![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the genome composition of parvovirus B19?
|
ssDNA (+ or -)
|
|
|
What is the virion shape and composiiton of parvovirus B19?
|
non-enveloped, icosahedral
|
|
|
What is the mode of replication of parvovirus B19?
|
Does not contain viral DNA polymerase. Unloads into nucleus and uses host transcription and translation mechanisms.
|
|
|
What is the host cell target of parvovirus B19?
|
Erythroid precursor cells. Receptor: erythrocyte pantigen
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission of parvovirus B19?
|
respiratory route
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of parvovirus B19?
|
slapped cheeks in children, the most prominent symptom of parvovirus infection in adults is joint soreness, lasting days to weeks. Joints most commonly affected are the hands, wrists, knees and ankles.
|
|
|
What are the classic signs of mumps?
|
swollen parotid (salivary) glands
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of mumps?
|
a bit of an enanthem in the mouth near the parotid gland
|
|
|
What are the epidemiological factors of mumps?
|
|
|
|
What are the classic signs of measles?
|
four day fevers, the three Cs—cough, coryza (runny nose) and conjunctivitis (red eyes), Koplik's spots seen inside the mouth are pathognomonic (diagnostic) for measles but are not often seen, even in real cases of measles, because they are transient and may disappear within a day of arising. The characteristic measles rash is classically described as a generalized, maculopapular, erythematous rash that begins several days after the fever starts. It starts on the head before spreading to cover most of the body, often causing itching.
|
|
|
What are the epidemiological factors of rubella?
|
|
|
|
What are the classic signs of rubella?
|
3 days of swollen glands (viremia), maculopapular rash and fever present later. Adults can have arthralgias as well as thrombocytopenia.
|
|
|
What are the epidemiological factors of mumps?
|
|
|
|
What pathogens does the MMR vaccine provide protection for?
|
live, attenuated vaccine
|
|
|
What is the form of type of vaccine used for measles?
|
live, attenuated vaccine
|
|
|
What is the form of type of vaccine used for mumps?
|
live, attenuated vaccine
|
|
|
What virus causes mumps?
|
mumps virus
|
|
|
What is the family of the mumps virus?
|
paramyxovirus
|
|
|
What is the genome structure of mumps virus?
|
(-) Rna
|
|
|
What is the virion structure of mumps virus?
|
Enveloped helical nucleocapsid
|
|
|
What are the surface antigens associated with mumps virus?
|
NP, P&L, M, HN. Has both H and N.
|
|
|
What is the replication mechanism of mumps virus?
|
Nucleus not involved, buds off.
|
|
|
What are the natural host cell/receptor for the mumps virus?
|
various salivary glands, testes, ovaries, pancreas, and brain
|
|
|
What virus causes measles (rubeola)?
|
measles/rubeola
|
|
|
What is the family of measles?
|
paramyxoviridae
|
|
|
What is the genome structure of measles virus?
|
(-) ssRNA unsegmented
|
|
|
What is the virion structure of measles virus?
|
helical enveloped
|
|
|
What are the surface antigens associated with measles virus?
|
H, P, F, L, M, only one serotype. H is most important (measles only has H while Mumps has both H and N)
|
|
|
What is the replication mechanism of measles virus?
|
Nucleus not involved, buds off.
|
|
|
What is measles interaction with the host?
|
CD46 on all nucleated cells and SLAM on T and B cells
|
|
|
What are the host cell targets for the measles virus?
|
Epithelial cells of the upper respiratory tract
|
|
|
Diseases associated with measles
|
respiratory disease, GI, Myocardial disease, measles enephalitis, B and T cell death, eye disease
|
|
|
types of measles encephalitis
|
"direct infection of neurons, post infectious encephalitis (demyelination of neurons), subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE)- characterized by changes in peronality, behavior, memory, myoclonic jerks, blindness and spasticity.
|
|
|
What virus causes rubella?
|
rubella virus
|
|
|
What family is rubella virus?
|
Togaviridae
|
|
|
What is the genome structure of rubella virus?
|
(+) ss RNA
|
|
|
What is the virion structure of rubella virus?
|
Enveloped icosahedral
|
|
|
What are the surface antigens associated with rubella virus?
|
C (capsid), E1, E2, E3 (glycoprotein spikes)
|
|
|
What is the replication mechanism of rubella virus?
|
binding, uncoating (acidification and fusion by F protein), translation 1 (early non-structural proteins), transcription (viral RNA polymerase), translation 2 (structural proteins), release from cell (C protein associates with E proteins in the membrane)
|
|
|
What are the natural host cell/receptor for the rubella virus?
|
Travels from the respiratory tract to the lymph nodes causing occipital lymphadenopathy
|
|
|
rubella and platelets
|
rubella can results in thrombocytopenia
|
|
|
How is rubella screened for in pregnancy?
|
specific IgG antibody test
|
|
|
What does the presence of rubella specific IgM indicate?
|
Recent acute infection of both mother and fetus
|
|
|
If rubella isnt a big deal to adults or children, why vaccinate?
|
Fetal risks are huge
|
|
|
What are the classic signs of Varicella-zoster virus (VCV)?
|
fever and a maculopapular rash that appear after an incubation period of approximately14 days.
|
|
|
What family is VCV?
|
Herpesviridae, Alphahepesvirinae
|
|
|
What is the genome structure of VCV?
|
HUGE, linear double stranded DNA
|
|
|
What is the virion structure of VCV?
|
Enveloped Icosahedral (big)
|
|
|
What is the replication mechanism of VCV?
|
budding through membrane
|
|
|
VCV interaction with host
|
budding through membrane
|
|
|
VCV transmission
|
respiratory route
|
|
|
VCV Host cell range
|
resp. lymph nodes, endothelial cells, skin epi
|
|
|
define exanthem
|
a wide spread rash usually occuring in children
|
|
|
define enanthem
|
a rash inside the body (mucous membranes) like Koplik's spots in measles
|
|
|
define maculopapular
|
flat, red area on the skin that is covered with small confluent bumps
|
|
|
define papule
|
a circumsribed, solid elevation of skin with no vidible fluid
|
|
|
define macular
|
flat discolored spots on the skin
|
|
|
define diffuse erythema
|
skin redness or inflammation that is spread over a large body surface
|
|
|
define pustule
|
small, inflamed, pus-filled, blister-like lesions on the skin surface
|
|
|
define erythematous plaques
|
redness or inflammation of a raised region of skin that is the result of dilation and congestion of superficial capillaries.
|
|
|
define petechial eruption
|
A small purplish spot on a body surface, such as the skin or a mucous membrane, caused by a minute hemorrhage
|
|
|
define pruritic vesicles
|
itchy lesions that are rasied regions of the skin less than 0.5 cm in diameter and containing liquid
|
|
|
define purpuric eruption
|
Purpura is the name given to the discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes due to hemorrhage from small blood vessels. Petechiae are small, purpuric lesions up to 2mm across. Ecchymoses or bruises are larger extravasations of blood.
|
|
|
define vesiculobullous eruption
|
A blistering rash characterized by serous fluid- filled vesicles ( blisters)
|
|
|
What are the viral systemic infections characterized by fever and rash?
|
varicella(chickpox), measles, rubella, roseola, 5th disease, kawasakis, rickettsial, smallpox, scarlet fever, mononucleosis, meningococcal disease
|
|
|
What is the genome architrcture of Human herpesvirus types 6&7?
|
double stranded DNA
|
|
|
What is the virion morphology of HHV 6&7?
|
enveloped icosahedral
|
|
|
What are the clinical manifestations of HHV6&7?
|
roseola infantum, The fever is followed by a erythematous macular rash that appears on the neck and trunk which resolves on it’s own
|
|
|
HHV 6&7 interaction with host
|
budding through membrane
|
|
|
Host cell range of HHV 6&7?
|
lymphocytes, epithelial cells, salivary gland and neurons
|
|
|
Coxsacki family
|
picroniviradae
|
|
|
Coxsackie structure
|
icosahedral
|
|
|
Coxsackie Genome
|
(+) RNA
|
|
|
Coxsackie diseases
|
herpangina, hand foot and mouth disease
|
|
|
coxsackie transmission route
|
fecal-oral
|
|
|
coxsackie host cell range
|
oropharynx epithelium, skin following a secondary viremia
|
|
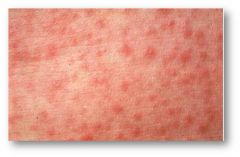
measles exanthem
|
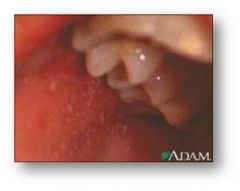
measles enanthem
|
|
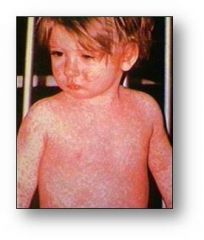
measles exanthem2
|
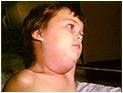
mumps
|
|
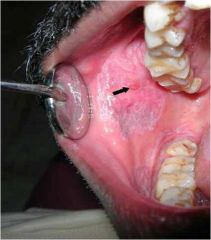
mumps 2
|
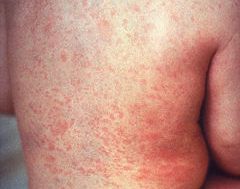
rubella_rash
|
|
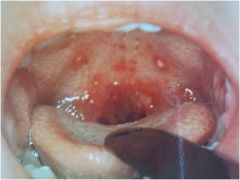
herpangina
|
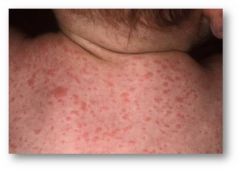
roseola
|

