![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
1. Give Lambert Beer Law with an equation and the description of the denotations. |
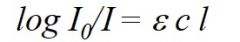
A- Absorbance (quatity without dimension) C-Concentration (mM) I- Length of light path.(cm) ε stands for the molar extinction coefficent. (cm^2/μmol) |
|
|
|
2. How would you calculate the concentration of the substance in the cuvette? Write the formula given that ε value of the studied substance is known. |
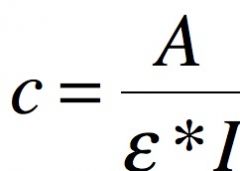
|
|
|
|
3. Define ε (in words) and its unit. |
ε stands for the so called molar extinction coeffiecent. It tells us the absorbance of a 1mM concentration solution in a 1 cm long cuvette at a given wavelength. It depends on the wavelength and some other parameters. Unit is cm^2/μmol |
|
|
|
4. What kind of light would you use for native protein concentration determination? And for the biuret method? |
Typical maximum absorption is at 280nm. In the biurtet method we use light at 540nm. |
|
|
|
5. What kind of material should cuvettes be composed of in the case of native protein concentration determination? And for the biuret method? |
Uv transparence for optical glass is weak. Best is optical quartz, but PMMA, or plexi have a satisfactory transparency for native protein. Biuret method: Borosilicate glass. |
|
|
|
6. In the lab practice we determine the protein concentration using the light absorbance of a particle. What is this particle? |
Peptide bond/ Cu^2+ -complex |
|
|
|
7. What is the role of tartarate and that of iodide ions in biuret reagent solution? |
Sodium potassium tartarate is a complexing agent.
Potassium iodide ions is an antioxidant |
|
|
|
8. How should a halving dilution series be prepared? (You may want to draw a figure.) |
. |
|
|
|
9. What is a blank sample? What is its use during protein concentration determination? |
Blank sample is used to take light intensity loss due to reflexion and scattering into consideration and correct for it, so the result only depends on the concentration of molecules capable of absorbing light. |
|
|
|
10. Why is it necessary to record a calibration curve during protein concentration determination using the biuret method? |
Since the absorbance/concentration ratio is unknown before measurement, we first need a calibration curve made by using a series of protein solutions with known concentrations. |
|
|
|
11. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. |
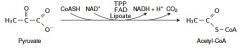
|
Tpp, fad, lipoate |
|
|
12. Write with names the overall reaction of the respiratory chain up to the reduction of O2. |
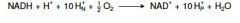
|
|
|
|
13. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by the cytosolic glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. |
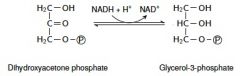
|
|
|
|
14. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by the mitochondrial glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. |
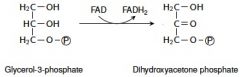
|
|
|
|
15. Write the reaction catalyzed by superoxide dismutase. |
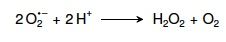
|
|
|
|
16. Write the reaction catalyzed by catalase. |
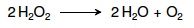
|
|
|
|
17. Write the reaction catalyzed by a peroxidase. |

|
|
|
|
18. Write the Fenton reaction. |

|
|
|
|
19. Write the Haber-Weiss reaction. |
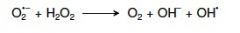
|
|
|
|
20. Write with structures the reaction catalyzed by NO synthase |
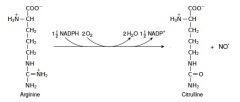
|
|
|
|
21. Write the reaction equation of the formation of peroxynitrite. |
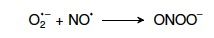
|
|
|
|
22. Write with names or abbreviations a reaction catalyzed by glutathione peroxidase. |
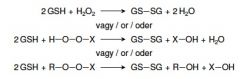
|
|
|
|
23. Write with names or abbreviations the reaction catalyzed by glutathione reductase. |
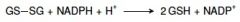
|
|
|
|
24. Write with names or abbreviations one the reaction catalyzed by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). |

|
|

