![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hepatic System |
|
|
|
Review of A&P of the Liver |
-largest gland of the body. -located in RUQ -avery vascular organ that receives blood from GI tract via the portal vein and from the hepatic artery |
|
|
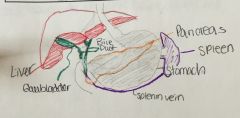
Food is digested in stomach, goes down from gastric vessel into portal vein (approx 80% of the blood supply comes from the portal vein which drains the GI tract and is rich in nutrients but lacks oxygen). The portal vein goes up anatomically. what is portal HTN? > |
this is when the liver is cirrhotic. causes build up and back flow in the portal vein and will then lead to back up gastric veins, esophageal veins and in the rectum. so with all this pressure, it will cause leakage of plasma (bc these cells are smaller), leaving solutes. protein molecules are big so they stay inside.(makes pt have low protein) this backup also causes splenic vein SPLENOMEGALY. (the spleen filters blood & removes worn out RBCs) so plt count low since plt getting stuck in spleen. ==(LOW PLT, PROTEIN and big spleen) |
|
|
Metabolic Functions of Liver |
-glucose, protein and fat metabolism -ammonia conversion -drug metabolism -vitamin and iron storage -bile formation -bilirubin excretion (if not excreted we look jaundiced) -10 of the 12 coagulation factors are produced in the liver (so if were missing then pt/inr will increase causing longer time to clot |
|
|
Liver Function Studies |
-AST (10-40norm), ALT(8-40 norm), GGT & GGTP (0-30 norms) ,LDH -serum protein (albumin/globulin~ this is bc proteins are manfc. by liver) -pigment studies (bilirubin~ measures ability of liver to conjugate & excrete it) -prothrombin time -serum alkaline phosphate 930-120 norm) -serum ammonia (15-45 norm~ liver converts ammonia to urea) -cholesterol (LDL <130; HDL m35-70 f 35-85) |
|
|
Additional Diagnostic Studies |
-liver biopsy (have FFP ready bc of bleeding possibility) -ultrasonogaphy -CT -MRI |
|
|
PANCREATITIS |
#1 NPO to reduce enzymes being produced, #2 PAIN mgmt, and assess fluid/electrolyte status. CA of it: whipple procedure removes parts that are cancerous and re conencts everything |
|
|
HEPATIC DYSFUNCTION: patho and causes |
acute or chronic (more common) cirrhosis of the liver (small and hard liver) causes: malnutrition RT alcoholism; infection; anoxia, metabolic disorders, nutritional deficiencies; hypersensitivity states; acetaminophen |
|
|
HEPATIC DYSFUNCTION: manifestations |
-jaundice (hemolytic where cells break open increased destruction of RBC or hepatocellular from damaged liver cells) -portal HTN, ascites, and varices (esophagus and rectal) -hepatic encephalopathy (PSE) or coma -nutritional deficiencies -thrombocytopenia -hepatomegaly, splenomegaly |
|
|
PORTAL HYPERTENSION 1/2 |
Portal HTN is an increase in the blood pressure within a system of veins called the portal venous system. Normally, the veins come from the stomach, intestine, spleen, and pancreas merge into the portal vein, which then branches into smaller vessels and travels through the liver. If the vessels in the liver are blocked, its hard for the blood to flow causing pressure in the portal system. |
|
|
Portal Hypertension 2/2 2 complications of portal HTN |
when the pressure becomes too high, the blood backs up and finds other ways to flow back to the heart. the blood can travel to te veins in the esophagus (esophageal varices), in the skin of the abdomen, and the veins of the rectum and anus (hemorrhoids) to get around the blockages in the liver. Results in: ascites and esophageal varices |
|
|
Complication #1 (of Portal HTN) Ascites: patho and tx |
the plasma leaks out bc of pressure and results in this condition. the leaking goes into the peritoneal cavity and you may even see fluid wave. tx: low sodium diet 2g, give diuretics (spironolactone, HCTZ- no furosemide), NO fluid restriction, bed rest proper posture, paracentesis(can cause low BP so u give albumin IV to raise it. complications bleeding, infection, peritonitis. postop bed rest, monitor site and BP ), administration of salt poor albumin (albumin sucks fluid back into vascular space. TIPS |
|
|
TIPS |
transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt controls hemorrhage by reducing portal pressure. you must consent and sedate complication: low success rate, bleeding, sepsis, HF and perforation the procedure helps with build up of fluids. "bypass of some of the blood vessels" its a tube between hepatic and portal vein. |
|
|
Complication #2 (of Portal HTN): Esophageal Varices: patho & manifestations |
patho: patients with cirrhosis and varices. s/s: hematemesis (vomit blood), melana(bloody stool) , general deterioration, s/s of bleeding, and shock |
|
|
Complication #2 (of Portal HTN): Esophageal Varices: Treatment |
-EGD (upper endo) ; -sclero (to make bleeding stop), -cauterization -banding (mst common. put rubber band around blood vessel to stop the bleeding. bun in the hair. caution w NG tube if they have these bands); -blakemore tube (tube in nose to esophagus and balloon is inflated pressure stops the bleeding. its held in place. temp and uncomfortable) Additional tx: oxygen, fluids,, volume expanders (vasopressin, somatostatin, octretide to decrease bleeding), vit K, blood products |
|
|
HEPATIC ENEPHALOPATHY aka "PSE" (portal systemic encephalopathy): patho/assessment and monitor |
a life threatening complication of liver disease. may result from the accumulation of ammonia and other toxins in blood -patho build up of ammonia (stimulates GABA which slows!!) swells astrocytes in brain and leads to confusion to coma. -GI bleeding causes large load of protein that cause an increase in ammonia Assessment: LOC changes, potential sz, asterixis. monitor LOC, ammonia levels, fluid and electrolyte levels |
|
|
HEPATIC ENEPHALOPATHY aka "PSE" (portal systemic encephalopathy): Treatment |
lactulose (lowers ammonia levels it grabs ammonia out of cells and puts in GI so lots of diarrhea) and neomycin (helps neutralize bacteria in intestine since the bacteria is causing high protein), protein restriction, hemodialysis, safety, and bleeding precautions |
|
|
HEPATITIS: VIRAL DEF |
Viral Hep: a systemic viral infection that causes necrosis and inflammation of live cells with characteristic symptoms and cellular ans biochemical changes. |
|
|
We will be looking at... |
Hep A Hep B Hep C |
|
|
Hepatitis A: type of transmission, incubation, dx, and manifestations |
-fecal oral transmission, spread by poor hygiene, hand to mouth contact, close contact and through food and fluids -Incubation: 15-50 days. illness may last 4-8 weeks -Dx: liver enzymes, Hep A antibody s/s: mid flu like symptoms, low grade fever, anorexia, later jaundice and dark urine, indigestion/epigastric distress, enlargement of spleen & liver |
|
|
Hepatitis A: Treatment and prevention |
TX: bed rest, small frequent feeding -immunoglobulin for contacts to provide passive immunity if not previously vaccinated prevention: good hand washing, safe water, proper sewage disposal, vaccine |
|
|
Hepatitis B: patho, incubation, dx, manifestations, whos at high risk? |
-patho: transmitted thru blood found in blood, saliva, semen, and vaginal secretions, STD and to infant at time of birth -incubation period 1-6M -dx: liver enzymes, hep B surface antigen, hep B DNA, hep B e antigen s/s: insidious and variable, similar to hep A, loss of appetite, dyspepsia, may have jaundice, ligh colored stool, dark urine. High risk? health care workers. |
|
|
Hepatitis B: prevention, tx, medications |
prevention: vaccine, standard precautions, blood screening, hygiene, disposable syringes tx: bed rest, nutritional support (2-3k calories per small. small frequent meals), decrease symptoms meds: alpha interferon and antiviral agents. -if exposed and unvaccinated tx is Hep B immune globulin |
|
|
Hepatitis C: patho, dx, s/s, tx |
patho: transmitted by blood and sexual contact, including needle sticks and sharing of needles and razors this the most common blood born infection dx: liver enzymes and hep C RNA s/s: usually milk, chronic carrier state leads to cirrhosis or CA tx: antivirals like interferon and ribavirin |
|
|
HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS types/patho/ss |
-alcoholic, post necrotic scar tissue from viral hep, biliary (occurs around bile ducts) -s/s: intermittent fever, abdominal pain, epistaxis, ankle edema, liver enlargement (cells loaded w fat causes pain) -portal obstruction ans ascites, infection and peritonitis, GI varices, edema, mental deterioration, Vit Deficiency and anemia |
|
|
Nursing Process - Care of Cirrhosis of Liver pt Assessment |
ABC! A-varices, pulm congestion? ascites; B fluid and diaphragm pressure -Alcohol use/abuse discuss only with client -dietary intake and nutritional status -exposure to toxic agents and drugs -assess mental status -abilities to carry on ADL/IADLs, maintain a job, maintain social reltionsh -monitor for s/s related to disease like indicators for bleeding, fluid volume changes, and lab data |

