![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Explain the action of clomiphene for ovulation induction and name the two other things also used for ovulation induction (mentioned in REI cases).
|
Clomiphene - is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). Completitively inhibits estrogen binding to estrogen receptors at hypothalamus and pituitary, thus causing gonadotropin release from pituitary which thus stimulates follicle development in ovaries.
Letrozole - Inhibits aromatase (in granulosa cells), thus disables the androgen to estrogen conversion. So, end result is increased FSH. Gonadotropins (LH and FSH) given as injections. |
|
|
Explain the action of letrozole for ovulation induction and name the two other things also used for ovulation induction (mentioned in REI cases).
|
Letrozole - Inhibits aromatase (in granulosa cells), thus disables the androgen to estrogen conversion. So, end result is increased FSH.
Clomiphene - is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). Completitively inhibits estrogen binding to estrogen receptors at hypothalamus and pituitary, thus causing gonadotropin release from pituitary which thus stimulates follicle development in ovaries. Gonadotropins (LH and FSH) given as injections. |
|
|
Explain the action of gonadotropin injections for ovulation induction and name the two other things also used for ovulation induction (mentioned in REI cases).
|
They stimulate the follicles like a normal dose would.
Letrozole - Inhibits aromatase (in granulosa cells), thus disables the androgen to estrogen conversion. So, end result is increased FSH. Clomiphene - is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). Completitively inhibits estrogen binding to estrogen receptors at hypothalamus and pituitary, thus causing gonadotropin release from pituitary which thus stimulates follicle development in ovaries. |
|
|
List some treatment options for hirsutism (7 mentioned).
|
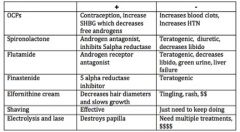
|
|
|
Sprinonolactone is a treatment option for hirsutism. How so? What are some positives and negatives?
|

|
|
|
Flutamide is a treatment option for _____________. How so? What are some positives and negatives?
|
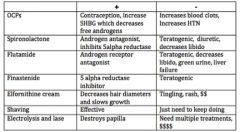
Hirsutism
|
|
|
Finasteride is a treatment option for _____________. How so? What are some positives and negatives?
|
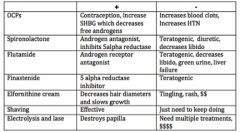
Hirsutism
|
|
|
Elfornithine cream is a treatment option for _____________. How so? What are some positives and negatives?
|
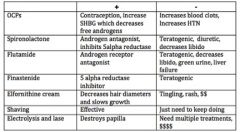
Hirsutism
|
|
|
Testolactone is an aromatase inhibitor used to treat
A. hirsutism B. McCune Albright syndrome C. precocious puberty D. PCOS |
B. McCune Albright syndrome
Remember, McCune Labright syndrome is the triad of precocious puberty + cafe au lait spots + bone changes |
|
|
Lupron is used to treat precicious puberty due to
A. follicular cysts B. ovarian tumors C. McCune Albright D. idiopathic dz E. profound hypothyroidism |
D. idiopathic dz
Lupron is used to treat precicious puberty due to idiopathic dz. |
|
|
What general class of drugs can be used to treat urge incontinence?
|
With urge incontinence you have an overactive bladder with urgency/frequency/nocturia. ANTI-CHOLINERGICS can be used to combat these but then you have SE of dry mouth and constipation.
|
|
|
Clomiphene produces both agonist and antagonist effects. Elaborate on that statement with reagrds to hypothalamic, pituitary and target tissue effects.
|
Clomiphene's effects:
Hypothalamic – binds to estrogen receptor and thus blocks negative feedback, thus increasing GnRH release to increase LH release Pituitary – slight agonist effect sensitizes pituitary cells to GnRH, enhances FSH and LH release Target tissue effect – competitive antagonist produces hot flashes |
|
|
Which of the following is CONTRAINDICATED with any of the following: Ovarian cysts, gestational administration, liver dz, unexplained ovulatory infertility.
A. Clomiphene B. hMG C. GnRH D. Leuprolide E. Bromocriptine |
A. Clomiphene
Is the only one of these fertility meds that have absolute CI. Rest have adverse effects only. |
|
|
Clomiphene's effects depend on the menopausal status of the individual.
A. If premenopausal... B. If postmenopausal... |
If premenopausal : increases GnRH release --> increases LH and FSH release --> ovulation
If postmenopausal: Acts as estrogen agonist and suppresses FSH and LH secretion |
|
|
What fertility drug is described: Is basically a 1:1 ratio of LH and FSH. Most effective in pts with low gonadotropin levels.
A. Clomiphene B. hMG C. GnRH D. Leuprolide E. Bromocriptine |
B. hMG
remember, an injection of hCG is required to mimic LH surge necessary for ovulation and leutinization. |
|
|
What drug is used as treatment of anovulation resulting from hyperprolactinemia?
|
Bromocriptine
Adverse: N/V, HA, orthostatic HTN, CNS effects. But NO problems like hyperstimulation, multiple gestations nor increased abortion rate like with others. |
|
|
What drug is used when you have hyperandrogenic anovulatory patients and in patients only when there is adrenal androgen excess?
A. A. Clomiphene B. hMG C. GnRH D. Leuprolide E. Bromocriptine F. Dexamethasone |
F. Dexamethasone: Decreases androgen synthesis in adrenals
|
|
|
When is treatment indicated for menopause? (Under what conditions?) (5)
|
- anovulatory cycles that yield irregular bleeding
- relief of vasomotor symptoms (hot flashes, sweating) and vaginal atrophy occurs to the point of disruption of quality of life - prevention of hot flashes - to treat osteoperosis - to treat vaginal dryness, loss of libido |
|
|
Menopause treatment regimen choice depends on whether or not the uterus is intact.
A. If uterus is intact, then use.... B. If no uterus, then use... |
A. If uterus is still intact, use estrogen + progesterone regimen
B. If no uterus, estrogen alone is fine |
|
|
Crabs and scabies can both be treated with what medication (albeit different dosages)?
A. Ivermectin B. Leuprolide C. Premetherin D. Pyrethrins |
C. Premetherin (cream)
Crabs with 1%, Scabies with 5% |
|
|
[ Crabs / Scabies ] is very contagious STD with a >95% transmission rate with each encounte that produces constant itching in pubic hair whereas [ Crabs / Scabies ] burrows under the skin and causes severe but intermittent itching that is worse at night. Which is treated with Premetherin 1% cream or pyrethrins and which is treated with Premertherin 5% cream or Ivermectin?
|
Crabs = v. contagious STD , treat with Primetherin 1% cream or pyrethrins
Scabes= worse at night itching, treat with Premetherin 5% cream or Ivermectin (oral) |
|
|
True or False:
Molluscum contagiosum is treated by topical agents or lasers. |
FALSE. That is condyloma acuminatum, caused by HPV that can be treated with topical agents or lasers. Molluscum contagiosum is an umbilicated papule that is treated by dermal curetting and treatment of the base.
|
|
|
What condition is described and what is its treatment?
CC of fishy smelling, then grey discharge. Diagnosis is via basic pH, positive Whiff test, and Clue cells on wet prep. A. Bacterial vaginosis B. Candidal vaginitis C. Condyloma acuminatum D. Mulloscum contagiosum E. Trichomonas vaginalis |
A. Bacterial vaginosis
CC of fishy smelling, then grey discharge. Diagnosis is via basic pH, positive Whiff test, and Clue cells on wet prep. Treatment is : Metronidazole (this is also the treatment for Trichomonas) |
|
|
What condition is described and what is its treatment?
Profuse frothy green discharge, strawberry red cervix (due to petichiae). A. Bacterial vaginosis B. Candidal vaginitis C. Condyloma acuminatum D. Mulloscum contagiosum E. Trichomonas vaginalis |
E. Trichomonas vaginalis
Profuse frothy green discharge, strawberry red cervix (due to petichiae). Flagellate protozoan, most prevalent nonviral STD in U.S. Treatment is: Metronidazole (this is also the treatment for BV) |
|
|
Treatment with ceftriaxone + azithrpmycin or doxycycline is indicated for [ chlamydia / gonnorrhea ] whereas treatment with just doxycycline or azithromycin is indicated for [ chlamydia / gonnorrhea ].
|
ceftriaxone + azithrpmycin or doxycycline = gonorrhea
just doxycycline or azithromycin = chlamydia |
|
|
For Her2/Neu positive breast cancers, what therapy is particularly useful?
A. Tamoxifen B. Trastuzumab C. Raloxifene D. Leuprolide |
B. Trastuzumab
aka Herceptin These are monoclonal antibodies |
|
|
With regards to pregnancy, what can MTX be used for?
|
MTX can be used to treat ectopic pregnancies less than 3.5 cm. Other options for treating ectopic rx is laparoscopy or laparotomy or just expectant waiting/observing.
|
|
|
What are the three drugs listed that help with genital herpes treatment and what is their general MoA?
|
Acyclovir (Zovirax)
Valacyclovir (Valtrex) Famciclovir (Famvir) |
|
|
What is the treatment for syphillis?
|
Penicillin G!
1 dose IM if in primary, secondary or early latent stages 1 dose Q wk for 3 weeks if late latent or latent unknown Prolonged IV penicillin for 10-14 days if neurosyphilis |
|
|
If pregnant woman with syphilis is allergic to Penicillin, how should she be treated?
|
She should be desensitized to Penicillin because it really is the BEST treatment for syphilis!!
|
|
|
What is the treatment for each of the following?
A. genital herpes B. syphilis C. chancroid D. donovanosis |
A. for genital herpes: Acyclovir (Zovirax), Valacyclovir (Valtrex), Famciclovir (Famvir)
B. for syphilis: Penicillin G intramuscularly! C. for chancroid: Azithryomycin / Ceftriaxone / Erythromycin / Ciprofloxacin + follow up in 3-7 days for improvement D. for donovanosis: doxycycline. alternatives can be Azithromycin, erythromycin, ciprofloxacin, Trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole |
|
|
Treatments for genital ulcer conditions are listed. Match each treatment to its condition.
1. Azithryomycin / Ceftriaxone / Erythromycin / Ciprofloxacin + follow up in 3-7 days for improvement 2. Acyclovir (Zovirax), Valacyclovir (Valtrex), Famciclovir (Famvir) 3. Penicillin G intramuscularly! 4. doxycycline |
1. chancroid
2. genital herpes 3. syphilis 4. donovanosis |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a proven helpful therapy for menopausal symptoms?
A. Anti-convulsant medications B. Behavioral changes C. Clonidine D. Estrogen E. Herbal remedies like black cohash F. Gabapentin G. Phytoestrogens H. Progestins I. SSRIs |
NOT Proven helpful for menopause:
A. Anti-convulsant medications E. Herbal remedies like black cohash G. Phytoestrogens |
|
|
How does estrogen decrease osteoporosis?
|
Estrogen reduces bone resorption by....
- blocking action of PTH - increasing calcitonin - stimulating osteoblasts - increasing calcium absorption Tamoxifen and reloxifene are other alternatives to help preserve bone. SSRIs, clonidine, gabapentin can also be used for the menopausal symptoms if estrogen can't be used. |
|
|
True or False:
Narcotics can cross into the placenta so if giving analgesia with systemic narcotics, needs to be short acting. |
TRUE, so that baby does not go into respiratory depression.
Systemic narcotics are: meperidine, morphine sulfate, bitorphanol |
|
|
What is the treatment for delivery for preeclampsia/ exlampsia?
|
DELIVERY OF FETUS/PLACENTA!!
If mild preeclampsia, deliver by 37 weeks If severe preeclampsia, eclampsia or HELLP syndrome, deliver immediately regardless of fetal gestation! |
|
|
If a woman with preeclampsia is starting to give birth, what medication is given to prevent eclampsia during labor and delivery?
|
magnesium sulfate
|
|
|
What is the treatment for hypotonic contractions?
|
Oxytocin! Pitocin is the synthetic analog that is pumped titrated into the mother. Will increase the strength and intensity of contractions.
|
|
|
With regards to breech presentation of baby, what is the
A. complete breech B. frank breech |
A. complete breech : cannonball
B. frank breech : pike position Frank is more common than complete if it is breech, but only 5% of babies present breech. |
|
|
How can you eliminate the bacterial reservoir of Group B Strep on mom and reduce the risk of Group B Strep early infection in baby?
|
Antibiotics (penicilin) during labor!
|
|
|
True or False:
Penicillin treatment to combat Group B Strep does not affect the incidence of late onset infection (meningitis). |
TRUE.
Only reduces the risk of early infection (sepsis of baby). |
|
|
True or False:
Group B Strep maternal infection is associated with preterm (<37 weeks) rupture of membranes (PROM). |
TRUE
|
|
|
How do you diagnose bacterial vaginosis?
|
Bacterial vaginosis, or when normal lactobacilli are replaced with anaerobes, can be diagnosed by doing a wet prep of vaginal discharge, and obtaining a + Whiff test (fishy odor)
|
|
|
The FIRST antidbody response is the very large (5 subunit) [ IgG / IgM ]. It does NOT cross the placenta.
The later responder is the very specific [ IgG / IgM ]. It does cross the placenta. |
IgM first responder, does NOT cross.
IgG DOES CROSS |
|
|
The most commonly acquired congenital infections are....
|
the TORCH infections!!
T = toxoplasmosis O= other (HIV, syphilis) R = rubella C = CMV H = Herpes |
|
|
Which commonly acquired congenital infection presents on mom as Shallow ulcer, all virus is at BASE of the lesion. Sometimes with vesicle over top and need to unroof the vesicles –is very painful to mum to culture.
|
This is Herpes simplex virus
|
|
|
Which is the most damaging/ dangerous to the baby?
A. congenital HSV B. neonatal HSV localized to skin eyes and mouth C. neonatal HSV disseminated |
C. neonatal HSV disseminated
Progression of SEM to disseminated occurs in 60-70%! |
|
|
This is the most common perinatal infection
A. Toxoplasmosis B. Syphilis C. HIV D. CMV E. Herpes |
D. CMV
1-2% of all livebirths Primary infection occurs in 0.7-4.1% of all pregnancies (very common!) Perinatal infections with primary and recurrent infections Sources of infection are: kids in daycare, lower SES |
|
|
True or False:
Maternal antibody to CMV prior to pregnancy does NOT confer immunity to the fetus, although it does provide some protection. |
TRUE
|
|
|
What is the maternal infection described?
Mononucleosis-like symptoms: Fever, fatigue, myalgias, pharyngitis, cough, diarrhea, headache, cervical/generalized lymphadenopathy A. Toxoplasmosis B. Syphilis C. HIV D. CMV E. Herpes |
D. CMV
diagnose by culture, antibody detection, DNA (PCR). Note that the presence of IgM for CMV can persist up to 18 months so not helpful for diagnosing recent infections! |
|
|
What are the FIVE cardinal signs of an intraamniotic infection? How is an intraamniotic infection treated?
|
Signs: maternal tachycardia, fetal tachycardia (occurs 1st), maternal fever, leukocytosis, uterine tenderness
Basically, uterus becomes a large abscess!!!! Treatment is to DRAIN THE ABSCESS, AKA DELIVER and start broad spectrum antibiotics. |
|
Fill in whether or not each is used for the purpose on the LEFT and if there are any contraindications to each.
|
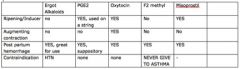
|
|
|
Which of the following labor inducing drugs have
1. the contraindication of HTN 2. the contraindication of asthmatic A. Ergot alkaloid B. PGE2 C. Oxytocin D. F2 methyl E. Misoprostil |
1. CI HTN: Ergot Alkaloid
2. CI asthmatic: F2methyl |
|
|
Match the following tocolytics with their mechanism:
B2 agonists, Mg, Nifedipine, Indomethacin 1. NSAID - blocks cycolooxygenase 2. Ca2+ channel blocker 3. sequestration of intracellular calcium, increased cAMP 4. inhibit calcium ion flow |
1. NSAID - blocks cycolooxygenase : Indomethacin
2. Ca2+ channel blocker : Nifedipine 3. sequestration of intracellular calcium, increased cAMP: B2 agonists 4. inhibit calcium ion flow: Mg |
|
|
ACE inhibitors are CI in pregnancy. What damage to the fetus occurs?
|
Causes oligohydroaminos due to changes in the fetal kidney!! (Not enough aminiotic fluid --> leads to less lung development for fetus since can't "practice" breathing.)
|
|
|
What is Mendelson's syndrome?
|
Increased aspiration risk when mom is under anesthetics. This is the #1 cause of OB anesthetic death! Progestrone relaxes esophageal sphincter and increases risk of aspiration of food or stomach contents into the tracheobronchial tree.
|
|
|
What can we give to the baby to help the ductus arteriosis close if it does not do so on its own shortly after birth?
|
Prostaglandins
|
|
|
Misoprostol, is a prostaglandin which, with Mifeprestone, causes the cervix to soften and dilate and the uterus to contract and expel the embryo. Used to induce labor. [ Mifeprestone / Misoprostol ] antagonizes progesterone, [ mifeprestone / misoprostol ] helps facilitate the completion of the abortion.
|
Mifeprestone antagonizes progesterone, misoprostol helps facilitate the completion of the abortion.
Taking just Mifeprestone which you can get online, without misoprostol, would still make the presence of POC still lodged in a woman. |
|
|
Beta 2 agonists have what effect on the uterus?
|
Beta 2 agonists like ritodrine and terbutaline, RELAX the uterus. This is a tocolytic. Increases cAMP, inceases protein phosphorylation, increases calcium sequestration, decreases muscle contraction.
Increase the IV doses until the contraction stops. Then they are given the oral preps while on bedrest or sent home. |
|
|
What is indomethacin's MoA?
|
NSAID - blocks cyclooxygenase!
Is a tocolytic. Indomethacin is a GREAT LABOR STOPPER!! So strong, that it has a rare effects on fetal kidneys (oligohydraminos). |
|
|
How do you treat hyperthyroidism in pregnancy?
|
First trimester: PTU + propanolol
Second and third trimester: methimazole + propranolol Iodine is used if thyroid storm is present. |
|
|
Regarding hyperthyroidism, when is each of the following used:
A. propranolol B. methimazole C. PTU (propylthiouracil) D. iodine |
First trimester: PTU + propanolol
Second and third trimester: methimazole + propranolol Iodine is used if thyroid storm is present. |
|
|
What is the risk to the fetus if the pregnant woman is taking
A. dilantin (phytoin) B. valproic acid C. tegretol |
These are all anticonvulsants.
A. dilantin has a 5-10% risk of fetal dilantin syndrome (Upturned nose, smooth philtrum, loewr posterior hairline, eyes are farther apart than normal, hypoplasia of fingernails) and 30% chance of mild facial and digital anomalies B. valproic acid and C. tegretol has a 1-2% risk of neural tube defects If you see the mmom before preconception, can perhaps advice her to take more folic acid to try to reduce this. |

