![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
106 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the definition of anatomy? |
The study of structure. |
|
|
|
Small anatomy |
Microscopic |
|
|
|
Big part of anatomy |
Gross |
|
|
|
What is fetus to adult |
Developmental Anatomy |
|
|
|
What is conception to birth Anatomy |
Embryology |
|
|
|
What is towards the head? |
Superior |
|
|
|
What is towards the feet? |
Inferior |
|
|
|
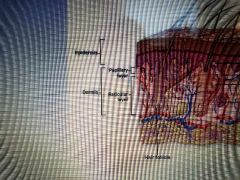
What are the three layers of the skin? |
Dermis, epidermis and subcutaneous membrane |
|
|
|
What is the definition of physiology |
The study of functions |
|
|
|
What are two general categories in which Anatomy can be divided |
Microscopic anatomy and gross anatomy |
|
|
|
What are the levels of organization of the human body? |
Microscopic: chemical, cellular and tissue. gross: organ and organ system |
|
|
|
What are examples at the chemical level? |
Sugar water molecule or vitamin |
|
|
|
Epi |
Upon or on. (Epicardium - membrane covering the heart) |
|
|
|
Infra |
Below |
|
|
|
Inter |
Between |
|
|
|
Intra |
Within |
|
|
|
Peri |
Around |
|
|
|
Sub |
Under |
|
|
|
Supra |
Above, upper |
|
|
|
Standing Palms facing forward is |
Anatomic position |
|
|
|
Name the plane sections and what they mean |
Coronal (frontal) midsagital (center ear to ear) sagital or parasagital (off center ear to ear) transverse (horizontal) |
|
|
|
What is the front called (2 terms) |
Anterior or ventral |
|
|
|
What is the back position called (2 terms) |
Posterior or dorsal |
|
|
|
When something is more towards the center of the body |
Medial |
|
|
|
When something is away from the center of the body |
Lateral |
|
|
|
Referencing appendages, closer to the point they connect to the body |
Proximal |
|
|
|
Referencing appendages further away from the point they connect to the body |
Distal |
|
|
|
What is the opposite of Deep |
Superficial |
|
|
|
What is the back of the hand called? |
The dorsal surface of the hand |
|
|
|
What is the Palm side surface of the hand called? |
The Palmar surface of the hand |
|
|
|
What is the top of the foot called? |
The dorsal surface of the foot |
|
|
|
What is the bottom of the foot called? |
The plantar surface of the foot |
|
|
|
What is the area including the head and torso |
Axial |
|
|
|
What is the area containing the appendages and the pelvic bone |
Appendicular |
|
|
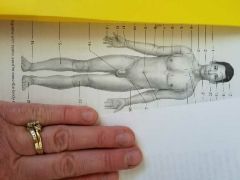
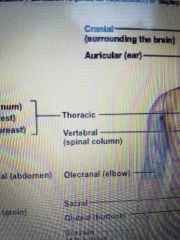
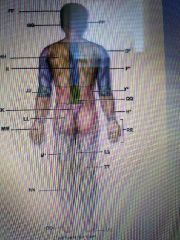
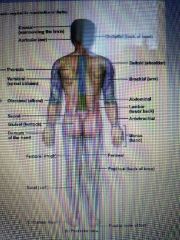
Anatomic regions |
|
|
|
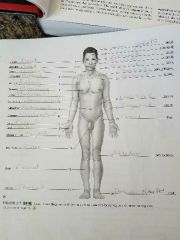
Anatomic regions |
|
|
|
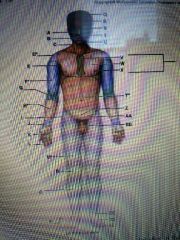
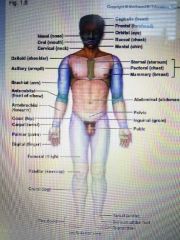
Anatomic regions |
|
|
|
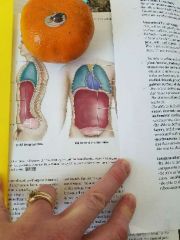
Name the cavity |
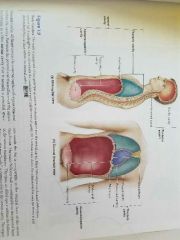
|
|
|
|
What divides the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities? |
The diaphragm |
|
|
|
What is the cavity that holds the heart? |
The mediastinum |
|
|
|
What do you call the organ in the balloon of tissue? |
Serous membrane |
|
|
|
What is the name of the layer of a serous membrane that is touching the organ? |
Visceral layer |
|
|
|
What is the outer layer of a serous membrane that touches the body? |
Parietal layer |
|
|
|
What do you call the space between the two layers of a serous membrane? |
Serous cavity (add al) |
|
|
|
What are the serous membranes associated with the heart |
Pericardium. Visceral pericardium - touches the heart. Parietal pericardium - the outer lining of the heart. Pericardial cavity is in between those two |
|
|
|
What are the serous membranes associated with the lungs? |
Pleural. Visceral pleura - touches the lungs. Parietal pleura - outer lining that touches the body. Pleural cavity - space in between. |
|
|
|
What are the serous membranes associated with the abdominopelvic cavity? |
Peritoneum. Visceral peritineum, parietal peritoneum, peritoneal cavity |
|
|
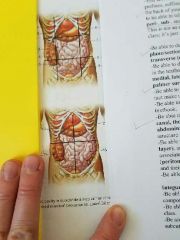
9 abdominopelvic regions and four abdominopelvic quadrants |
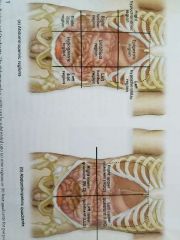
Umbilical region, epigastric region, hypogastric region, right hypochondriac region, left hypochondriac region, right lumbic region, left lumbic region, right illiac region, left illiac region |
|
|
|
What is the skin called? |
Integument or cutaneous membrane |
|
|
|
What are the components of the integumentary system? |
Skin, hair, nails, and endocrine glands one being sebaceous glands the other being sweat glands |
|
|
|
What are the seven functions of the integumentary system? |
Thermal regulation, metabolic, immune response, protection, excretion, prevention of water loss, sensory |
T.M.I.P.E.P.S. |
|
|
What is an example of thermoregulation |
Sweat , vessel dilation and construction |
|
|
|
What is an example of sensory |
Pressure, temperature |
|
|
|
What is an example of immune response |
Shoves out harmful cells like cancer cells |
|
|
|
What is an example of excretion |
Sweating out salt |
|
|
|
What is an example of prevention of water loss |
Skin is waterproof and holds the water in |
|
|
|
What is an example of metabolic regulation |
Vitamin D from the Sun |
|
|
|
What is an example of protection |
Protect from bumps, Sun, infection, chemicals |
|
|
|
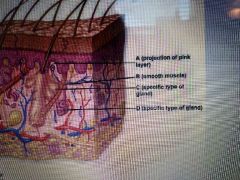
What are the two major layers of the integument? |
Epidermis. dermis. Don't forget the subcutaneous layer although it is not part of the integumentary system. |
|
|
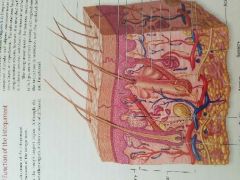
Structure of the integument |
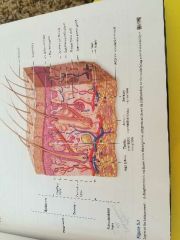
|
|
|
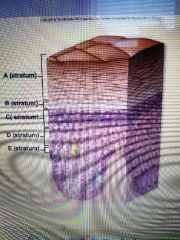
What are the five layers of the integument? |
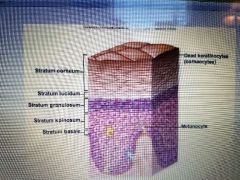
Stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum |
|
|
|
Which layer of the epidermis is found only in thick skin? |
Stratum lucidum |
|
|
|
Which layer of the epidermis contains the stem cells that give rise to new keratinocytes? |
Stratum basale |
|
|
|
What are the spiny tan things in the stratum basale |
Melanocytes |
|
|
|
Define melanocytes |
UV radiation causes them to produce darker melanin causing the skin color to be darker. Your melanin is hereditary for the color and the amount of melanin released by the melanocytes |
|
|
|
What is the term when it does not contain blood vessels |
Avascular |
|
|
|
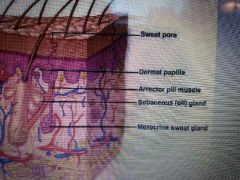
What are the small muscles attached to hair follicles that make Goosebumps? |
Arrector pili |
|
|
|
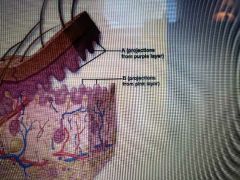
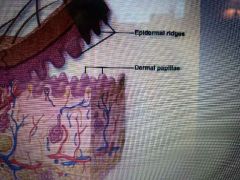
What are the finger-like structures coming up from the most superficial of the dermis layer? |
Dermal papilla |
|
|
|
What is the finger like layer pointing downward that connect the epidermis to the dermis? |
Epidermal Ridge |
|
|
|
What are stretch marks called? |
Striae |
|
|
|
What do you call the direction the fibers are aligned? |
Lines of cleavage |
|
|
|
What is the deepest layer of the skin |
Subcutaneous layer |
|
|
|
What is it called when skin appears blue for lack of oxygen? |
Cyanosis |
|
|
|
What is cyanosis |
When skin appears blue for lack of oxygen |
|
|
|
What is it called when skin appears abnormally red |
Erythema |
|
|
|
What is erythema and what can cause it? |
Skin appears that normally red. Exercise, sunburn, excess heat, and motions resulting in increased blood flow and dilated blood vessels in the dermis |
|
|
|
What is it called when the skin and sclera (whites of the eyes) appear yellow? |
Jaundice |
|
|
|
What is jaundice, and what can be the cause? |
Yellowing of the skin and sclera white the eyes. Elevated functions of bilirubin due to poor liver function. |
|
|
|
What is it called when skin appears white or pale |
Pallor |
|
|
|
What is pallor and what are possible causes? |
Skin appears pale. decreased blood flow, low blood pressure, cold temperature, anemia, shock |
|
|
|
What is a mole called? |
Nevi or nevus |
|
|
|
What is nevi |
A mole |
|
|
|
What causes freckles? |
Excessive melanocytes activity, not an increase in Malena site numbers period of freckles degree of pigmentation varies and depends on both some exposure and heredity |
|
|
|
What is a colored birthmark or a port wine stain? |
Hemangioma. Capillary hemangioma or cavernous hemangioma (port wine stain). |
|
|
|
What is a hemangioma |
Birthmark or port wine stain capillary Hemangioma or cavernous hemangioma |
|
|
|
What is a finger print called |
Friction ridges |
|
|
|
What is another name for integumentary structures? |
Epidermal derivatives of the integument |
|
|
|
What are Merocrine glands? |
Located over most the body , ducts secrete onto surface of the epidermis |
|
|
|
What are the glands that cover most of the body and the ducts secrete onto the surface of the epidermis |
Merocrine glands |
|
|
|
Apocrine glands |
Located in the axillary, pubic, anal and areola regions - ducts secrete into the hair follicles |
|
|
|
What do you call the sweat glands located in the axillary, pubic, anal, and areola regions - Ducks secrete into hair follicles |
Apocrine glands |
|
|
|
What is a sebaceous gland |
Ducts secrete oil into hair follicles |
|
|
|
What secretes oil into hair follicles? |
Sebaceous glands |
|
|
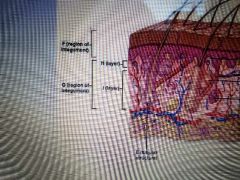
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
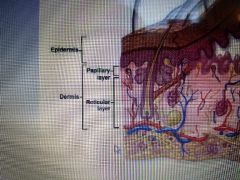
What is the lower layer of the dermis called |
Reticular layer |
|
|
|
What is the upper layer of the dermis called |
Papillary layer |
|
|
|
Describe the papillary layer |
It has dermal papillae which connect with the epidermal ridges. Most superficial of the dermis. |
|
|
|
Describe the reticular layer |
The deeper layer of the dermis that helps transport nutrients to the epidermis |
|
|
|
What are the things that judge sensory in the skin called |
Tactile receptors |
|
|
|
What's the cell that causes elasticity |
Epidermal dendritic cell. |
|
|
|
Which cell is attached to the sensory nerve ending |
Tactile cell |
|
|
|
What is the lowest layer along the bottom line of cells in the dermis called |
Basement membrane. |
|
|
|
What is the living organism that is rising up through the dermis |
Keratinocyte |
|

