![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
process of membrane trafficking begins with the transport of material from the rER to the ... this is performed by budding off of membrane-bound vesicles called ...
|
Golgi
transport vesicles |
|
|
vesicles formed from the rER are coated on the ... side of the membrane by ... protein.
|
cytoplasmic
COPII |
|
|
The membranes of the transport vesicles lose their coat and fuse with the membranes of the ...-face of the ...
|
cis
Golgi |
|
|
transported material and membranes are then further transported through other stacks of the Golgi by a similar process of ... and ...
and along the way, cargo proteins are modified by various ... within the different stacks |
budding
fusion enzymes |
|
|
terminal N- and O-glycosylation and phosphorylation of lysosomal enzymes happens in ...
|
golgi
|
|
|
cis-most cisternae contain a higher content of ... in their membranes and thus can be identified by osmium tetroxide reduction.
|
lipid
|
|
|
middle and trans-side cisternae contain a higher content of ... enzymes and can be identified by reactions for these enzymes activities.
|
glycosylation
|
|
|
trans-most cisternae (trans Golgi network) is the site where ... are produced and contain ... marker activities.
|
lysosomes
lysosomal |
|
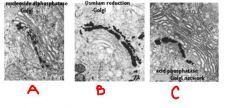
identify what part of golgi is being stained:
a. b. c. |
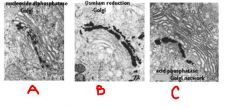
a. middle and trans-side cisternae
b. cis-most cisternae c. trans-most cisternae |
|
|
Golgi is the major center for trafficking of:
1. 2. 3. |
1. membrane proteins
2. secretory proteins 3. lysosomes |
|
|
there is also a retrograde transport between the Golgi stacks and the ...
|
rER
|
|
|
retrograde transport involves an ER receptor and a coating protein called ... Thus, the ... is also the source of mature proteins for the ...
|
COPI
Golgi rER |
|
|
what are the 2 types of secretion for proteins:
1. 2. |
1. constitutive
2. regulated |
|
|
digestion of extracellular substances and intracellular organelles by ... is called ...
|
lysosomes
autophagy |
|
|
lysosomal enzymes and lysosomal membrane proteins are transported to primary lysosomes by a ... system.
|
mannose-6-phosphate receptor
|
|
|
Several highly glycosylated integral membrane glycoproteins have been identified in lysosomes which have been found to be ... by lysosomal enzymes
|
resistant to degradation
|
|
|
the following are examples of what:
-Defects in genes that code specific enzymes -Molecules to be degraded build up & are stored in lysosomes -Some organs affected more than others -Most often kidney, liver & brain -Symptoms mild to death -I cell disease: Defect in M6P phosphotransferase – enzymes secreted |
Lysosomal Storage Diseases
|
|
|
one of the glycosylated integral membarane proteins identified in the lysosome is an ATP-driven proton pump, which is believed to be responsible for ... found in the lumen of the lysosome
|
maintenance of the pH < 5.0
|

