![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
internal carotid artery is intracranial except for ...
|
forehead
|
|
|
external carotid is extracranial except for ...
|
meninges
|
|
|
spinal nerves have ... and ... functions, some cranial nerves are strictly ..., some are strictly ... and some are mixed
|
sensory
motor motor sensory |
|
|
CN 2 (sensory/motor/mixed)
|
sensory
|
|
|
CN 6 (sensory/motor/mixed)
|
motor
|
|
|
CN 5 (sensory/motor/mixed)
|
mixed
|
|
|
which CN's have parasympathetic function
|
3, 7, 9, and 10
|
|
|
Lateral Rectus (eye muscle) is innervated by:
|
CN6
|
|
|
Superior Oblique (eye muscle) is innervated by:
|
CN4
|
|
|
the muscles of the eye are innervated by ... with the exception of 2 mucscles
|
CN3
|
|
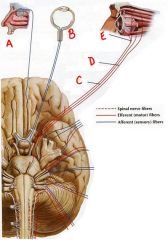
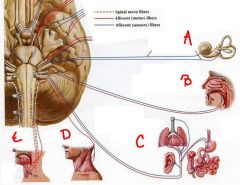
identify the labeled cranial nerves by name and number:
a. b. c. d. e. |
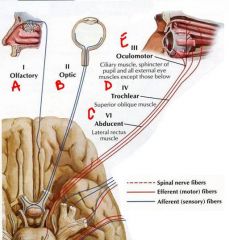
a. cn1 olfactory
b. cn2 optic c. cn6 abducent d. cn4 trochlear e. cn3 oculomotor |
|
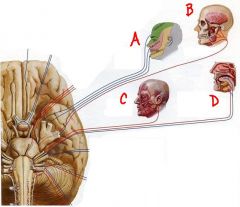
identify the labeled nerve and a brief description of function:
a. b. c. d. |
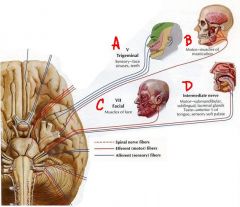
a. cn5 (trigeminal)- sensory face
b. cn5 (trigeminal)- muscles of mastication c. ch7 (facial)- muscles of facial expression d. intermediate nerve - taste ant. 2/3 tongue(sensory) and submandibular, sublingual, lacrimal glands (motor) |
|
identify the cranial nerves by name and number:
a. b. c. d. e. |
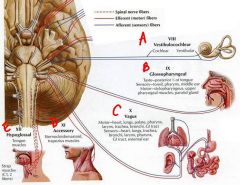
a. cn8 - vestibulocochlear
b. cn9 - glossopharyngeal c. cn10 - vagus d. cn11 - accessory e. cn12 - hypoglossal |
|
identify the labeled structures/areas:
a. b. c. d. e. identify the target tissue: 1. 2. 3. |
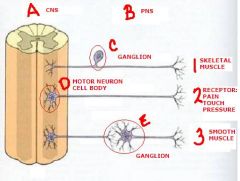
a. cns
b. pns c. ganglion d. motor neuron cell body e. ganglion 1. skeletal muscle 2. receptors: pain/pressure/touch 3. smooth muscle |
|
|
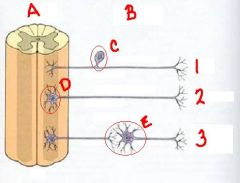
sensory ganglia have cell bodies an (no/a) synapse. autonomic ganglia have cell
bodies and (no/a) synapse. |
no
a |
|
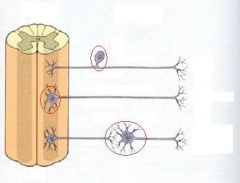
identify the directions of the nerve impulses:
|
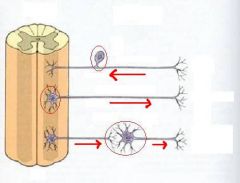
<--
--> --> |
|
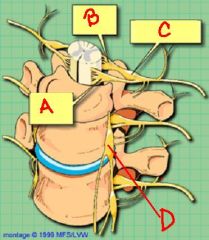
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. d. where are the cell bodies of origin for axons at this point? |
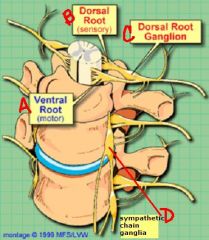
a. ventral root
b. dorsal root c. dorsal root ganglion d. sympathetic chain ganglia |
|
|
cranial nerves that have sensory function have sensory ganglia like DRGs but these ganglia are individually named. CN 5 has the ... ganglion and CN 7 has the ... ganglion
|
Trigeminal
Geniculate |
|
|
sympathetic nerves come from the ... regions of the spinal cord. The preganglionic nerves are (long/short) and synapse where? the postganlionic fibers are (long/shrort)
|
thoracolumbar
short adjacent to the spinal cord long |
|
|
parasympathetic nerves come from the ... regions of the CNS. They have (long/short) preganglionic nerves which synapse where? the postganlionic fibers are (long/shrort)
|
craniosacral
long ganglia near or on target organ short |
|
|
what is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
|
the 4 f's
fight flight fear sex |
|
|
what is the function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
|
homeostasis
|
|
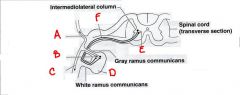
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. d. e. f. |
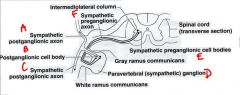
a. sympathetic postganglionic axon
b. postganglionic cell body c. sympathetic postganglionic axon d. paravertebral (sympathetic) ganglion e. sympathetic preganglionic cell body f. sympathetic preganglionic axon |
|
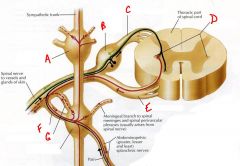
identify the labeled structures:
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. |
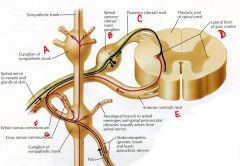
(answers on slide)
|
|
|
a. T1
b. L2 The only place you will find white rami are from T1 to L2 |
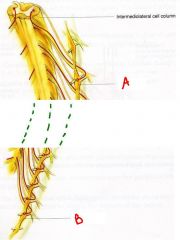
identify T1 and L2 ganglion:
a. b. what makes L2 different from L3? |
|
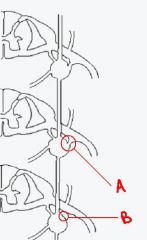
how does a differ from b?
|
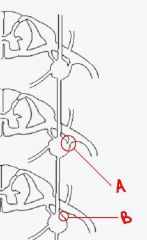
a has white rami while b does not. a is the rami at L2 and b is the rami at L3
|
|
|
sympathetics to the head virtually all come from the ... spinal cord level
|
T1
|
|
|
sympathetics to the head do what to the eyelid?
|
keep the eyelid open
|
|
|
sympathetics to the head ... the pupil while parasympathetics ... the pupil
|
dialate
constrict |
|
|
sympathetics to the head ... the blood vessels in the face
|
constrict
|
|
|
(sympathetics/parasympathetics) innervate the sweat glands?
|
sympathetics
|
|
|
what happens if you lose the sympathetics to the face? (what is this syndrome called)
|
Horner’s Syndrome
|
|
|
what are the symptoms of horner's syndrome:
1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. constricted pupil
2. droopy eyelid 3. red Face 4. dry Face |
|
|
what are some possible lesions for horner's syndrome?
1. 2. 3. 4. |
1. lower brachial plexus injury
2. tumor of the lung 3. problems with the carotid artery 4. whiplash |
|
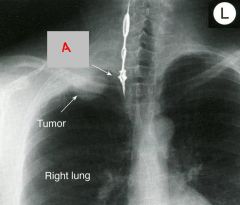
identify the labeled structure:
a. what is the significance of this xray? |
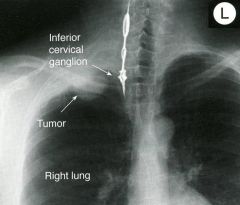
inferior cervical ganglion
the tumor can possibly compress the ganglion causing horner's syndrome |

