
|
vascular tunic
|
|
|
Innermost portion of choroid contains numerous capillaries (choriocapillary layer), which provides nutritional exchange for outermost layers of the retina through ... (basal lamina).
|
Bruch's membrane
|
|
|
... contains the ... muscle (smooth muscle) which is used to change the shape of the lens by way of the ... fibers.
|
ciliary body
ciliary ciliary zonule |
|
|
the ... is in the anterior portion of uvea. It is a diaphragm which controls amount of light entering the eye
|
iris
|
|
|
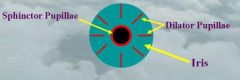
... and ... muscles in the stroma of the iris control pupillary size.
|
sphincter pupillae
dilator pupillae |
|
|
the stroma of the iris also contains pigmented cells called ...
|
melanocytes
|
|
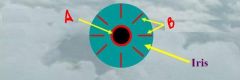
identify the labeled iris muscles:
a. b. |
(see figure)
|
|
|
the lens is a transparent, flexible, biconvex disc which functions in near and distant vision. Changes of its curvature (shape), due to the action of the ... and ... change the focal point on the retina.
|
zonule fibers
ciliary muscles |
|
|
to what do the ciliary zonule fibers attach?
|
lens capsule
|
|
|
the anterior portion of the lens is covered with ... cells and the lens substance is composed of laminated interdigitating elongated cells called ...
|
simple cuboidal epithelial
lens fibers |
|
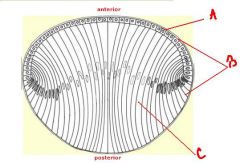
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. |
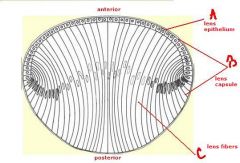
(see figure)
|
|
|
what is accommodation:
|
when the eye accommodates for close vision
|
|
|
what happens in accommodation:
1. 2. 3. |
convergence of eyes
curvature of lens increased pupil constricts |
|
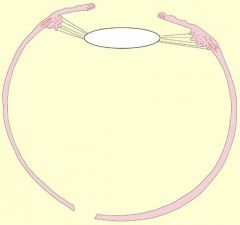
is this near or far vision?
|
far vision
|
|
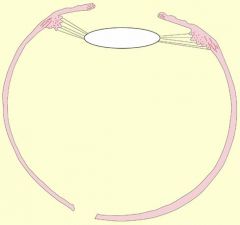
is this near or far vision?
|
near vision
|
|
|
what is the aqueous humor composed of and what is it produced by:
|
mostly water and practically no proteins, and is produced by the cells on the ciliary processes
|
|
|
where is the aqueous humor located:
|
anterior and posterior chambers of the eye
|
|
|
Fills the space (vitreous cavity) between lens and retina. This gel is 99% water and also contains collagen fibers and glycosaminoglycans (mainly hyaluronic acid).
|
Vitreous Body
|
|
|
circular channel in the eye that collects aqueous humor from the anterior chamber and delivers it into the bloodstream
|
canal of Schlemm
|
|
|
spongy, mesh-like tissue surrounding the iris that allows the aqueous fluid (humor) to flow to Schlemm's canal then out of the eye through ocular veins.
|
spaces of fontana
|
|
|
what layer of the eye does this describe:
The inner coat of the posterior part of the eye that contains photoreceptors |
Nervous Tunic (Retina)
|
|
|
specialized area where vision is most acute is the ... where photoreceptors are essentially bare
|
fovea centralis (macula)
|
|
|
fovea centralis (macula) contains only ...
|
cones
|
|
|
the ... where the optic nerve leaves the eye and there are no photoreceptors
|
optic papilla
|
|
|
... layer of the retina prevents diffusion of light between photoreceptors and makes contact with ... membrane of the choroid
|
Pigment epithelium
Bruch's |
|
|
the next layer after the pigment epithelium is the layer of ... followed by the ... layer that contains ... belonging to ...
|
rods and cones
Outer nuclear nuclei rods and cones |
|
|
photoreceptors are ...
|
rods and cones
|
|
|
the layer where rods and cones synapse with bipolar cells is called the ... layer
|
Outer plexiform
|
|
|
the ... layer contains nuclei belonging to bipolar cells
|
Inner nuclear
|
|
|
the ... layer is where bipolar cells synapse with ganglion cells
|
Inner plexiform layer
|
|
|
the ... layer contains nuclei of ganglion cells
|
Ganglion cell
|
|
|
the ... layer consists of the central processes (axons) of the ganglion cells which gather together at the optic papilla, pass through the sclera and leave the eye as the optic nerve.
|
Optic nerve fiber
|
|
|
as the optic nerve leaves the rear of the eyeball, the optic nerve fibers become myelinated by the action of ...
|
oligodendrocytes
|
|
|
... make interconnections with rods and cones
|
horizontal cells
|
|
|
... make interconnections with ganglion cells
|
amacrine cells
|
|
|
... are supportive neuroglial cells
|
Müller cells
|
|
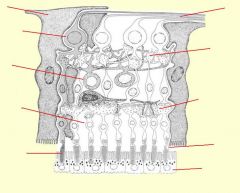
identify the layers of the retina:
|
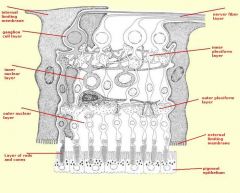
(see figure)
|
|
|
the ... is a movable fold of skin which protects and lubricates the eye
|
eyelid
|
|
|
the ... is Mucous membrane which covers inner surface of eyelid and part of sclera. It is continuous with the anterior corneal epithelium at the limbus
|
conjunctiva
|
|
|
the ... located in superior lateral region of orbit, it produces tears which act to lubricate the conjunctival surface of the eyeball and eyelid
|
lacrimal gland
|
|
|
the lacrimal gland has several excretory ducts which open laterally into the ... of the eye
|
fornix
|
|
|
Tears are drained ... from the eye surface into the ... that open up into the superior and inferior ... then into the ... and down to the ...
|
medially
lacrimal puncta lacrimal canaliculi lacrimal sac nasolacrimal duct |
|
|
the eye arises from the ... around the 22nd-28th day, and induces special structures that develop out of ... and ...
|
diencephalon
ectoderm mesoderm |
|
|
the initial structure of the eye is called the ...
as it develops it interacts with ectoderm and mesoderm to form the structure that we ultimately see as the eye. |
optic vesicle
|
|
|
Optic cup forms at ... days which is induced by the ...
Lens vesicle forms at ... days which is formed from ... |
32
Lens vesicle 30 ectoderm |
|
|
Lens vesicle induces invagination of optic vesicle to become ... at 32 days.
|
optic cup
|
|
|
Mesodermal derivatives of eye:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. Sclera
2. Choroid layer 3. Ciliary body 4. Muscles of iris |
|
|
Ectodermal derivatives of the eye:
|
1. Lens
2. Cornea |
|
|
Neural derivatives of eye:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. Pigment epithelium
2. Neural retina 3. Pigmented portion of iris 4. Optic nerve |
|
|
Note, vitreous humor and aqueous humor spaces were formerly ... cells left to create acellular space.
|
mesodermal
|
|
|
The optic cup leaves a slit on its inferior portion, called the ... that allows the central artery of the retina to grow into it
|
choroid fissure
|
|
|
Failure of fusion of the choroid fissure creates ... that may only involve iris, or may include inferior part of retina
|
a slit under the eye
|

