![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
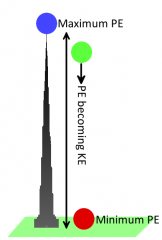
Gravitational Potential Energy
|
An object possesses because of its position in a gravitational field.
|
|
|
|
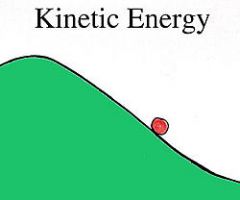
Kinetic Energy
|
Is an energy that it possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity.
|
|
|
|
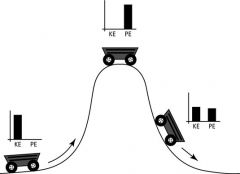
Mechanical Energy
|
Is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy. It is the energy associated with the motion and position of an object.
|
|
|
|
Conservation of Energy
|
The law states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant - it is said to be conserved over time.
|
|
|
|
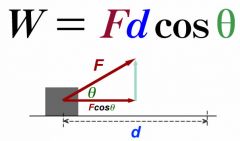
Work
|
Work is done when a force that is applied to an object moves that object.
|
|
|
|
Power
|
Is the rate of doing work. It is equivalent to an amount of energy consumed per unit time.
|
|
|
|
Simple Machines
|
Is a mechanical device that changes the direction or magnitude of a force.
|

|
|
|
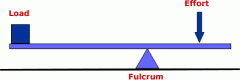
Lever
|
Is a machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or fulcrum.
|
|
|
|
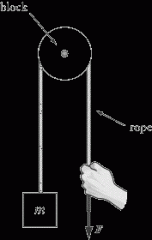
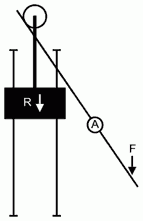
Pulley
|
A machine consisting of a wheel over which a pulled rope or chain runs to change the direction of the pull used for lifting a load.
|
|
|
|
Incline Plane
|
A sloping ramp up which heavy loads can be raised by ropes or chains.
|
|
|
|
Wedge
|
A piece of hard metal with two principal faces meeting in a sharply acute angle, for raising, holding, or splitting objects by applying a pounding or driving force, as from a hammer.
|
|
|
|
Screw
|
A metal fastener having a tapered shank with a helical thread, and topped with a slotted head, driven into wood or like by rotating, especially by means of a screwdriver.
|
|
|
|
Wheel & Axle
|
A simple machine consisting, in its typical form, of a cylindrical drum to which a wheel concentric with the drum is firmly fastened.
|
|
|
|
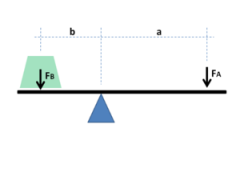
Mechanical Advantage
|
Is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system.
|
|
|
|
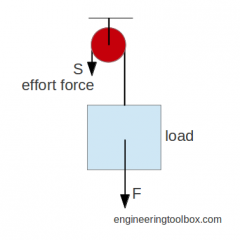
Effort ( input ) Force
|
Is the force that moves an object over a distance by overcoming a resistance force.
|
|
|
|
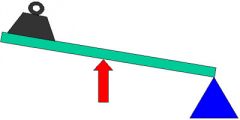
Resistance (output) Force
|
Is the force which an effort force must overcome in order to do work on an object via a simple machine.
|
|
|
|
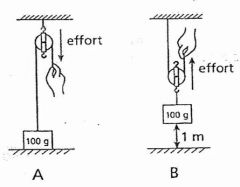
Effort (input) Distance
|
The distance from the effort on a lever to the fulcrum.
|
|
|
|
Resistance (output) Distance
|
Between two vertices of a simple connected graph, G, is equal to the resistance between two equivalent points of an electrical network.
|
|

