![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
30 year old woman with complaint of floaters and flashes, but full vision. The posterior fundus shows multiple blurred light yellowish lesions at the level of the retinal pigment epithelium. After 4 weeks complete recovery to normal. Etiology: Hereditary sex-linked disease or virus infection?
|
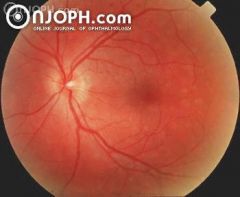
Multiple Evanescent White Dot Syndrome (MEWDS)
|
|
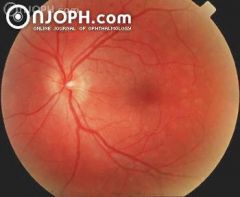
Hyperfluorescent granular appearing spots at the posterior pole at the level of the pigment epithelium. These disapppear completely with after some time.
|
Multiple Evanescent White Dot Syndrome (MEWDS)
|
|
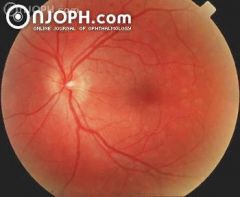
41 years, female, complaining of photopsia for one week, with visual acuity of 20/20. Funduscopy revealed spots difficult to define and gray-white lesions in the posterior pole, mainly temporal to the fovea.
|
Multiple-Evanescent-White-Dot-Syndrom (MEWDS)
|
|
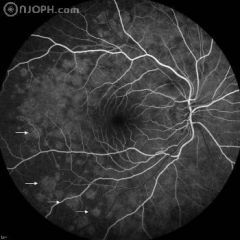
41 years, female, complaining of photopsia for one week, with visual acuity of 20/20. Fluorescein angiogram (FA) showed early hyperfluorescent dots with late staining.
|
Multiple-Evanescent-White-Dot-Syndrom (MEWDS)
|
|
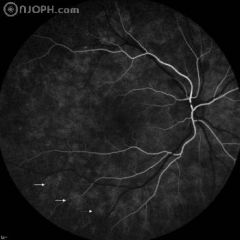
41 years, female, complaining of photopsia for one week, with visual acuity of 20/20. Funduscopy revealed spots difficult to define and gray-white lesions in the posterior pole, mainly temporal to the fovea. Early fluorescein angiogram (FA) showed early hyperfluorescent dots with late staining.
|
Multiple-Evanescent-White-Dot-Syndrom (MEWDS)
|
|
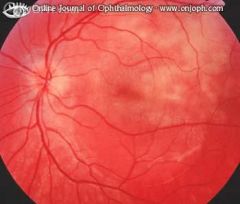
Multiple patchy grayish-white often confluent lesions, not sharply defined and at the level of the RPE. Usually without, but in this case with a serous retinal detachment
Author(s): |
Acute Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
|
|
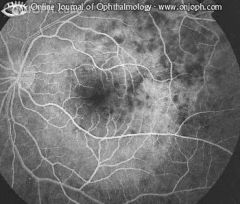
Fluorescence is blocked in the early angiogram by the lesions
|
Acute Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy (AMPPE)
|
|
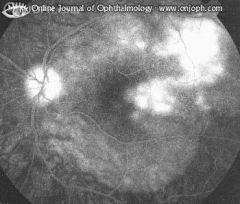
In the late angiogram the lesions are stained.
|
Acute Multifocal Placoid Ppigment Epitheliopathy (AMPPE)
|
|
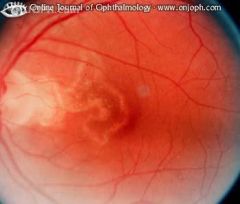
Recurrent creeping inflammation of the inner choroidal layers, the RPE and outer retina, starting posteriorly and extending peripherally. Presently inactive.
|
Serpiginous (Geographic) Choroiditis
|
|
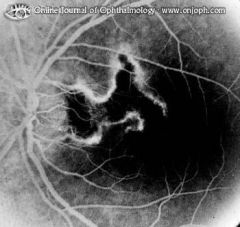
The scarred area does not stain. Along its edge the rim of remaining choriocapillaris is seen.
|
Serpiginous (Geographic) Choroiditis, Angiogram
|

