![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

What does the bone need remodeling ? Why is it important? |
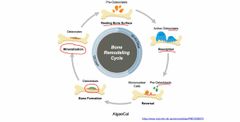
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is the function of bone? |
Provide firm framework for the body Protect delicate structures like the brain and the spinal cord Serves as levers, working with muscles to produce movement Storage for calcium Production site for blood cells Storage of fats |
|
|
|
Bones: Two main groups by location |
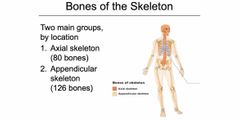
1. Axial Skeleton (80 bones) inner 2. Appendicular skeleton (126 bones) |
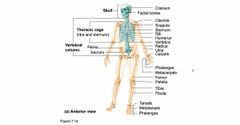
Bones of the skeleton |
|
|
Classification of Bones by Shape |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Classification of Bones by Shape |

Back (Definition) |
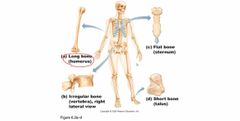
|
|
|
Gross Anatomy: Bone Structure |
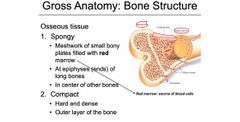
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Macroscopic Anatomy of Long Bones |

Back (Definition) |
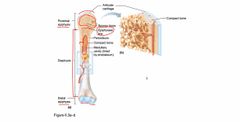
|
|
|
Homeostatic Imbalance in Bone: Osteoporosis |
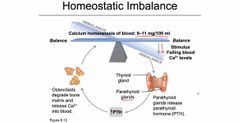
Zsddd
|

|
|
|
Clinical Relevance |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Indicate what you think happens to the activity level of each of the bone cell types below in an individual with osteoporosis? |
Osteoblast Activity: Decreases Osteoclast Activity: Increases |
|
|
|
Indicate below whether each of the conditions below would be protective (decrease the probability of a patient getting osteoporosis) or a risk (increase the probability of a patient getting osteoporosis). |
1. Diet high in calcium and vitamin D (Protective Factor) 2. Regular weight-bearing exercise (Protective Factor) 3. Small body frame (Risk Factor) 4. Lack of estrogen (Risk Factor) |
|
|
|
List a prevention strategy and one treatment strategy for osteoporosis. |
Prevention - Eat food that support bone health with sufficient calcium, Vitamin D and protein each day. Treatment - Maintain a healthy diet and weight-bearing exercise to prevent bone loss or strengthen already weak bones. |
|
|
|
What factors put someone at a higher risk? |
Female sex Estrogen decrease Calcium decrease Vitamin decrease Activity level decrease Genetics |
|
|
|
Joints and their classification |

Back (Definition) |

|
|

Synovial Joints |

Back (Definition) |
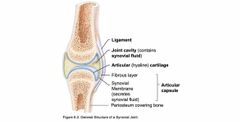
|
|
|
Synovial Joints: Cont. |

Back (Definition) |
|
|

Other features of Synovial Joints |
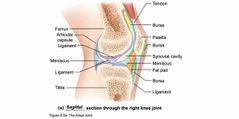
Back (Definition) |
|
|

Other features of Synovial Joints |
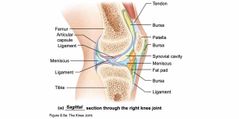
Back (Definition) |
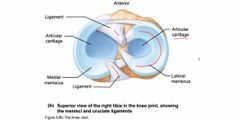
|
|
|
Muscle: Overview |
Producing movement - For example: skeleton, heart, blood vessels, organs Maintenance of posture Stabilizing joints Generation of heat |
Overview and Types of Muscle |
|
|
Special Characteristics of Muscle Tissue |

Back (Definition) |

|
|
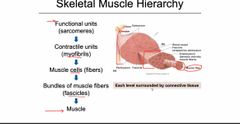
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
|

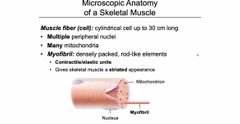
Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|
|

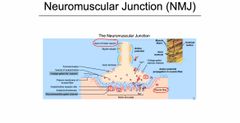
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
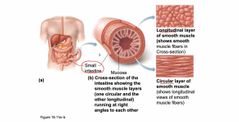
|
|
|
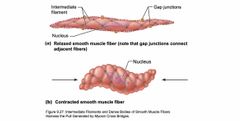
Structure of smooth muscle fibers |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Altering the Neuromuscular Junction |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Where can osteogenic cells be found? |
Periosteum |
|
|
|
Which of the following system’s manufactures vitamin D to aid in calcium absorption? |
Integumentary system |
|
|
|
Indicate the movement that best describes each of the statement below: |
A. Bringing the lower leg toward the dorsal thigh is flexion at the knee. B. Moving the thumb towards the fingers is adduction at the first thumb joint. C. Reaching toward a person sitting in front of you involves flexion at the shoulder |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle fibers differ from “typical” cells in that these muscle fibers: (select all that apply) |
A. Are up to 1 meter long B. Have many nuclei |
|
|
|
Which of the following displays the correct hierarchy of muscle tissue (from largest to smallest)? |
Muscle, fascicle, muscle fiber, myofibril |
|
|
|
The main ion involved in skeletal muscle contraction is: |
Calcium |
|
|
|
Which muscle type is correctly matched with its characteristics? |
A. Cardiac: involuntary, striated |
|

